Chapter 7 Impulse and Momentum
... Chapter 7 is about the COLLISION of two masses. Both masses are needed to understand their interaction. Newton's 3rd Law plays a very important part. Collisions involve two new concepts: Impulse and Momentum. Impulse concept leads to the Momentum definition. Also applied to two (or more) masses blow ...
... Chapter 7 is about the COLLISION of two masses. Both masses are needed to understand their interaction. Newton's 3rd Law plays a very important part. Collisions involve two new concepts: Impulse and Momentum. Impulse concept leads to the Momentum definition. Also applied to two (or more) masses blow ...
Conservation of Lateral Momentum in Heterostructure
... electron motion in z-direction and in x-y plane is decoupled and one should change T(E) to T(E0) in equation (1), which means that the transmission probability depends on the quantized energy inside the well. This will significantly decrease the number of electrons passing the barrier. The role of s ...
... electron motion in z-direction and in x-y plane is decoupled and one should change T(E) to T(E0) in equation (1), which means that the transmission probability depends on the quantized energy inside the well. This will significantly decrease the number of electrons passing the barrier. The role of s ...
week 1
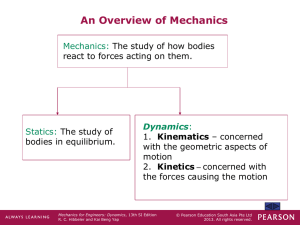
... The text shows the details, but for a system of particles: F = m aG where F is the sum of the external forces acting on the entire system. Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics, 13th SI Edition R. C. Hibbeler and Kai Beng Yap ...
... The text shows the details, but for a system of particles: F = m aG where F is the sum of the external forces acting on the entire system. Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics, 13th SI Edition R. C. Hibbeler and Kai Beng Yap ...
ANTI-MATTER FROM PRIMORDIAL BLACK HOLES
... Do quantum dynamical evolution remain deterministic through classical singularities ? Is there an « other side » ? The Hamiltonian formulation generally serves as the royal road to quantum theory. But absence of background metric constraints, no external time. ...
... Do quantum dynamical evolution remain deterministic through classical singularities ? Is there an « other side » ? The Hamiltonian formulation generally serves as the royal road to quantum theory. But absence of background metric constraints, no external time. ...
The quantum mechanical tipping pencil--
... Thanks to the anonymous reviewer who has gently shown me that since neither classical nor quantum mechanics predicts that the pencil necessarily falls over, ‘ . . . one is left believing that this system should remain in its nearly unstable equilibrium situation for a very long time.’ This is nothin ...
... Thanks to the anonymous reviewer who has gently shown me that since neither classical nor quantum mechanics predicts that the pencil necessarily falls over, ‘ . . . one is left believing that this system should remain in its nearly unstable equilibrium situation for a very long time.’ This is nothin ...
lattice model - Virtual Math Museum
... which zl varies but z1 , . . . , zl−1 , zl+1 , . . . , zN are constant. For example, if the initial shape of the transverse display is sinusoidal, only one normal mode is “excited”, but to produce this kind of motion almost all particles of the lattice have to move. Now consider the nonlinear case. ...
... which zl varies but z1 , . . . , zl−1 , zl+1 , . . . , zN are constant. For example, if the initial shape of the transverse display is sinusoidal, only one normal mode is “excited”, but to produce this kind of motion almost all particles of the lattice have to move. Now consider the nonlinear case. ...
Making FORS2 fit for exoplanet observations (again)
... decay experiments M. Sistia,b,∗, D. R. Artusac,e , F. T. Avignone IIIc , O. Azzolinid , M. Balatae , T. I. Banksf,g,e , G. Barih , J. Beemani , F. Bellinij,k , A. Bersanim , M. Biassonia,b , C. Brofferioa,b , C. Buccie , X. Z. Cain , A. Camachod , A. Caminatam , L. Canonicae , X. G. Caon , S. Capell ...
... decay experiments M. Sistia,b,∗, D. R. Artusac,e , F. T. Avignone IIIc , O. Azzolinid , M. Balatae , T. I. Banksf,g,e , G. Barih , J. Beemani , F. Bellinij,k , A. Bersanim , M. Biassonia,b , C. Brofferioa,b , C. Buccie , X. Z. Cain , A. Camachod , A. Caminatam , L. Canonicae , X. G. Caon , S. Capell ...
Quantum mechanical interaction-free measurements | SpringerLink
... interacting with the object). For example, assume it is known that an object is located in one out of two boxes. Looking and not finding it in one box tells us that the object is located inside the other box. A more sophisticated example of obtaining information in a nonlocal way is the measurement ...
... interacting with the object). For example, assume it is known that an object is located in one out of two boxes. Looking and not finding it in one box tells us that the object is located inside the other box. A more sophisticated example of obtaining information in a nonlocal way is the measurement ...
From Quantum theory to Quantum theology: Abstract J
... Max Planck's quantum hypothesis4 was the first indication that the inexorable determinism of classic3I physics had to be abandoned. Again, the implications of this hypothesis were not realised until 1926 when Werner Heisenberg formulated his famous uncertainty principleS. Particles no longer had sep ...
... Max Planck's quantum hypothesis4 was the first indication that the inexorable determinism of classic3I physics had to be abandoned. Again, the implications of this hypothesis were not realised until 1926 when Werner Heisenberg formulated his famous uncertainty principleS. Particles no longer had sep ...
Gauges - ETH Zürich
... The analysis above has long been accepted as conclusive evidence for gauge invariance as a fundamental and unambiguous principle of electrodynamics. ...
... The analysis above has long been accepted as conclusive evidence for gauge invariance as a fundamental and unambiguous principle of electrodynamics. ...