Document
... Chemistry 130 (Lecture VII-VIII) Answer 1. Which of the following statements is not consistent with a quantum mechanical view of nature? a. Matter can be thought of as waves b. Excited atoms can emit all possible energies c. Knowing the exact speed of an electron means we do not know anything about ...
... Chemistry 130 (Lecture VII-VIII) Answer 1. Which of the following statements is not consistent with a quantum mechanical view of nature? a. Matter can be thought of as waves b. Excited atoms can emit all possible energies c. Knowing the exact speed of an electron means we do not know anything about ...
1. dia
... the quantum system. They often describe specifically the energies of electrons in atoms, but other possibilities include angular momentum, spin etc. It is already known from the Bohr’s atom model that the energy of the electrons is quantized so they can have only one value. The energy values are det ...
... the quantum system. They often describe specifically the energies of electrons in atoms, but other possibilities include angular momentum, spin etc. It is already known from the Bohr’s atom model that the energy of the electrons is quantized so they can have only one value. The energy values are det ...
Lewis
... •atomic orbitals and quantum states (with quantum numbers n, m, l, s), • the energy levels of the different shells, subshells, orbitals, • the maximum number of shells, subshells, orbitals, and electrons, • the numbers and/or maximum numbers of bonds, an atom likes to or can build or have, • the Lew ...
... •atomic orbitals and quantum states (with quantum numbers n, m, l, s), • the energy levels of the different shells, subshells, orbitals, • the maximum number of shells, subshells, orbitals, and electrons, • the numbers and/or maximum numbers of bonds, an atom likes to or can build or have, • the Lew ...
UNIT 3 VOCABULARY MATCHING and mole problems
... ____ 1.) center part of an atom; contains almost all of the mass of an atom ____ 2.) equal to the number of protons in an atom; whole number on the Periodic Table ____ 3.) equal to the number of protons plus the number of neutrons in an atom ____ 4.) discovered the electron using a cathode ray tube ...
... ____ 1.) center part of an atom; contains almost all of the mass of an atom ____ 2.) equal to the number of protons in an atom; whole number on the Periodic Table ____ 3.) equal to the number of protons plus the number of neutrons in an atom ____ 4.) discovered the electron using a cathode ray tube ...
Electronics
... – where h is Planck's Constant and has been found experimentally to be 6.626 x 10 34 Js. Using these discrete energy values of hf, Planck was able to fit a mathematical equation to the entire blackbody curve. • Revolutionary Idea: Energy exists only in discrete amounts!!!!! • Smallest amount of ene ...
... – where h is Planck's Constant and has been found experimentally to be 6.626 x 10 34 Js. Using these discrete energy values of hf, Planck was able to fit a mathematical equation to the entire blackbody curve. • Revolutionary Idea: Energy exists only in discrete amounts!!!!! • Smallest amount of ene ...
Atomic and Molecular Physics for Physicists Ben-Gurion University of the Negev
... 1. Show that if a phase shifter (adding phase α) is introduced into one of the arms of the MZ from the previous slide, the photon detection probability in the bright detector goes like ½ (1+cos2α) 2. Explain why two photons meeting at a beam splitter always go together to One of the sides (a process ...
... 1. Show that if a phase shifter (adding phase α) is introduced into one of the arms of the MZ from the previous slide, the photon detection probability in the bright detector goes like ½ (1+cos2α) 2. Explain why two photons meeting at a beam splitter always go together to One of the sides (a process ...
The Quantum-Mechanical Model of the Atom
... The Bohr Atomic Model The Bohr model didn’t work for atoms other than hydrogen. It also failed to explain the fine splitting of the lines of the emission spectrum. Though limited, Bohr’s approach did attempt to explain the quantized energy levels of electrons. Later developments showed that any att ...
... The Bohr Atomic Model The Bohr model didn’t work for atoms other than hydrogen. It also failed to explain the fine splitting of the lines of the emission spectrum. Though limited, Bohr’s approach did attempt to explain the quantized energy levels of electrons. Later developments showed that any att ...
L 35 Modern Physics [1]
... and the Bohr Atom • Niels Bohr, a Danish physicist, used the quantum concept to explain the nature of the atom. • Recall that the orbiting electrons, according to classical ideas, should very quickly radiate away all of its energy • If this were so, then we would observe that atoms emit light over a ...
... and the Bohr Atom • Niels Bohr, a Danish physicist, used the quantum concept to explain the nature of the atom. • Recall that the orbiting electrons, according to classical ideas, should very quickly radiate away all of its energy • If this were so, then we would observe that atoms emit light over a ...
Physics 1020 Ch 10-12 Practice Exam (2).
... b. any electron present in an atom can have the same quantum state, since all electrons in an atom have the same mass and charge. c. there can be infinitely amount of electrons occupying an orbital as long as enough energy is provided. d. no two electrons can occupy the same quantum state. 11. The A ...
... b. any electron present in an atom can have the same quantum state, since all electrons in an atom have the same mass and charge. c. there can be infinitely amount of electrons occupying an orbital as long as enough energy is provided. d. no two electrons can occupy the same quantum state. 11. The A ...
Trends in the Periodic Table
... • A: How does temperature affect ionization energy? • Q: Temperature has no affect on ionization energy. Heat is only powerful enough to change kinetic energy of a particle or molecule. ...
... • A: How does temperature affect ionization energy? • Q: Temperature has no affect on ionization energy. Heat is only powerful enough to change kinetic energy of a particle or molecule. ...
Quantum Numbers and Electronic Configuration
... 1. The Principal Quantum Number. Given the symbol “n”. This denotes the energy level (shell). This has integer values 1, 2, 3. 2. The Angular Momentum Quantum Number. Given the symbol “l ” It denotes the number of sub-levels (orbitals) in each energy level and the shape of these orbitals. The number ...
... 1. The Principal Quantum Number. Given the symbol “n”. This denotes the energy level (shell). This has integer values 1, 2, 3. 2. The Angular Momentum Quantum Number. Given the symbol “l ” It denotes the number of sub-levels (orbitals) in each energy level and the shape of these orbitals. The number ...
Notes on the Electronic Structure of Atoms
... 1. Spectral lines are produced by atoms one at a time 2. A single electron is responsible for each line 3 The Rutherford nuclear atom is the correct ...
... 1. Spectral lines are produced by atoms one at a time 2. A single electron is responsible for each line 3 The Rutherford nuclear atom is the correct ...
Name: Date: Chemistry Enriched Per. ______ Midterm Review
... A tree grows in the woods…It is then chopped down and cut into firewood. You split the logs and let them “season” (dry out) for at least 6 months. You then burn the firewood in your highly efficient, “clean” burning wood stove. Describe the chemical and physical processes taking place…and describe h ...
... A tree grows in the woods…It is then chopped down and cut into firewood. You split the logs and let them “season” (dry out) for at least 6 months. You then burn the firewood in your highly efficient, “clean” burning wood stove. Describe the chemical and physical processes taking place…and describe h ...
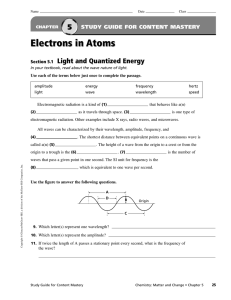
Electrons in Atoms
... All waves can be characterized by their wavelength, amplitude, frequency, and . The shortest distance between equivalent points on a continuous wave is ...
... All waves can be characterized by their wavelength, amplitude, frequency, and . The shortest distance between equivalent points on a continuous wave is ...
Quantum Numbers, Orbitals, Electron Configurations, Periodic Trends
... Convert the numbers is questions 1a – 1d into scientific notation. a) c) b) d) Convert the following numbers that are in scientific notation into decimal form. a) 1.2340 × 107 d) 7.0 × 104 b) 3.980 × 102 e) 5.00134 × 10-4 c) 9.23 × 10-5 f) 6.626 × 10-34 A box measures 2.56 in × 4.21 in × 12.00 in. W ...
... Convert the numbers is questions 1a – 1d into scientific notation. a) c) b) d) Convert the following numbers that are in scientific notation into decimal form. a) 1.2340 × 107 d) 7.0 × 104 b) 3.980 × 102 e) 5.00134 × 10-4 c) 9.23 × 10-5 f) 6.626 × 10-34 A box measures 2.56 in × 4.21 in × 12.00 in. W ...
Quantum Numbers, Orbitals, Electron Configurations, Periodic Trends
... Convert the numbers is questions 1a – 1d into scientific notation. a) c) b) d) Convert the following numbers that are in scientific notation into decimal form. a) 1.2340 × 107 d) 7.0 × 104 b) 3.980 × 102 e) 5.00134 × 10-4 c) 9.23 × 10-5 f) 6.626 × 10-34 A box measures 2.56 in × 4.21 in × 12.00 in. W ...
... Convert the numbers is questions 1a – 1d into scientific notation. a) c) b) d) Convert the following numbers that are in scientific notation into decimal form. a) 1.2340 × 107 d) 7.0 × 104 b) 3.980 × 102 e) 5.00134 × 10-4 c) 9.23 × 10-5 f) 6.626 × 10-34 A box measures 2.56 in × 4.21 in × 12.00 in. W ...
So where did all the matter on Earth come from - Bennatti
... atoms with two protons in the nucleus. Each element is represented with a chemical symbol. Most chemical symbols are one or two letters. The first letter is always capitalized. If it has two or three letters only the first letter is capitalized. For example the chemical symbol for the element magnes ...
... atoms with two protons in the nucleus. Each element is represented with a chemical symbol. Most chemical symbols are one or two letters. The first letter is always capitalized. If it has two or three letters only the first letter is capitalized. For example the chemical symbol for the element magnes ...
Slide 1
... established a rule is known as the Pauli exclusion principle. Pauli exclusion principle: the principle that states that two particles of a certain class cannot be in the exact same energy state. In plain English: no two electrons in the same atom can have the same four ...
... established a rule is known as the Pauli exclusion principle. Pauli exclusion principle: the principle that states that two particles of a certain class cannot be in the exact same energy state. In plain English: no two electrons in the same atom can have the same four ...
Bohr model
In atomic physics, the Rutherford–Bohr model or Bohr model, introduced by Niels Bohr in 1913, depicts the atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons that travel in circular orbits around the nucleus—similar in structure to the solar system, but with attraction provided by electrostatic forces rather than gravity. After the cubic model (1902), the plum-pudding model (1904), the Saturnian model (1904), and the Rutherford model (1911) came the Rutherford–Bohr model or just Bohr model for short (1913). The improvement to the Rutherford model is mostly a quantum physical interpretation of it. The Bohr model has been superseded, but the quantum theory remains sound.The model's key success lay in explaining the Rydberg formula for the spectral emission lines of atomic hydrogen. While the Rydberg formula had been known experimentally, it did not gain a theoretical underpinning until the Bohr model was introduced. Not only did the Bohr model explain the reason for the structure of the Rydberg formula, it also provided a justification for its empirical results in terms of fundamental physical constants.The Bohr model is a relatively primitive model of the hydrogen atom, compared to the valence shell atom. As a theory, it can be derived as a first-order approximation of the hydrogen atom using the broader and much more accurate quantum mechanics and thus may be considered to be an obsolete scientific theory. However, because of its simplicity, and its correct results for selected systems (see below for application), the Bohr model is still commonly taught to introduce students to quantum mechanics or energy level diagrams before moving on to the more accurate, but more complex, valence shell atom. A related model was originally proposed by Arthur Erich Haas in 1910, but was rejected. The quantum theory of the period between Planck's discovery of the quantum (1900) and the advent of a full-blown quantum mechanics (1925) is often referred to as the old quantum theory.












![L 35 Modern Physics [1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001689016_1-3e506855e2f70cb00e132a79d00855e2-300x300.png)