lecture31
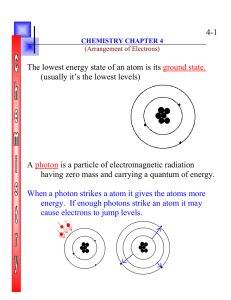
... • Energy levels depend on n and l, except in hydrogen. The other quantum numbers also result in small energy differences • Pauli exclusion principle: no two electrons in the same atom can be in the same quantum state • Electrons are grouped into shells and subshells • Periodic table reflects shell s ...
... • Energy levels depend on n and l, except in hydrogen. The other quantum numbers also result in small energy differences • Pauli exclusion principle: no two electrons in the same atom can be in the same quantum state • Electrons are grouped into shells and subshells • Periodic table reflects shell s ...
The quantum Heisenberg group H(1)q
... The Hopf algebra H( 1) 4 just defined is clearly different from the algebra of the q-deformed creation and annihilation operators used in the Jordan-Schwinger map of SU (2) 4;4 as it has been shown in Ref. 5 the right quantum structure for these q-deformed operators is B( O( 1) 9. This fact is relat ...
... The Hopf algebra H( 1) 4 just defined is clearly different from the algebra of the q-deformed creation and annihilation operators used in the Jordan-Schwinger map of SU (2) 4;4 as it has been shown in Ref. 5 the right quantum structure for these q-deformed operators is B( O( 1) 9. This fact is relat ...
Document
... In the case of SE , wave function gives the information in terms of probabilities and not specific numbers. Therefore, instead of finding the average value of any term (for example position of particle x ), we find the expectation value of that.
Ni xi
...
... In the case of SE , wave function gives the information in terms of probabilities and not specific numbers. Therefore, instead of finding the average value of any term (for example position of particle x ), we find the expectation value
What is quantum simulation
... Locality means that only these single-particle elements are relevant: on-site potential: ...
... Locality means that only these single-particle elements are relevant: on-site potential: ...
PARTICLE IN AN INFINITE POTENTIAL WELL
... This process may be performed for any other observable. For example, the average momentum or the expectation value of the momentum of a particle in the n-th state of the box. The only difference in the procedure to determine the expectation value of position is to replace the position operator with ...
... This process may be performed for any other observable. For example, the average momentum or the expectation value of the momentum of a particle in the n-th state of the box. The only difference in the procedure to determine the expectation value of position is to replace the position operator with ...
Geometry,
... two subsets, which are bi-normalized and bi-overcomplete. The two subsets are built up as eigenstates of two annihilation operators b and b̃ = ηbη −1 of respectively H and H + where η is the Hermitian and invertible operator that ensures the pseudo-Hermiticity of the Hamiltonian H = η −1 H + η. ...
... two subsets, which are bi-normalized and bi-overcomplete. The two subsets are built up as eigenstates of two annihilation operators b and b̃ = ηbη −1 of respectively H and H + where η is the Hermitian and invertible operator that ensures the pseudo-Hermiticity of the Hamiltonian H = η −1 H + η. ...
Rotation, Time Revolution and its Biological effect
... In the universe the passing of time cannot be clearly perceived as matter and space directly; one can perceive only irreversible physical, chemical, and biological changes in the physical space-the space in which material objects exists. On the basis of elementary perception (sight) one can conclude ...
... In the universe the passing of time cannot be clearly perceived as matter and space directly; one can perceive only irreversible physical, chemical, and biological changes in the physical space-the space in which material objects exists. On the basis of elementary perception (sight) one can conclude ...
11 Applications III
... Quantum behavior dominates at the atomic and molecular levels although classical models are usually sufficiently accurate at moderate to high temperatures. Conversely, quantum effects become more noticeable at low temperatures. Here we apply techniques introduced in the last chapter to quantum model ...
... Quantum behavior dominates at the atomic and molecular levels although classical models are usually sufficiently accurate at moderate to high temperatures. Conversely, quantum effects become more noticeable at low temperatures. Here we apply techniques introduced in the last chapter to quantum model ...