Ionic Bonding - cloudfront.net
... Occurs when more than ___ valid Lewis Structure can be written for a molecule or ion ...
... Occurs when more than ___ valid Lewis Structure can be written for a molecule or ion ...
Chapter 3
... When a solid is heated, it emits electromagnetic radiation, known as blackbody radiation, over a wide range of wavelengths. The amount of energy given off at a certain temperature depends on the wavelength. Classical physics failed to completely explain the phenomenon. Assumed that radiant energy ...
... When a solid is heated, it emits electromagnetic radiation, known as blackbody radiation, over a wide range of wavelengths. The amount of energy given off at a certain temperature depends on the wavelength. Classical physics failed to completely explain the phenomenon. Assumed that radiant energy ...
Mod6QM1
... •This does not mean that the system was at X before the measurement - it is not meaningful to say it was localized at all before the measurement. ...
... •This does not mean that the system was at X before the measurement - it is not meaningful to say it was localized at all before the measurement. ...
Unit 2 Spiraling
... 1. A sample of copper with a mass of 63.5 grams contains 6.02 x 10 23 atoms. Calculate the mass of a single copper atom. 2. Calculate the atomic mass of bromine. The two istopes of bromine have atomic masses and relative abundance of 78.92 amu (50.69%) and 80.92 amu (49.31%) Show your work and calcu ...
... 1. A sample of copper with a mass of 63.5 grams contains 6.02 x 10 23 atoms. Calculate the mass of a single copper atom. 2. Calculate the atomic mass of bromine. The two istopes of bromine have atomic masses and relative abundance of 78.92 amu (50.69%) and 80.92 amu (49.31%) Show your work and calcu ...
The Quantum Mechanics of MRI
... barrel), what is the minimum uncertainty in its momentum? c) If the accuracy of the bullet were determined only by the uncertainty principle (an unreasonable assumption), by how much might the bullet miss a pinpoint target 200m away?. h 6.6 1034 (a) Wavelength 3.06 1034 m p 0.012 180 h ...
... barrel), what is the minimum uncertainty in its momentum? c) If the accuracy of the bullet were determined only by the uncertainty principle (an unreasonable assumption), by how much might the bullet miss a pinpoint target 200m away?. h 6.6 1034 (a) Wavelength 3.06 1034 m p 0.012 180 h ...
Chapter 2
... • 1911, British physicist Ernest Rutherford – Gold foil experiment – Most alpha particles pass straight through gold foil – Most of atom = empty space – If a golf ball was the nucleus, the atom would be about 3 miles in diameter ...
... • 1911, British physicist Ernest Rutherford – Gold foil experiment – Most alpha particles pass straight through gold foil – Most of atom = empty space – If a golf ball was the nucleus, the atom would be about 3 miles in diameter ...
Optically polarized atoms_ch_2_Atomic_States
... In this approximation, energy of a configuration is just sum of Ei No reference to projections of li or to spins degeneracy If we go beyond the central-field approximation some of the degeneracies will be lifted Also spin-orbit (ls) interaction lifts some degeneracies In general, both effects nee ...
... In this approximation, energy of a configuration is just sum of Ei No reference to projections of li or to spins degeneracy If we go beyond the central-field approximation some of the degeneracies will be lifted Also spin-orbit (ls) interaction lifts some degeneracies In general, both effects nee ...
Optically polarized atoms_ch_2
... In this approximation, energy of a configuration is just sum of Ei No reference to projections of li or to spins degeneracy If we go beyond the central-field approximation some of the degeneracies will be lifted Also spin-orbit (ls) interaction lifts some degeneracies In general, both effects nee ...
... In this approximation, energy of a configuration is just sum of Ei No reference to projections of li or to spins degeneracy If we go beyond the central-field approximation some of the degeneracies will be lifted Also spin-orbit (ls) interaction lifts some degeneracies In general, both effects nee ...
Periodic Trends & the Periodic Table
... are comparing an atom and its ion • When an atom has a negative charge, you have added electrons • Which makes it bigger • For example, which will be larger: • Cl or Cl-1 ...
... are comparing an atom and its ion • When an atom has a negative charge, you have added electrons • Which makes it bigger • For example, which will be larger: • Cl or Cl-1 ...
Section 5-1
... • Contrast continuous electromagnetic spectra and atomic emission spectra. radiation: the rays and particles —alpha particles, beta particles, and gamma rays—that are emitted by radioactive material ...
... • Contrast continuous electromagnetic spectra and atomic emission spectra. radiation: the rays and particles —alpha particles, beta particles, and gamma rays—that are emitted by radioactive material ...
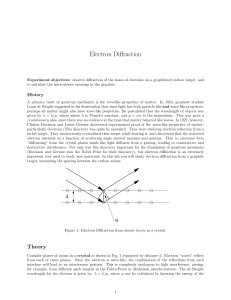
Electron Diffraction
... Louis de Broglie suggested in his dissertation that since light has both particle-like and wave-like properties, perhaps all matter might also have wave-like properties. He postulated that the wavelength of objects was given by λ = h/p, where where h is Planck’s constant, and p = mv is the momentum. ...
... Louis de Broglie suggested in his dissertation that since light has both particle-like and wave-like properties, perhaps all matter might also have wave-like properties. He postulated that the wavelength of objects was given by λ = h/p, where where h is Planck’s constant, and p = mv is the momentum. ...
HMWK 7
... The electron has enough energy to excite the atom to the n = 2 stationary state (E2 – E1 = 4.0 eV). However, it does not have enough energy to excite the atom into the n = 3 state, which requires a total energy of 6.0 eV. ...
... The electron has enough energy to excite the atom to the n = 2 stationary state (E2 – E1 = 4.0 eV). However, it does not have enough energy to excite the atom into the n = 3 state, which requires a total energy of 6.0 eV. ...
summer learning G10
... 12. Combine each pair of ions to get the formula of the compound they form and give the name of the compound formed https://youtu.be/C6cTM8jRY7o?t=114 ...
... 12. Combine each pair of ions to get the formula of the compound they form and give the name of the compound formed https://youtu.be/C6cTM8jRY7o?t=114 ...
Super-Shell Structure in Two-Component Dilute Fermionic Gases
... Dilute gases of Fermionic Atoms Atom-atom interaction is short-ranged (1-10 Å) and much smaller than interparticle range (~ 10-6 m) (dilute gas) Approximate int. with: ...
... Dilute gases of Fermionic Atoms Atom-atom interaction is short-ranged (1-10 Å) and much smaller than interparticle range (~ 10-6 m) (dilute gas) Approximate int. with: ...
V. Chemical reactions
... d. What particles are in equal numbers in a neutral atom? protons & electrons e. How is the number of protons determined? by atomic number f. How is the number of neutrons determined? subtract atomic number from mass number g. How is the number of electrons determined in a neutral atom? Equal to the ...
... d. What particles are in equal numbers in a neutral atom? protons & electrons e. How is the number of protons determined? by atomic number f. How is the number of neutrons determined? subtract atomic number from mass number g. How is the number of electrons determined in a neutral atom? Equal to the ...
Document
... A hydrogen atom electron is excited to an energy of −13.6/4 eV. How many different quantum states could the electron be in? That is, how many wave functions ynℓm have this energy? ...
... A hydrogen atom electron is excited to an energy of −13.6/4 eV. How many different quantum states could the electron be in? That is, how many wave functions ynℓm have this energy? ...
The angular part of the wavefunction, A(θ, Φ)
... of the wavefunction associated with the boundary surface of the s orbital has a constant sign. For a p orbital, there is one phase change with respect to the boundary surface and this occurs at a nodal plane as is shown for the pz orbital in Figure 1. The amplitude of a wavefunction may be positive ...
... of the wavefunction associated with the boundary surface of the s orbital has a constant sign. For a p orbital, there is one phase change with respect to the boundary surface and this occurs at a nodal plane as is shown for the pz orbital in Figure 1. The amplitude of a wavefunction may be positive ...
Chap. 3. Elementary Quantum Physics
... Fig. 3.3: Diffraction patterns obtained by passing X-rays through crystals can only be explained by using ideas based on the interference of waves. (a) Diffraction of X-rays from a single crystal gives a diffraction pattern of bright spots on a photographic film. (b) Diffraction of X-rays from a pow ...
... Fig. 3.3: Diffraction patterns obtained by passing X-rays through crystals can only be explained by using ideas based on the interference of waves. (a) Diffraction of X-rays from a single crystal gives a diffraction pattern of bright spots on a photographic film. (b) Diffraction of X-rays from a pow ...
Bohr model
In atomic physics, the Rutherford–Bohr model or Bohr model, introduced by Niels Bohr in 1913, depicts the atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons that travel in circular orbits around the nucleus—similar in structure to the solar system, but with attraction provided by electrostatic forces rather than gravity. After the cubic model (1902), the plum-pudding model (1904), the Saturnian model (1904), and the Rutherford model (1911) came the Rutherford–Bohr model or just Bohr model for short (1913). The improvement to the Rutherford model is mostly a quantum physical interpretation of it. The Bohr model has been superseded, but the quantum theory remains sound.The model's key success lay in explaining the Rydberg formula for the spectral emission lines of atomic hydrogen. While the Rydberg formula had been known experimentally, it did not gain a theoretical underpinning until the Bohr model was introduced. Not only did the Bohr model explain the reason for the structure of the Rydberg formula, it also provided a justification for its empirical results in terms of fundamental physical constants.The Bohr model is a relatively primitive model of the hydrogen atom, compared to the valence shell atom. As a theory, it can be derived as a first-order approximation of the hydrogen atom using the broader and much more accurate quantum mechanics and thus may be considered to be an obsolete scientific theory. However, because of its simplicity, and its correct results for selected systems (see below for application), the Bohr model is still commonly taught to introduce students to quantum mechanics or energy level diagrams before moving on to the more accurate, but more complex, valence shell atom. A related model was originally proposed by Arthur Erich Haas in 1910, but was rejected. The quantum theory of the period between Planck's discovery of the quantum (1900) and the advent of a full-blown quantum mechanics (1925) is often referred to as the old quantum theory.