Chapter 16 Evoluti 09 NF
... often called the theory of evolution by natural selection. – This theory can be summarized in the following four logical steps—overproduction, variation, selection, and adaptation. Each species becomes adapted to its environment as a result of living in it over time. An adaptation is an inherited tr ...
... often called the theory of evolution by natural selection. – This theory can be summarized in the following four logical steps—overproduction, variation, selection, and adaptation. Each species becomes adapted to its environment as a result of living in it over time. An adaptation is an inherited tr ...
Ashley Stein`s Portfolio
... population of insects living near the thin-fruited trees had a much shorter beak than the bugs living by the thick-fruited tree. The short-beaked bugs living on the thin-fruited trees are descendants of the long-beaked bugs that lived on the thick-fruited trees because a shorter beak was now what th ...
... population of insects living near the thin-fruited trees had a much shorter beak than the bugs living by the thick-fruited tree. The short-beaked bugs living on the thin-fruited trees are descendants of the long-beaked bugs that lived on the thick-fruited trees because a shorter beak was now what th ...
Biology II – CHAPTER 1: An Introduction to Life on Earth
... o Living things have the capacity to evolve, therefore, over time mutations and variable offspring create diversity in the genetic material of a species or evolution. o The scientific theory of evolution states that modern organisms descended – with modification – from preexisting life-forms, ultima ...
... o Living things have the capacity to evolve, therefore, over time mutations and variable offspring create diversity in the genetic material of a species or evolution. o The scientific theory of evolution states that modern organisms descended – with modification – from preexisting life-forms, ultima ...
Chapter 13 - Evolution
... ancestral species that were different from present-day ones • Evolution describes the genetic changes in a population over time ...
... ancestral species that were different from present-day ones • Evolution describes the genetic changes in a population over time ...
Chapter 05_lecture
... Genetic drift- change in the genetic composition of a population over time as a result of random ...
... Genetic drift- change in the genetic composition of a population over time as a result of random ...
Evolutionary Theory, according to Darwin
... are by definition more fit and better adapted than I am. ...
... are by definition more fit and better adapted than I am. ...
3.3 The Process of Evolution: How Does Natural Selection Work?
... 3.3 The Process of Evolution: How Does Natural Selection Work? • Lamarck and other researchers has already proposed evolution as a pattern in nature long before Darwin began his work • Darwin’s crucial insight lay in recognizing a process called natural selection ...
... 3.3 The Process of Evolution: How Does Natural Selection Work? • Lamarck and other researchers has already proposed evolution as a pattern in nature long before Darwin began his work • Darwin’s crucial insight lay in recognizing a process called natural selection ...
Chapter Test A
... 17. What are the functions of the three forelimbs in Figure 10.3? Structure A is a human arm, which is used for lifting and carrying items. Structure B is the fin of a whale and is used for swimming. Structure C is the wing of a bat and is used for flying. 18. What do these structures indicate about ...
... 17. What are the functions of the three forelimbs in Figure 10.3? Structure A is a human arm, which is used for lifting and carrying items. Structure B is the fin of a whale and is used for swimming. Structure C is the wing of a bat and is used for flying. 18. What do these structures indicate about ...
Fulltext PDF
... reasonable definition of biological success. Man began his career as a rare animal, living somewhere in the tropics or subtropics of the Old World, probably in Africa. From this obscure beginning, mankind multiplied to become one of the most numerous mammals, for there will soon be about three billi ...
... reasonable definition of biological success. Man began his career as a rare animal, living somewhere in the tropics or subtropics of the Old World, probably in Africa. From this obscure beginning, mankind multiplied to become one of the most numerous mammals, for there will soon be about three billi ...
Darwin - Integrative Biology
... homologous structures: a homologous structure is an anatomical, developmental, behavioral, or genetic feature shared between two different organisms because they inherited it from a common ancestor, i.e., same evolutionary origin. The feature, e.g., anatomical structure, may now differ in function ...
... homologous structures: a homologous structure is an anatomical, developmental, behavioral, or genetic feature shared between two different organisms because they inherited it from a common ancestor, i.e., same evolutionary origin. The feature, e.g., anatomical structure, may now differ in function ...
E - Bio @ Horton AP Biology
... 1. Darwin decided adaptations develop over time; he sought a mechanism by which adaptations might arise. 2. Natural selection was proposed by both Alfred Russel Wallace and Darwin as a driving mechanism of evolution caused by environmental selection of organisms most fit to reproduce, resulting in a ...
... 1. Darwin decided adaptations develop over time; he sought a mechanism by which adaptations might arise. 2. Natural selection was proposed by both Alfred Russel Wallace and Darwin as a driving mechanism of evolution caused by environmental selection of organisms most fit to reproduce, resulting in a ...
Darwin - Integrative Biology
... thinking about the huge diversity of living organisms • fossils related to living animals in the same area • oceanic islands species: related to each other and to species on closest mainland • geographic distribution of species: animals and plants of Australia and South America not related (although ...
... thinking about the huge diversity of living organisms • fossils related to living animals in the same area • oceanic islands species: related to each other and to species on closest mainland • geographic distribution of species: animals and plants of Australia and South America not related (although ...
1 Evolution, Variation, and Adaptation
... -the result of variations within populations over long periods of time -it can result in: -different forms of beaks (morphology) -changes in use (bat wing vs. human hand) -changes in behavior (feeding, mating, …) -biologists observed that living organisms were different from the fossil organisms -th ...
... -the result of variations within populations over long periods of time -it can result in: -different forms of beaks (morphology) -changes in use (bat wing vs. human hand) -changes in behavior (feeding, mating, …) -biologists observed that living organisms were different from the fossil organisms -th ...
1 Evolution, Variation, and Adaptation
... -how do variations occur? 1. genetic recombination- some of the genes are contributed by both parents 2. mutations- changes in nitrogenous bases in DNA that may result in differences in offspring 3. crossing over 4. random fertilization 5. independent assortment -why is variation important? -differe ...
... -how do variations occur? 1. genetic recombination- some of the genes are contributed by both parents 2. mutations- changes in nitrogenous bases in DNA that may result in differences in offspring 3. crossing over 4. random fertilization 5. independent assortment -why is variation important? -differe ...
Page 203 “Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection”
... A variation is a slight difference in an inherited trait of individual members of a species. Variations arise naturally in populations. They occur in the offspring as a result of sexual reproduction. Variations are caused by random mutations, or changes in genes. Mutations can lead to chan ...
... A variation is a slight difference in an inherited trait of individual members of a species. Variations arise naturally in populations. They occur in the offspring as a result of sexual reproduction. Variations are caused by random mutations, or changes in genes. Mutations can lead to chan ...
Ch 15 Summary
... that changed Earth in the past were the same as the processes that are still changing Earth in the present. Knowing that Earth could change over time helped Darwin realize that life might change as well. Knowing that Earth was very old convinced Darwin that there had been enough time for life to evo ...
... that changed Earth in the past were the same as the processes that are still changing Earth in the present. Knowing that Earth could change over time helped Darwin realize that life might change as well. Knowing that Earth was very old convinced Darwin that there had been enough time for life to evo ...
evolution Darwin Carolus Linnaeus
... Wallace’s paper and extracts of Darwin’ Darwin’s essay were presented to the Linnaean Society of London. • Darwin quickly finished The Origin of Species and published it the next year. • While both Darwin and Wallace developed similar ideas independently, independently, the essence of evolution by n ...
... Wallace’s paper and extracts of Darwin’ Darwin’s essay were presented to the Linnaean Society of London. • Darwin quickly finished The Origin of Species and published it the next year. • While both Darwin and Wallace developed similar ideas independently, independently, the essence of evolution by n ...
Chapter 7 notes
... adaptations survive better than other members of the same species. 2. How is your answer for number one similar to Darwin's theory of Evolution by Means of Natural Selection? It is the same. Darwin says that these organisms survive and are more likely to produce offspring with the same adaptations. ...
... adaptations survive better than other members of the same species. 2. How is your answer for number one similar to Darwin's theory of Evolution by Means of Natural Selection? It is the same. Darwin says that these organisms survive and are more likely to produce offspring with the same adaptations. ...
Evolution - Harrison High School
... – All of these mechanisms can cause changes in the frequencies of genes in populations, and so all of them are mechanisms of evolutionary change. – However, natural selection and genetic drift cannot operate unless there is genetic variation—that is, unless some individuals are genetically different ...
... – All of these mechanisms can cause changes in the frequencies of genes in populations, and so all of them are mechanisms of evolutionary change. – However, natural selection and genetic drift cannot operate unless there is genetic variation—that is, unless some individuals are genetically different ...
Chapters 13/14 Power Point
... • Because new species form from existing species, Darwin predicted that transitional forms, intermediate stages between older and newer species, would be found in the fossil record • There are now many good examples of evolutionary transitions • For instance, modern whales are the descendants of fou ...
... • Because new species form from existing species, Darwin predicted that transitional forms, intermediate stages between older and newer species, would be found in the fossil record • There are now many good examples of evolutionary transitions • For instance, modern whales are the descendants of fou ...
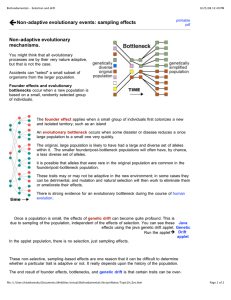
BioFundamentals - Selection and drift
... The original, large population is likely to have had a large and diverse set of alleles within it. The smaller founder/post-bottleneck populations will often have, by chance, a less diverse set of alleles. it is possible that alleles that were rare in the original population are common in the founde ...
... The original, large population is likely to have had a large and diverse set of alleles within it. The smaller founder/post-bottleneck populations will often have, by chance, a less diverse set of alleles. it is possible that alleles that were rare in the original population are common in the founde ...
Biology Core Vocabulary List
... Students recognize that the specific genetic instructions for any organism are contained within genes composed of DNA molecules located in chromosomes. They explain the mechanism for the direct production of specific proteins based on inherited DNA. Students diagram how occasional modifications in g ...
... Students recognize that the specific genetic instructions for any organism are contained within genes composed of DNA molecules located in chromosomes. They explain the mechanism for the direct production of specific proteins based on inherited DNA. Students diagram how occasional modifications in g ...
Biology Core Vocabulary List
... Students recognize that the specific genetic instructions for any organism are contained within genes composed of DNA molecules located in chromosomes. They explain the mechanism for the direct production of specific proteins based on inherited DNA. Students diagram how occasional modifications in g ...
... Students recognize that the specific genetic instructions for any organism are contained within genes composed of DNA molecules located in chromosomes. They explain the mechanism for the direct production of specific proteins based on inherited DNA. Students diagram how occasional modifications in g ...
Evolution

Evolution is change in the heritable traits of biological populations over successive generations. Evolutionary processes give rise to diversity at every level of biological organisation, including the levels of species, individual organisms, and molecules.All of life on earth shares a common ancestor known as the last universal ancestor, which lived approximately 3.5–3.8 billion years ago. Repeated formation of new species (speciation), change within species (anagenesis), and loss of species (extinction) throughout the evolutionary history of life on Earth are demonstrated by shared sets of morphological and biochemical traits, including shared DNA sequences. These shared traits are more similar among species that share a more recent common ancestor, and can be used to reconstruct a biological ""tree of life"" based on evolutionary relationships (phylogenetics), using both existing species and fossils. The fossil record includes a progression from early biogenic graphite, to microbial mat fossils, to fossilized multicellular organisms. Existing patterns of biodiversity have been shaped both by speciation and by extinction. More than 99 percent of all species that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates of Earth's current species range from 10 to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented.In the mid-19th century, Charles Darwin formulated the scientific theory of evolution by natural selection, published in his book On the Origin of Species (1859). Evolution by natural selection is a process demonstrated by the observation that more offspring are produced than can possibly survive, along with three facts about populations: 1) traits vary among individuals with respect to morphology, physiology, and behaviour (phenotypic variation), 2) different traits confer different rates of survival and reproduction (differential fitness), and 3) traits can be passed from generation to generation (heritability of fitness). Thus, in successive generations members of a population are replaced by progeny of parents better adapted to survive and reproduce in the biophysical environment in which natural selection takes place. This teleonomy is the quality whereby the process of natural selection creates and preserves traits that are seemingly fitted for the functional roles they perform. Natural selection is the only known cause of adaptation but not the only known cause of evolution. Other, nonadaptive causes of microevolution include mutation and genetic drift.In the early 20th century the modern evolutionary synthesis integrated classical genetics with Darwin's theory of evolution by natural selection through the discipline of population genetics. The importance of natural selection as a cause of evolution was accepted into other branches of biology. Moreover, previously held notions about evolution, such as orthogenesis, evolutionism, and other beliefs about innate ""progress"" within the largest-scale trends in evolution, became obsolete scientific theories. Scientists continue to study various aspects of evolutionary biology by forming and testing hypotheses, constructing mathematical models of theoretical biology and biological theories, using observational data, and performing experiments in both the field and the laboratory. Evolution is a cornerstone of modern science, accepted as one of the most reliably established of all facts and theories of science, based on evidence not just from the biological sciences but also from anthropology, psychology, astrophysics, chemistry, geology, physics, mathematics, and other scientific disciplines, as well as behavioral and social sciences. Understanding of evolution has made significant contributions to humanity, including the prevention and treatment of human disease, new agricultural products, industrial innovations, a subfield of computer science, and rapid advances in life sciences. Discoveries in evolutionary biology have made a significant impact not just in the traditional branches of biology but also in other academic disciplines (e.g., biological anthropology and evolutionary psychology) and in society at large.