Particle Physics
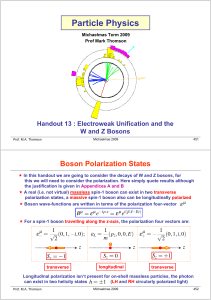
... The total W-decay rate is independent of polarization; this has to be the case as the decay rate cannot depend on the arbitrary definition of the z-axis For a sample of unpolarized W boson each polarization state is equally likely, for the average matrix element sum over all possible matrix elem ...
... The total W-decay rate is independent of polarization; this has to be the case as the decay rate cannot depend on the arbitrary definition of the z-axis For a sample of unpolarized W boson each polarization state is equally likely, for the average matrix element sum over all possible matrix elem ...
Three problems from quantum optics
... The third topic, fermion coherent states, deals with generalization to fermion fields of coherent states, one of the key concepts of quantum optics. Each of these topics is described briefly below and in detail in a separated chapter. I have tried to write this thesis clearly so that a physicist not ...
... The third topic, fermion coherent states, deals with generalization to fermion fields of coherent states, one of the key concepts of quantum optics. Each of these topics is described briefly below and in detail in a separated chapter. I have tried to write this thesis clearly so that a physicist not ...
Multiprobe quantum spin Hall bars
... In conclusion, we have studied multi-terminal QSH devices based on the Büttiker approach of ballistic edge transport. We have derived expressions for resistances in three-, four- and six-terminal geometries and compared these to the ones obtained for the corresponding QH bars. Furthermore, we have ...
... In conclusion, we have studied multi-terminal QSH devices based on the Büttiker approach of ballistic edge transport. We have derived expressions for resistances in three-, four- and six-terminal geometries and compared these to the ones obtained for the corresponding QH bars. Furthermore, we have ...
Path Integrals in Quantum Field Theory
... from the canonical formulation of quantum mechanics, using, for example, the timedependent Schrödinger equation. However, if one defines the amplitude associated with a given trajectory as eiS , then it is possible to derive the Schrödinger equation2 . We can even “derive” the classical principle ...
... from the canonical formulation of quantum mechanics, using, for example, the timedependent Schrödinger equation. However, if one defines the amplitude associated with a given trajectory as eiS , then it is possible to derive the Schrödinger equation2 . We can even “derive” the classical principle ...
quantum teleportation
... entangled particles. These entangled particles will form a pathway for the instantaneous data transfer of the information of the particle. However for the verification of quantum teleportation it classical information line between the sending and the receiving station is necessary, which excludes in ...
... entangled particles. These entangled particles will form a pathway for the instantaneous data transfer of the information of the particle. However for the verification of quantum teleportation it classical information line between the sending and the receiving station is necessary, which excludes in ...
Linear Momentum - University of Colorado Boulder
... (almost!) The Initial KE just before collision is converted to elastic PE as the ball compresses during the first half of its collision with the floor. But then the elastic PE is converted back into KE as the ball uncompresses during the second half of its collision with the floor. inelastic collisi ...
... (almost!) The Initial KE just before collision is converted to elastic PE as the ball compresses during the first half of its collision with the floor. But then the elastic PE is converted back into KE as the ball uncompresses during the second half of its collision with the floor. inelastic collisi ...
fundamental mathematics of consciousness
... measure of the energy of the system. Although the above formalism is accepted by all practicing physicists dealing with quantum systems as QM and quantum field theory are incredibly successful, the role of measurement, the implied role of the observer, and in fact the reality of the state vector giv ...
... measure of the energy of the system. Although the above formalism is accepted by all practicing physicists dealing with quantum systems as QM and quantum field theory are incredibly successful, the role of measurement, the implied role of the observer, and in fact the reality of the state vector giv ...
Work-Kinetic Energy Theorem for Rotational Motion
... moment of inertia, force with torque, kinetic energy with rotational kinetic energy, and momentum with angular momentum. The relationships between the rotational terms are identical to the relationships between the linear motion terms. Furthermore, we can often convert linear motion expressions to r ...
... moment of inertia, force with torque, kinetic energy with rotational kinetic energy, and momentum with angular momentum. The relationships between the rotational terms are identical to the relationships between the linear motion terms. Furthermore, we can often convert linear motion expressions to r ...
Pauli`s Principle in Probe Microscopy
... particles are those which have the same intrinsic (or “internal”) properties (and the same values associated with those intrinsic properties), i.e. mass, charge, spin. So two electrons are identical to each other. And two protons, or two neutrons, are similarly identical to each other. But electrons ...
... particles are those which have the same intrinsic (or “internal”) properties (and the same values associated with those intrinsic properties), i.e. mass, charge, spin. So two electrons are identical to each other. And two protons, or two neutrons, are similarly identical to each other. But electrons ...
Optically polarized atoms_Atomic_Transitions
... • Imagine a transition between levels for which E1 angular-momentum selection rules are satisfied, but parity rule is not • Notice: m is a pseudo-vector (= axial vector), i.e. it is invariant with respect m ...
... • Imagine a transition between levels for which E1 angular-momentum selection rules are satisfied, but parity rule is not • Notice: m is a pseudo-vector (= axial vector), i.e. it is invariant with respect m ...























