Unit A * Biological Diversity
... • This usually consists of inserting a desirable gene from one species into another • Example: Some genetically modified bacteria now produce insulin because of a gene inserted into them • Diabetics need insulin and since bacteria grow so quickly they can produce a lot of insulin which allows it to ...
... • This usually consists of inserting a desirable gene from one species into another • Example: Some genetically modified bacteria now produce insulin because of a gene inserted into them • Diabetics need insulin and since bacteria grow so quickly they can produce a lot of insulin which allows it to ...
Evolution Review - LFHS AP Biology
... generation to the next if the population is large and there is no natural selection. b. only natural selection, resulting in unequal reproductive success, will cause evolution. c. the square root of the frequency of individuals showing the recessive trait will always equal the frequency of q. d. gen ...
... generation to the next if the population is large and there is no natural selection. b. only natural selection, resulting in unequal reproductive success, will cause evolution. c. the square root of the frequency of individuals showing the recessive trait will always equal the frequency of q. d. gen ...
BIOLOGY
... ______ On the Galápagos Islands, Darwin observed that the characteristics of many animals and plants A. all looked alike B. were completely unrelated C. were acquired through use D. varied from island to island ...
... ______ On the Galápagos Islands, Darwin observed that the characteristics of many animals and plants A. all looked alike B. were completely unrelated C. were acquired through use D. varied from island to island ...
EVOLUTION NOTES
... make certain individuals better adapted to survive. Exs. Size, color, structure • Survival of the fittest • Natural Selection variations that are more helpful are a natural selection agent against organisms that can’t adapt. • A population evolves not the individual ...
... make certain individuals better adapted to survive. Exs. Size, color, structure • Survival of the fittest • Natural Selection variations that are more helpful are a natural selection agent against organisms that can’t adapt. • A population evolves not the individual ...
Biology I Evolution Test
... 1. Amoeba Sisters "Natural Selection" hftps: /lwww.youtube.com/watch?v=TVM9YxmULuo 2. Five Fingers of Evolution https:l/wwwyoutube.comlwatch?v=5NdMnlt2keE 3. Teacher's Pet'"Three types ofNatural Selection" https: /lwwwyoutube.com/watch?v=64J UJdZdDQo ...
... 1. Amoeba Sisters "Natural Selection" hftps: /lwww.youtube.com/watch?v=TVM9YxmULuo 2. Five Fingers of Evolution https:l/wwwyoutube.comlwatch?v=5NdMnlt2keE 3. Teacher's Pet'"Three types ofNatural Selection" https: /lwwwyoutube.com/watch?v=64J UJdZdDQo ...
Name ______ Pd ___ Biology Evolution Review – SMITH 2016 KEY
... Protect life from UV radiation from the Sun, act as a filter from the sun 28. When Darwin published his theory of evolution, he included many ideas. List his principles. Principle 1 – individuals in a population show differences Principle 2 – Variations are inherited Principle 3 – Animals have more ...
... Protect life from UV radiation from the Sun, act as a filter from the sun 28. When Darwin published his theory of evolution, he included many ideas. List his principles. Principle 1 – individuals in a population show differences Principle 2 – Variations are inherited Principle 3 – Animals have more ...
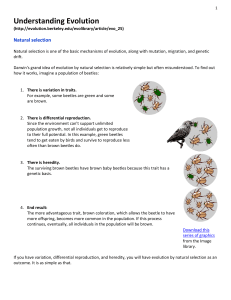
Natural Selection
... The surviving brown beetles have brown baby beetles because this trait has a genetic basis (trait is passed down from one generation to the next). ...
... The surviving brown beetles have brown baby beetles because this trait has a genetic basis (trait is passed down from one generation to the next). ...
Evolution Review
... expected amount of C-14 of a similar sample created today. Approximately how long ago did the tiger die? ...
... expected amount of C-14 of a similar sample created today. Approximately how long ago did the tiger die? ...
Evolution
... changes in the inherited characteristics of a population. • These changes increase a species’ fitness in its environment. – Natural selection cannot be seen directly; it can only be observed as changes in a population over many successive generations. ...
... changes in the inherited characteristics of a population. • These changes increase a species’ fitness in its environment. – Natural selection cannot be seen directly; it can only be observed as changes in a population over many successive generations. ...
Name: Date - Ms. Ottolini`s Biology Wiki!
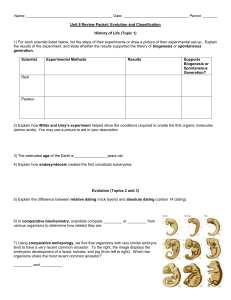
... 17) Explain the difference between the two models of the rate of evolutionary change: gradualism and punctuated equilibrium. Please include a picture/diagram to support your explanation. ...
... 17) Explain the difference between the two models of the rate of evolutionary change: gradualism and punctuated equilibrium. Please include a picture/diagram to support your explanation. ...
chapter 15 test
... 39. _________ First became interested in natural history after studying under John Henslow, a professor of botany at Cambridge University 40. _________ Was the first to state that types of organisms change over time and new organisms are modified descendents of older types ...
... 39. _________ First became interested in natural history after studying under John Henslow, a professor of botany at Cambridge University 40. _________ Was the first to state that types of organisms change over time and new organisms are modified descendents of older types ...
Evolution
... Darwin’s Theory of Natural Selection Through his travels to SA and Galapagos Islands, collecting and observing different species By reading the works of other scientists who ...
... Darwin’s Theory of Natural Selection Through his travels to SA and Galapagos Islands, collecting and observing different species By reading the works of other scientists who ...
Evolution Notes
... Evolution of Dance In order for evolution to occur variation (changes) in genes such as mutations, must exist Organism’s genes change because of mutations—which can be helpful, harmful, or have no effect. ...
... Evolution of Dance In order for evolution to occur variation (changes) in genes such as mutations, must exist Organism’s genes change because of mutations—which can be helpful, harmful, or have no effect. ...
Darwin–Lab - Mrs. Hoenshell Science 2016
... Hundreds of years ago, the bark of these trees was light colored, and most of these moths were light colored, so they could blend into the bark of the trees in their environment. This camouflage allowed them to hide from predators. In the 1800’s, the growth of industry began polluting the air in the ...
... Hundreds of years ago, the bark of these trees was light colored, and most of these moths were light colored, so they could blend into the bark of the trees in their environment. This camouflage allowed them to hide from predators. In the 1800’s, the growth of industry began polluting the air in the ...
lesson-21-natural-selection
... of the many stops that his ship made on its long voyage. Actually, Darwin did not recognize the importance of variations in these birds until he had returned to England, There he took his time in taking a much closer look at the finches, especially their beaks. There turns out to be 14 species of fi ...
... of the many stops that his ship made on its long voyage. Actually, Darwin did not recognize the importance of variations in these birds until he had returned to England, There he took his time in taking a much closer look at the finches, especially their beaks. There turns out to be 14 species of fi ...
Understanding Evolution Reading Assignment
... Scientists have worked out many examples of natural selection, one of the basic mechanisms of evolution. Any coffee table book about natural history will overwhelm you with full-page glossies depicting amazing adaptations produced by natural selection, such as the examples below. ...
... Scientists have worked out many examples of natural selection, one of the basic mechanisms of evolution. Any coffee table book about natural history will overwhelm you with full-page glossies depicting amazing adaptations produced by natural selection, such as the examples below. ...
Warm Up - Dickinson ISD
... In their early stages of development, many animals look similar, providing evidence that they shared a common ancestry. ...
... In their early stages of development, many animals look similar, providing evidence that they shared a common ancestry. ...
Biological Evolution - Shenandoah Baptist Church
... He Put His Faith in Science “A look at Darwing’s life can show you how horrible the results are when you put your faith in science. Science is limited and is constantly changing. What we thought were scientific laws less than a century ago are now known to be wrong. We now know that most of Darwin’ ...
... He Put His Faith in Science “A look at Darwing’s life can show you how horrible the results are when you put your faith in science. Science is limited and is constantly changing. What we thought were scientific laws less than a century ago are now known to be wrong. We now know that most of Darwin’ ...
Quiz 4 - Lone Star College
... 23) A change in the frequency of a phenotype in a population is likely caused by: A) artificial selection. B) uniformitarianism. C) Natural selection D) Continuism ...
... 23) A change in the frequency of a phenotype in a population is likely caused by: A) artificial selection. B) uniformitarianism. C) Natural selection D) Continuism ...
Natural Selection
... 1. Evolution is the gradual change in a species, or populations over time, not individuals. 2. Darwin was the first scientist to realize that evolution can work by natural selection. a) Natural Selection – Is a mechanism for change in populations. It occurs when organisms with favorable variations ...
... 1. Evolution is the gradual change in a species, or populations over time, not individuals. 2. Darwin was the first scientist to realize that evolution can work by natural selection. a) Natural Selection – Is a mechanism for change in populations. It occurs when organisms with favorable variations ...
Chapter 15—Evolution I. Section 1:Darwin`s Theory of
... - only members of the ____________ species can breed - ____________ is the process by which some members of a population change so much that they can no longer produce fertile offspring - there are two mechanisms by which speciation can occur 1. ____________ ____________ prevents reproduction by mak ...
... - only members of the ____________ species can breed - ____________ is the process by which some members of a population change so much that they can no longer produce fertile offspring - there are two mechanisms by which speciation can occur 1. ____________ ____________ prevents reproduction by mak ...
Descent With Modification
... got the credit because he wrote it first and because Wallace was cool about it. ...
... got the credit because he wrote it first and because Wallace was cool about it. ...
Natural selection

Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype; it is a key mechanism of evolution. The term ""natural selection"" was popularised by Charles Darwin, who intended it to be compared with artificial selection, now more commonly referred to as selective breeding.Variation exists within all populations of organisms. This occurs partly because random mutations arise in the genome of an individual organism, and these mutations can be passed to offspring. Throughout the individuals’ lives, their genomes interact with their environments to cause variations in traits. (The environment of a genome includes the molecular biology in the cell, other cells, other individuals, populations, species, as well as the abiotic environment.) Individuals with certain variants of the trait may survive and reproduce more than individuals with other, less successful, variants. Therefore, the population evolves. Factors that affect reproductive success are also important, an issue that Darwin developed in his ideas on sexual selection, which was redefined as being included in natural selection in the 1930s when biologists considered it not to be very important, and fecundity selection, for example.Natural selection acts on the phenotype, or the observable characteristics of an organism, but the genetic (heritable) basis of any phenotype that gives a reproductive advantage may become more common in a population (see allele frequency). Over time, this process can result in populations that specialise for particular ecological niches (microevolution) and may eventually result in the emergence of new species (macroevolution). In other words, natural selection is an important process (though not the only process) by which evolution takes place within a population of organisms. Natural selection can be contrasted with artificial selection, in which humans intentionally choose specific traits (although they may not always get what they want). In natural selection there is no intentional choice. In other words, artificial selection is teleological and natural selection is not teleological.Natural selection is one of the cornerstones of modern biology. The concept was published by Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace in a joint presentation of papers in 1858, and set out in Darwin's influential 1859 book On the Origin of Species, in which natural selection was described as analogous to artificial selection, a process by which animals and plants with traits considered desirable by human breeders are systematically favoured for reproduction. The concept of natural selection was originally developed in the absence of a valid theory of heredity; at the time of Darwin's writing, nothing was known of modern genetics. The union of traditional Darwinian evolution with subsequent discoveries in classical and molecular genetics is termed the modern evolutionary synthesis. Natural selection remains the primary explanation for adaptive evolution.