Vegetables in the Cabbage Family
... Look up a breed of dog and discuss why it was bred with certain traits and not others. (due Thursday). ...
... Look up a breed of dog and discuss why it was bred with certain traits and not others. (due Thursday). ...
What is the Hierarchy Theory of Evolution?
... endless debate on multilevel selection, or to puzzling but crucial notions such as fitness or species or information. On the other hand, much work is still to be done on clarifying the two hierarchies: their nature, their general organization principles, the levels that compose them, all the process ...
... endless debate on multilevel selection, or to puzzling but crucial notions such as fitness or species or information. On the other hand, much work is still to be done on clarifying the two hierarchies: their nature, their general organization principles, the levels that compose them, all the process ...
Evolution Spring 2010
... • Actually is just another way to say speciation • Usually occurs due to individuals adapting to new environments • Adaptive – development of adaptations to “fit” new environments • Radiation – to spread out, become different ...
... • Actually is just another way to say speciation • Usually occurs due to individuals adapting to new environments • Adaptive – development of adaptations to “fit” new environments • Radiation – to spread out, become different ...
Ertertewt ertwetr - Campbell County Schools
... between islands, but females would only mate with other finches with large beaks. This is behavioral reproductive isolation – they can mate, but they don’t. The gene pools of each population remained isolated – even though they were living together. These 2 populations are now considered to be separ ...
... between islands, but females would only mate with other finches with large beaks. This is behavioral reproductive isolation – they can mate, but they don’t. The gene pools of each population remained isolated – even though they were living together. These 2 populations are now considered to be separ ...
Evidence for evolution
... envisaged process similar to artificial selection that had produced organisms we see today. He called it Natural Selection. ...
... envisaged process similar to artificial selection that had produced organisms we see today. He called it Natural Selection. ...
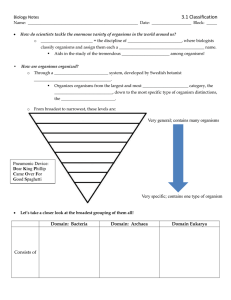
3.1 Classification
... Each organism has a_______________________________ name, describing its ___________________________ (the group of closely related ________________________ it belongs to) and _______________________________ (unique to each _________________________ in the group.) ...
... Each organism has a_______________________________ name, describing its ___________________________ (the group of closely related ________________________ it belongs to) and _______________________________ (unique to each _________________________ in the group.) ...
EVOLUTION: Unifying Concept in Biology
... populations over time change in allele frequencies (genetic composition) or the heritable change in the expression of those alleles (epigenetic inheritance) Acts by removing individuals from the population, or by allowing some to leave more offspring By population, we are referring to a group of i ...
... populations over time change in allele frequencies (genetic composition) or the heritable change in the expression of those alleles (epigenetic inheritance) Acts by removing individuals from the population, or by allowing some to leave more offspring By population, we are referring to a group of i ...
Bio 1B, Spring, 2007, Evolution section 1 of 3 Updated 2/22/07 9:22
... struggle for existence is against other members of the same species, against members of other species and against the physical environment. All animals and plants have many more offspring than can possibly survive, making the struggle for existence inevitable. The view of nature that Darwin presente ...
... struggle for existence is against other members of the same species, against members of other species and against the physical environment. All animals and plants have many more offspring than can possibly survive, making the struggle for existence inevitable. The view of nature that Darwin presente ...
Review for Final - Woodland Hills School District
... 51. Define decomposer. • An organism that feeds by breaking down organic matter from dead organisms; examples include bacteria and fungi. ...
... 51. Define decomposer. • An organism that feeds by breaking down organic matter from dead organisms; examples include bacteria and fungi. ...
spatial sorting - The University of Sydney
... In PNAS, Shine et al. (1) discussed the empirical evidence for, and evolutionary importance of, “spatial sorting,” where reproduction between fast-dispersing individuals at a rangeexpansion front generates novel phenotypes, even in the absence of conventional natural selection. Here, I suggest why t ...
... In PNAS, Shine et al. (1) discussed the empirical evidence for, and evolutionary importance of, “spatial sorting,” where reproduction between fast-dispersing individuals at a rangeexpansion front generates novel phenotypes, even in the absence of conventional natural selection. Here, I suggest why t ...
Station 2 - kroymbhs
... Observe Figure D and answer the following question. 1. Discuss the importance of fossils as a record of evolutionary change over time. The questions below relate to Figure E, showing a hypothetical rock profile from two locations separated by a distance of 67 km. There are some differences between t ...
... Observe Figure D and answer the following question. 1. Discuss the importance of fossils as a record of evolutionary change over time. The questions below relate to Figure E, showing a hypothetical rock profile from two locations separated by a distance of 67 km. There are some differences between t ...
Bio 1B, Spring, 2008, Evolution section 1 of 3 Updated 2/28/08 10
... struggle for existence is against other members of the same species, against members of other species, and against the physical environment. All animals and plants have many more offspring than can possibly survive, making the struggle for existence inevitable. The view of nature that Darwin present ...
... struggle for existence is against other members of the same species, against members of other species, and against the physical environment. All animals and plants have many more offspring than can possibly survive, making the struggle for existence inevitable. The view of nature that Darwin present ...
Chapter 14
... One of the 18th & 19th centuries’ biologists who hypothesized that traits of species are not immutable, i.e., they can evolve See timeline Fig. 22.2 ...
... One of the 18th & 19th centuries’ biologists who hypothesized that traits of species are not immutable, i.e., they can evolve See timeline Fig. 22.2 ...
Welcome to Biology Class2
... They all need to function (work) together in an orderly, living system. ...
... They all need to function (work) together in an orderly, living system. ...
naturally selected
... • Deeper analysis of the selection event on G. fortis during 1976-77 indicated that an optimal evolutionary response would have been to have birds with deeper and narrower beaks, that is, for beak shape as well as size to evolve. But beak depth and beak width are positively correlated (both phenotyp ...
... • Deeper analysis of the selection event on G. fortis during 1976-77 indicated that an optimal evolutionary response would have been to have birds with deeper and narrower beaks, that is, for beak shape as well as size to evolve. But beak depth and beak width are positively correlated (both phenotyp ...
Answers to Mastering Concepts Questions
... 1. How did James Hutton, Georges Cuvier, Georges-Louis Buffon, Jean Baptiste de Lamarck, Charles Lyell, and Thomas Malthus influence Charles Darwin’s thinking? James Hutton influenced Darwin by suggesting that changes in nature were gradual and uniform (a concept called uniformitarianism). Georges C ...
... 1. How did James Hutton, Georges Cuvier, Georges-Louis Buffon, Jean Baptiste de Lamarck, Charles Lyell, and Thomas Malthus influence Charles Darwin’s thinking? James Hutton influenced Darwin by suggesting that changes in nature were gradual and uniform (a concept called uniformitarianism). Georges C ...
Plate tectonics
... because new clades arise that are genetically separated from other lineages. When gene flow stops between two populations or two lineages, the lineages are reproductively isolated from one another. Example: mammals. 4. There is a fourth possible outcome for changes within populations – extinction. E ...
... because new clades arise that are genetically separated from other lineages. When gene flow stops between two populations or two lineages, the lineages are reproductively isolated from one another. Example: mammals. 4. There is a fourth possible outcome for changes within populations – extinction. E ...
File
... His research was based on observations made during his long voyage on the HMS Beagle, between 1831 and 1836. This made him realise that the Earth is very old and that major changes have taken place over long periods of time. Outline Darwin’s approach using the giraffe as an example Darwin • As a res ...
... His research was based on observations made during his long voyage on the HMS Beagle, between 1831 and 1836. This made him realise that the Earth is very old and that major changes have taken place over long periods of time. Outline Darwin’s approach using the giraffe as an example Darwin • As a res ...
Guidelines for Evolution Quiz
... Be able identify the 3 different types of adaptations Be able to describe the 3 major patterns of evolution and know examples Be able to describe the 3 major types of natural selection Be able to identify organism characteristics which may be determined by fossil evidence Be able to descri ...
... Be able identify the 3 different types of adaptations Be able to describe the 3 major patterns of evolution and know examples Be able to describe the 3 major types of natural selection Be able to identify organism characteristics which may be determined by fossil evidence Be able to descri ...
GAD EvoTalk
... How much medical research is done on humans? Only about 10%. The rest is done on rats, cats, dogs, pigs, monkeys. The fact is, we can advance our knowledge of human physiology by studying the same processes in other animals. This is based on common ancestry that yields physiological similarities. By ...
... How much medical research is done on humans? Only about 10%. The rest is done on rats, cats, dogs, pigs, monkeys. The fact is, we can advance our knowledge of human physiology by studying the same processes in other animals. This is based on common ancestry that yields physiological similarities. By ...
Evolution PowerPoint
... 1. Describe 5 processes by which fossils may be formed. 2. Explain why fossils are often found in sedimentary rocks. 3. Differentiate relative and absolute dating. 4. Explain how radioactive dating can determine the age of rocks. 5. Define the terms correlation and index fossil. 6. Explain what is m ...
... 1. Describe 5 processes by which fossils may be formed. 2. Explain why fossils are often found in sedimentary rocks. 3. Differentiate relative and absolute dating. 4. Explain how radioactive dating can determine the age of rocks. 5. Define the terms correlation and index fossil. 6. Explain what is m ...
Revised Exam 3 Review
... traits with potential costs to survival that are outweighed by reproductive fitness gains 17. Secondary sexual characteristics: those characteristics that develop just before an organism’s adult phase that may distinguish the sexes of a species 18. Sexual Dimorphism: when males and females differ in ...
... traits with potential costs to survival that are outweighed by reproductive fitness gains 17. Secondary sexual characteristics: those characteristics that develop just before an organism’s adult phase that may distinguish the sexes of a species 18. Sexual Dimorphism: when males and females differ in ...
Evolution

Evolution is change in the heritable traits of biological populations over successive generations. Evolutionary processes give rise to diversity at every level of biological organisation, including the levels of species, individual organisms, and molecules.All of life on earth shares a common ancestor known as the last universal ancestor, which lived approximately 3.5–3.8 billion years ago. Repeated formation of new species (speciation), change within species (anagenesis), and loss of species (extinction) throughout the evolutionary history of life on Earth are demonstrated by shared sets of morphological and biochemical traits, including shared DNA sequences. These shared traits are more similar among species that share a more recent common ancestor, and can be used to reconstruct a biological ""tree of life"" based on evolutionary relationships (phylogenetics), using both existing species and fossils. The fossil record includes a progression from early biogenic graphite, to microbial mat fossils, to fossilized multicellular organisms. Existing patterns of biodiversity have been shaped both by speciation and by extinction. More than 99 percent of all species that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates of Earth's current species range from 10 to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented.In the mid-19th century, Charles Darwin formulated the scientific theory of evolution by natural selection, published in his book On the Origin of Species (1859). Evolution by natural selection is a process demonstrated by the observation that more offspring are produced than can possibly survive, along with three facts about populations: 1) traits vary among individuals with respect to morphology, physiology, and behaviour (phenotypic variation), 2) different traits confer different rates of survival and reproduction (differential fitness), and 3) traits can be passed from generation to generation (heritability of fitness). Thus, in successive generations members of a population are replaced by progeny of parents better adapted to survive and reproduce in the biophysical environment in which natural selection takes place. This teleonomy is the quality whereby the process of natural selection creates and preserves traits that are seemingly fitted for the functional roles they perform. Natural selection is the only known cause of adaptation but not the only known cause of evolution. Other, nonadaptive causes of microevolution include mutation and genetic drift.In the early 20th century the modern evolutionary synthesis integrated classical genetics with Darwin's theory of evolution by natural selection through the discipline of population genetics. The importance of natural selection as a cause of evolution was accepted into other branches of biology. Moreover, previously held notions about evolution, such as orthogenesis, evolutionism, and other beliefs about innate ""progress"" within the largest-scale trends in evolution, became obsolete scientific theories. Scientists continue to study various aspects of evolutionary biology by forming and testing hypotheses, constructing mathematical models of theoretical biology and biological theories, using observational data, and performing experiments in both the field and the laboratory. Evolution is a cornerstone of modern science, accepted as one of the most reliably established of all facts and theories of science, based on evidence not just from the biological sciences but also from anthropology, psychology, astrophysics, chemistry, geology, physics, mathematics, and other scientific disciplines, as well as behavioral and social sciences. Understanding of evolution has made significant contributions to humanity, including the prevention and treatment of human disease, new agricultural products, industrial innovations, a subfield of computer science, and rapid advances in life sciences. Discoveries in evolutionary biology have made a significant impact not just in the traditional branches of biology but also in other academic disciplines (e.g., biological anthropology and evolutionary psychology) and in society at large.