Double-Slit Experiment
... Curved (accelerated) motion means that electron should do what? = ASSUMPTIONS BASED IN CLASSICAL PHYSICS!!! Quantum physics: ...
... Curved (accelerated) motion means that electron should do what? = ASSUMPTIONS BASED IN CLASSICAL PHYSICS!!! Quantum physics: ...
Steve Hansen`s second test - Kwantlen Polytechnic University
... Instructions: There are 29 questions on this exam. Part A consists of multiple choice questions and Part B is a problem solving section. ALL WORK MUST BE SHOWN IN PART B TO RECEIVE ANY CREDIT. A periodic chart is included with this exam. Rough Calculations may be done on the back side of a page. Max ...
... Instructions: There are 29 questions on this exam. Part A consists of multiple choice questions and Part B is a problem solving section. ALL WORK MUST BE SHOWN IN PART B TO RECEIVE ANY CREDIT. A periodic chart is included with this exam. Rough Calculations may be done on the back side of a page. Max ...
Quantum Numbers and Electron Configurations Worksheet
... Use a phrase to describe why the 2s orbital is more stable (lower energy) versus 2p. When you superimpose the total radial probability of 2s and 2p onto the plot of 1s, you notice that the 2s has a small peak that is inside the 1s shield, which causes them to have more exposure to the full nuclear c ...
... Use a phrase to describe why the 2s orbital is more stable (lower energy) versus 2p. When you superimpose the total radial probability of 2s and 2p onto the plot of 1s, you notice that the 2s has a small peak that is inside the 1s shield, which causes them to have more exposure to the full nuclear c ...
Set #4
... 4. A long time ago, in a galaxy far, far away, electric charge had not yet been invented, and atoms were held together by gravitational forces. Compute the Bohr radius and the n=2 to n = 1 transition energy in a gravitationally hound hydrogen atom. (Krane, P33, pg. 204) 5. The fine structure constan ...
... 4. A long time ago, in a galaxy far, far away, electric charge had not yet been invented, and atoms were held together by gravitational forces. Compute the Bohr radius and the n=2 to n = 1 transition energy in a gravitationally hound hydrogen atom. (Krane, P33, pg. 204) 5. The fine structure constan ...
Example 27-1
... •When electron changes to a lower n it emits a photon of energy equal to the energy difference. •Electron must be given energy to move to a higher n •This formula can be used for any single electron atom or ion such as a singly-ionized He ion in which case Z=2. •The radius of the orbit is given by C ...
... •When electron changes to a lower n it emits a photon of energy equal to the energy difference. •Electron must be given energy to move to a higher n •This formula can be used for any single electron atom or ion such as a singly-ionized He ion in which case Z=2. •The radius of the orbit is given by C ...
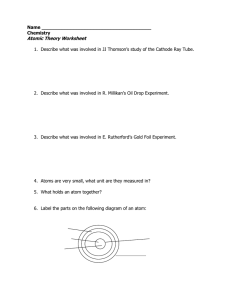
Atomic Theory Worksheet
... 1. Describe what was involved in JJ Thomson’s study of the Cathode Ray Tube. ...
... 1. Describe what was involved in JJ Thomson’s study of the Cathode Ray Tube. ...
Chapter 6. Electronic Structure of Atoms.
... Limitations of the Bohr model. The Bohr model only works for atoms/ions with a single electron (e.g. H or He+). It cannot account for the more numerous lines in multi-electron atoms such as Na or He. It does, however, make two important postulates: 1) electrons exist only in discrete energy levels, ...
... Limitations of the Bohr model. The Bohr model only works for atoms/ions with a single electron (e.g. H or He+). It cannot account for the more numerous lines in multi-electron atoms such as Na or He. It does, however, make two important postulates: 1) electrons exist only in discrete energy levels, ...
Lecture 1.1 Some preliminary chemistry knowledge, ppt file
... atom, the single electron is held in its orbital by its attraction to the proton in the nucleus. ...
... atom, the single electron is held in its orbital by its attraction to the proton in the nucleus. ...
IB HL Physics More Problems on Quantum and Nuclear Physics_
... In 1924, Davisson and Germer carried out an experiment in which electrons were accelerated through a potential difference of 54 V. The electrons were scattered at the surface of a nickel crystal. (i) ...
... In 1924, Davisson and Germer carried out an experiment in which electrons were accelerated through a potential difference of 54 V. The electrons were scattered at the surface of a nickel crystal. (i) ...
homework answers - SPHS Devil Physics
... f. What is this pattern of black lines called? g. What is the Balmer formula for the wavelengths in the hydrogen spectra? ...
... f. What is this pattern of black lines called? g. What is the Balmer formula for the wavelengths in the hydrogen spectra? ...
Prelab notes
... If a wave has a frequency of 9.33x106 Hz, what is it’s energy? 6.18x10-27 J What is the frequency of a wave if its energy is 4.32x10-31 J? 652 Hz ...
... If a wave has a frequency of 9.33x106 Hz, what is it’s energy? 6.18x10-27 J What is the frequency of a wave if its energy is 4.32x10-31 J? 652 Hz ...
Unit 1 Inorganic Flashcards
... surrounding molecules or ions by dative covalent bonds (also known as coordinate bonds). ...
... surrounding molecules or ions by dative covalent bonds (also known as coordinate bonds). ...
Bohr model
In atomic physics, the Rutherford–Bohr model or Bohr model, introduced by Niels Bohr in 1913, depicts the atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons that travel in circular orbits around the nucleus—similar in structure to the solar system, but with attraction provided by electrostatic forces rather than gravity. After the cubic model (1902), the plum-pudding model (1904), the Saturnian model (1904), and the Rutherford model (1911) came the Rutherford–Bohr model or just Bohr model for short (1913). The improvement to the Rutherford model is mostly a quantum physical interpretation of it. The Bohr model has been superseded, but the quantum theory remains sound.The model's key success lay in explaining the Rydberg formula for the spectral emission lines of atomic hydrogen. While the Rydberg formula had been known experimentally, it did not gain a theoretical underpinning until the Bohr model was introduced. Not only did the Bohr model explain the reason for the structure of the Rydberg formula, it also provided a justification for its empirical results in terms of fundamental physical constants.The Bohr model is a relatively primitive model of the hydrogen atom, compared to the valence shell atom. As a theory, it can be derived as a first-order approximation of the hydrogen atom using the broader and much more accurate quantum mechanics and thus may be considered to be an obsolete scientific theory. However, because of its simplicity, and its correct results for selected systems (see below for application), the Bohr model is still commonly taught to introduce students to quantum mechanics or energy level diagrams before moving on to the more accurate, but more complex, valence shell atom. A related model was originally proposed by Arthur Erich Haas in 1910, but was rejected. The quantum theory of the period between Planck's discovery of the quantum (1900) and the advent of a full-blown quantum mechanics (1925) is often referred to as the old quantum theory.