Development of a Glass Resistive Plate Chamber for the Phase
... due to symmetry breaking that the current particle colliders are not able to detect them. ...
... due to symmetry breaking that the current particle colliders are not able to detect them. ...
ELECTRONIC IMAGING OF IONIZING RADIATION WITH LIMITED AVALANCHES IN GASES G
... of modern theories. They make up a long list: the ionization chamber, the cloud chamber, Geiger-Müller counters, proportional counters, scintillation counters, semiconductor detectors, nuclear emulsions, bubble chambers, spark and streamer chambers, multiwire and drift chambers, various calorimeters ...
... of modern theories. They make up a long list: the ionization chamber, the cloud chamber, Geiger-Müller counters, proportional counters, scintillation counters, semiconductor detectors, nuclear emulsions, bubble chambers, spark and streamer chambers, multiwire and drift chambers, various calorimeters ...
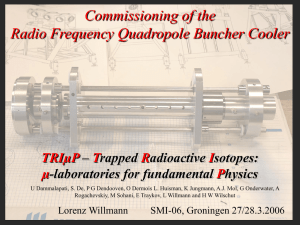
Commissioning of the Radiofrequency quadrupole cooler
... Simple Diagostic Tool: MCP with phosphor screen • Positional resolution, transverse emittance • Counting mode for low rate ...
... Simple Diagostic Tool: MCP with phosphor screen • Positional resolution, transverse emittance • Counting mode for low rate ...
P6.3.1.1 - LD Didactic
... today, yellow-green zinc-cadmium-sulfide is used almost exclusively. The fluorescent substance is applied to lead glass, which protects the observer from the harmful effects of x-rays. Fluorescence is a luminous phenomenon that occurs in certain materials when these are exposed to light, x-ray or pa ...
... today, yellow-green zinc-cadmium-sulfide is used almost exclusively. The fluorescent substance is applied to lead glass, which protects the observer from the harmful effects of x-rays. Fluorescence is a luminous phenomenon that occurs in certain materials when these are exposed to light, x-ray or pa ...
Features of the gas discharge in the narrow gap
... changes in values of both members in the expression (2), especially in the large background of alpha-particles. Coefficient can be substantially reduced through the use of helium as a buffer gas and also by means of increasing the electronegative addition such as SF6 up to two percent. What is con ...
... changes in values of both members in the expression (2), especially in the large background of alpha-particles. Coefficient can be substantially reduced through the use of helium as a buffer gas and also by means of increasing the electronegative addition such as SF6 up to two percent. What is con ...
chapter 7 health physics instrumentations
... accelerated ions. In this case, the electric charge is proportional to the voltage applied: ...
... accelerated ions. In this case, the electric charge is proportional to the voltage applied: ...
AN5
... shorter is the distance required for the electrons to gain sufficient kinetic energy to generate extra ions by collision with the surrounding gas molecules. The charge collected at the electrodes is larger than that in an ionisation chamber and it is roughly proportional to the number of ions produc ...
... shorter is the distance required for the electrons to gain sufficient kinetic energy to generate extra ions by collision with the surrounding gas molecules. The charge collected at the electrodes is larger than that in an ionisation chamber and it is roughly proportional to the number of ions produc ...
geiger1
... 5.2 Resolving time of the GM counter: Violation of Poisson addition Theorem (Optional) There is an interval of time following the production of a pulse in the GM tube during which no other pulse can be recorded. This interval is called the resolving time of the system. If this time is known it can ...
... 5.2 Resolving time of the GM counter: Violation of Poisson addition Theorem (Optional) There is an interval of time following the production of a pulse in the GM tube during which no other pulse can be recorded. This interval is called the resolving time of the system. If this time is known it can ...
Geiger Muller counter
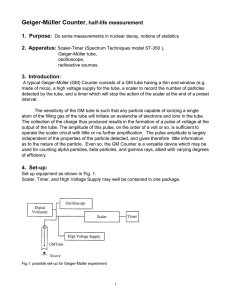
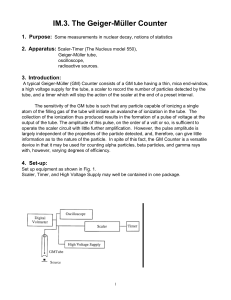
... A typical Geiger-Müller (GM) Counter consists of a GM tube having a thin end-window (e.g. made of mica), a high voltage supply for the tube, a scaler to record the number of particles detected by the tube, and a timer which will stop the action of the scaler at the end of a preset interval. The sens ...
... A typical Geiger-Müller (GM) Counter consists of a GM tube having a thin end-window (e.g. made of mica), a high voltage supply for the tube, a scaler to record the number of particles detected by the tube, and a timer which will stop the action of the scaler at the end of a preset interval. The sens ...
Geiger Muller counter - FSU
... 5.1 Characteristics of the GM counter: Put a radioactive source below the GM tube. Put the counter in a counting mode and raise the voltage until counts are observed. Note the shape of the pulse and what happens as the voltage on the GM tube is increased. Do not exceed 900 volts at this time. What i ...
... 5.1 Characteristics of the GM counter: Put a radioactive source below the GM tube. Put the counter in a counting mode and raise the voltage until counts are observed. Note the shape of the pulse and what happens as the voltage on the GM tube is increased. Do not exceed 900 volts at this time. What i ...
Poisson Statistics and Gamma Ray Absorption
... a positive potential and an outer cylinder held at ground potential. The potential difference should be preset to about 900 V. The GM tube is filled with a gas that is ionized when radiation passes through the tube. The electrons from these ions are so rapidly accelerated toward the positive wire th ...
... a positive potential and an outer cylinder held at ground potential. The potential difference should be preset to about 900 V. The GM tube is filled with a gas that is ionized when radiation passes through the tube. The electrons from these ions are so rapidly accelerated toward the positive wire th ...
Linear particle accelerator (LINAC)
... Within the chamber, electrically isolated cylindrical electrodes (“drift tubes” in Figure 2) are placed, whose length varies with the distance along the pipe. The length of each electrode is determined by the frequency and power of the driving power source and the nature of the particle to be accele ...
... Within the chamber, electrically isolated cylindrical electrodes (“drift tubes” in Figure 2) are placed, whose length varies with the distance along the pipe. The length of each electrode is determined by the frequency and power of the driving power source and the nature of the particle to be accele ...
0NesamostStvrtaci
... Consider: the energy of Cu-Ka is 8.04 keV, so, using Ar detector gas, n = 8040/26.4 = 304 primary electron-ion pairs. This number is too small to detect, but placing a potential across the gas from wire to tube wall produces amplification. The electrons produced by the incoming X-ray are accelerate ...
... Consider: the energy of Cu-Ka is 8.04 keV, so, using Ar detector gas, n = 8040/26.4 = 304 primary electron-ion pairs. This number is too small to detect, but placing a potential across the gas from wire to tube wall produces amplification. The electrons produced by the incoming X-ray are accelerate ...
Objective 1: Summarize the development of atomic theory
... sodium metal. a. What is the minimum frequency of light necessary to emit electrons from sodium via the photoelectric effect? ...
... sodium metal. a. What is the minimum frequency of light necessary to emit electrons from sodium via the photoelectric effect? ...
Topic 7: Atomic and nuclear physics 7.1 The atom
... • A Geiger–Müller tube consists of a tube filled with a low-pressure (~0.1 Atm) inert gas such as helium, neon or argon and an organic vapor or a halogen gas and contains electrodes, between which there is a potential difference of several hundred volts, but no current flowing. The walls of the tube ...
... • A Geiger–Müller tube consists of a tube filled with a low-pressure (~0.1 Atm) inert gas such as helium, neon or argon and an organic vapor or a halogen gas and contains electrodes, between which there is a potential difference of several hundred volts, but no current flowing. The walls of the tube ...
Wideroe accelerator Concept Analysis
... It can be seen that our system is like a parallel plate capacitor. Where dQ = C(v)*dV And C = (A/d) εr ε0 This presents another issue: The fact that our ‘d’ is increasing as we make our tube longer, this decreases the capacitance. ...
... It can be seen that our system is like a parallel plate capacitor. Where dQ = C(v)*dV And C = (A/d) εr ε0 This presents another issue: The fact that our ‘d’ is increasing as we make our tube longer, this decreases the capacitance. ...
PROPOTIONAL COUNTER
... The field strength close to anode increases rapidly as r decreases. So field strength near central wire become very high . At such a high electric field ,primary electrons are accelerated towards central wire and gain enough energy to ionize other atoms. The ions so produced cause further ionization ...
... The field strength close to anode increases rapidly as r decreases. So field strength near central wire become very high . At such a high electric field ,primary electrons are accelerated towards central wire and gain enough energy to ionize other atoms. The ions so produced cause further ionization ...
cathode-ray-tube-qrg
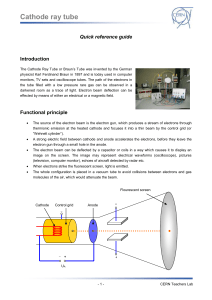
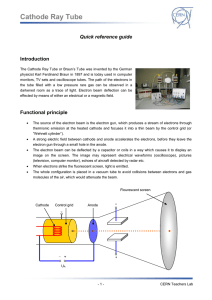
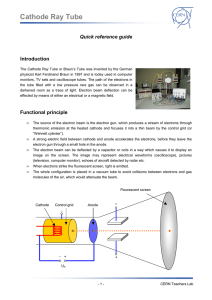
... monitors, TV sets and oscilloscope tubes. The path of the electrons in the tube filled with a low pressure rare gas can be observed in a darkened room as a trace of light. Electron beam deflection can be effected by means of either an electrical or a magnetic field. ...
... monitors, TV sets and oscilloscope tubes. The path of the electrons in the tube filled with a low pressure rare gas can be observed in a darkened room as a trace of light. Electron beam deflection can be effected by means of either an electrical or a magnetic field. ...
doc
... monitors, TV sets and oscilloscope tubes. The path of the electrons in the tube filled with a low pressure rare gas can be observed in a darkened room as a trace of light. Electron beam deflection can be effected by means of either an electrical or a magnetic field. ...
... monitors, TV sets and oscilloscope tubes. The path of the electrons in the tube filled with a low pressure rare gas can be observed in a darkened room as a trace of light. Electron beam deflection can be effected by means of either an electrical or a magnetic field. ...
Cathode Ray Tube
... monitors, TV sets and oscilloscope tubes. The path of the electrons in the tube filled with a low pressure rare gas can be observed in a darkened room as a trace of light. Electron beam deflection can be effected by means of either an electrical or a magnetic field. ...
... monitors, TV sets and oscilloscope tubes. The path of the electrons in the tube filled with a low pressure rare gas can be observed in a darkened room as a trace of light. Electron beam deflection can be effected by means of either an electrical or a magnetic field. ...
health physics note 3: radiation detection and measurement
... In region A, VDC is relatively low so that recombination of positive ions and electrons occurs. As a result, not all ion pairs are collected and the voltage pulse height is relatively low. It does increase as the dc voltage increases, however, as the amount of recombination reduces. In region B, VDC ...
... In region A, VDC is relatively low so that recombination of positive ions and electrons occurs. As a result, not all ion pairs are collected and the voltage pulse height is relatively low. It does increase as the dc voltage increases, however, as the amount of recombination reduces. In region B, VDC ...
physics 225, 2nd year lab - University of Toronto Physics
... sufficiently high energy that they exhibit particle-like behaviour. α, (He nucleii), β, (electrons), β+, (positrons) radiation are massive particles. Obviously, they behave differently, but they may often be detected by similar methods. Other emissions in this energy range, (e.g., neutrons) need sep ...
... sufficiently high energy that they exhibit particle-like behaviour. α, (He nucleii), β, (electrons), β+, (positrons) radiation are massive particles. Obviously, they behave differently, but they may often be detected by similar methods. Other emissions in this energy range, (e.g., neutrons) need sep ...
detectors
... REGION 5: FOR MORE HIGHER VOLTAGE IN WHICH PULSE HEIGHT IS LARGER INDEPENDENT OF INITIAL IONS CALLE GEIGER REGION. REGION6: AT END OF GEIGER REGION THERE IS A CONTINOUS DISCHARGE ,ITS RTEALLY NOT CONTINOUS BUT CONSIST OF MULTIPLE PULSES. ...
... REGION 5: FOR MORE HIGHER VOLTAGE IN WHICH PULSE HEIGHT IS LARGER INDEPENDENT OF INITIAL IONS CALLE GEIGER REGION. REGION6: AT END OF GEIGER REGION THERE IS A CONTINOUS DISCHARGE ,ITS RTEALLY NOT CONTINOUS BUT CONSIST OF MULTIPLE PULSES. ...
phys586-lec20-ion3
... reduce the effective electric field around the anode and eventually terminate the chain reaction ...
... reduce the effective electric field around the anode and eventually terminate the chain reaction ...
Geiger Counter
... As the voltage between the electrodes is increased, the tube goes through three phases: if the voltage is lower than a particular value, the gas in the tube will not be ionised and no current will flow. Above this particular voltage (the ‘striking’ voltage), the gas ionises and a small current flows ...
... As the voltage between the electrodes is increased, the tube goes through three phases: if the voltage is lower than a particular value, the gas in the tube will not be ionised and no current will flow. Above this particular voltage (the ‘striking’ voltage), the gas ionises and a small current flows ...
Geiger–Müller tube

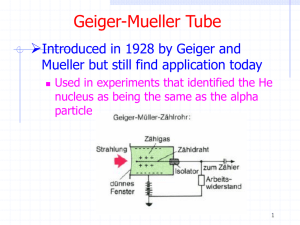
The Geiger–Müller tube or G-M tube is the sensing element of the Geiger counter instrument used for the detection of ionizing radiation. It was named after Hans Geiger, who invented the principle in 1908, and Walther Müller, who collaborated with Geiger in developing the technique further in 1928 to produce a practical tube that could detect a number of different radiation types.It is a gaseous ionization detector and uses the Townsend avalanche phenomenon to produce an easily detectable electronic pulse from as little as a single ionising event due to a radiation particle. It is used for the detection of gamma radiation, X-rays, and alpha and beta particles. It can also be adapted to detect neutrons. The tube operates in the ""Geiger"" region of ion pair generation. This is shown on the accompanying plot for gaseous detectors showing ion current against applied voltage.Whilst it is a robust and inexpensive detector, the G-M is unable to measure high radiation rates efficiently, has a finite life in high radiation areas and is unable to measure incident radiation energy, so no spectral information can be generated and there is no discrimination between radiation types.