Ch.5 VocabReview
... 5. the amount of energy required to move an electron from its present energy level to the next higher one ...
... 5. the amount of energy required to move an electron from its present energy level to the next higher one ...
Chapter 5 Powerpoint
... • In the Bohr model, the lone electron in the hydrogen atom can have only certain specific energies. • When the electron has its lowest possible energy, the atom is in its ground state. • Excitation of the electron by absorbing energy raises the atom from the ground state to an excited ...
... • In the Bohr model, the lone electron in the hydrogen atom can have only certain specific energies. • When the electron has its lowest possible energy, the atom is in its ground state. • Excitation of the electron by absorbing energy raises the atom from the ground state to an excited ...
Basics of wave functions - Department of Physics | Oregon State
... regions of space (few nm). For one thing, they can behave as if they are in an artificial atom. They emit light of particular frequencies … we can make a solid state laser! GaInP/AInP Quantum Well Laser Diode ...
... regions of space (few nm). For one thing, they can behave as if they are in an artificial atom. They emit light of particular frequencies … we can make a solid state laser! GaInP/AInP Quantum Well Laser Diode ...
lecture2
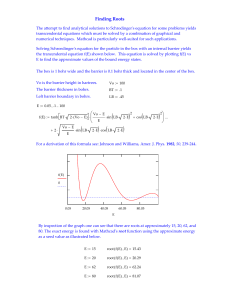
... calculate E for the fixed values of rAB. If we change the value of rAB, a corresponding value of E(rAB) can be got. Thus it should be possible to make a plot of E(rAB) against rAB in the figure below (Figure (x; ...
... calculate E for the fixed values of rAB. If we change the value of rAB, a corresponding value of E(rAB) can be got. Thus it should be possible to make a plot of E(rAB) against rAB in the figure below (Figure (x; ...
Recap of Lectures 12-2
... Harmonic oscillator illustrates quantum-classical transition at high quantum number n. Truly classical behaviour (observable change with time) requires physical state to be a superposition of energy states. ...
... Harmonic oscillator illustrates quantum-classical transition at high quantum number n. Truly classical behaviour (observable change with time) requires physical state to be a superposition of energy states. ...
Section 2 Notes
... number to describe the electrons in the atom. Only the size of the orbit was important in the Bohr Model, which was described by the n quantum number. Schrödinger described an atomic model with electrons in three dimensions. This model required three coordinates, or three quantum numbers, to describ ...
... number to describe the electrons in the atom. Only the size of the orbit was important in the Bohr Model, which was described by the n quantum number. Schrödinger described an atomic model with electrons in three dimensions. This model required three coordinates, or three quantum numbers, to describ ...
Atoms, molecules and ions
... • For an oxyacid (general formula HmXOn) it often happens that there are multiple possible values of n for each element X, and as such, within this series of compounds, – There is always an acid in the series that ends with “ic” • Adding another oxygen to the “ic” acid produces the “per….ic” acid • ...
... • For an oxyacid (general formula HmXOn) it often happens that there are multiple possible values of n for each element X, and as such, within this series of compounds, – There is always an acid in the series that ends with “ic” • Adding another oxygen to the “ic” acid produces the “per….ic” acid • ...
quantum numbers - Cloudfront.net
... Also known as sublevel or subshell Indicates the shape of the orbital within a shell Only integer values between 0 and n-1 are allowed Affects orbital energies (bigger l = higher energy) All electrons in an atom with the same value of l are said to belong to the same subshell Sometimes called the or ...
... Also known as sublevel or subshell Indicates the shape of the orbital within a shell Only integer values between 0 and n-1 are allowed Affects orbital energies (bigger l = higher energy) All electrons in an atom with the same value of l are said to belong to the same subshell Sometimes called the or ...
Quantum mechanics is the theory that we use to describe the
... Quantum mechanics is the theory that we use to describe the microscopic world. The microscopic world is the realm of atoms, photons, nuclei, electrons, neutrons, and a whole host of other subatomic particles. These particles are the “building blocks” of our universe, in the sense that everything tha ...
... Quantum mechanics is the theory that we use to describe the microscopic world. The microscopic world is the realm of atoms, photons, nuclei, electrons, neutrons, and a whole host of other subatomic particles. These particles are the “building blocks” of our universe, in the sense that everything tha ...
4.4 The Hamiltonian and its symmetry operations
... This is the adequate description of the state of a system described by the Hamiltonian H. This representation allows to calculate the time evolution easily. REMARK: This is just one example in natural science where discussing the symmetries serve fundamental information on the system. The search for ...
... This is the adequate description of the state of a system described by the Hamiltonian H. This representation allows to calculate the time evolution easily. REMARK: This is just one example in natural science where discussing the symmetries serve fundamental information on the system. The search for ...
Phys202_Final_Exam_Spr2006.doc
... 32. The equation for the magnetic field in terms of an infinitesimal current segment a distance r away is whose equation: a. Faraday’s b. ~ Biot & Savart’s c Amperes d. Gauss’ ...
... 32. The equation for the magnetic field in terms of an infinitesimal current segment a distance r away is whose equation: a. Faraday’s b. ~ Biot & Savart’s c Amperes d. Gauss’ ...
Matter: a Material World
... • How can we use spectra to determine the composition of a distant object? • How can we use spectra to determine the temperature of distant objects? • How can we use spectra to tell us how fast something is moving? ...
... • How can we use spectra to determine the composition of a distant object? • How can we use spectra to determine the temperature of distant objects? • How can we use spectra to tell us how fast something is moving? ...
1s 2s 2p - Solon City Schools
... The angular momentum quantum number (l ) can be any integer between 0 and n - 1. For n = 3, l can be either 0, 1, or 2. The magnetic quantum number (ml) can be any integer between -l and +l. For l = 2, m can be either -2, -1, 0, +1, +2. ...
... The angular momentum quantum number (l ) can be any integer between 0 and n - 1. For n = 3, l can be either 0, 1, or 2. The magnetic quantum number (ml) can be any integer between -l and +l. For l = 2, m can be either -2, -1, 0, +1, +2. ...
quantum number, n - Clayton State University
... established, the spectra suggested that electrons were allowed only in certain discrete energy levels. • In 1911, Niels Bohr proposed a model for the hydrogen atom, based on its spectrum. • Bohr assumed: • that the electron followed a circular orbit about the nucleus; and • that the angular momentum ...
... established, the spectra suggested that electrons were allowed only in certain discrete energy levels. • In 1911, Niels Bohr proposed a model for the hydrogen atom, based on its spectrum. • Bohr assumed: • that the electron followed a circular orbit about the nucleus; and • that the angular momentum ...
Hydrogen atom
A hydrogen atom is an atom of the chemical element hydrogen. The electrically neutral atom contains a single positively charged proton and a single negatively charged electron bound to the nucleus by the Coulomb force. Atomic hydrogen constitutes about 75% of the elemental (baryonic) mass of the universe.In everyday life on Earth, isolated hydrogen atoms (usually called ""atomic hydrogen"" or, more precisely, ""monatomic hydrogen"") are extremely rare. Instead, hydrogen tends to combine with other atoms in compounds, or with itself to form ordinary (diatomic) hydrogen gas, H2. ""Atomic hydrogen"" and ""hydrogen atom"" in ordinary English use have overlapping, yet distinct, meanings. For example, a water molecule contains two hydrogen atoms, but does not contain atomic hydrogen (which would refer to isolated hydrogen atoms).