1.1 - Newtonian Gravitation and Orbits - K
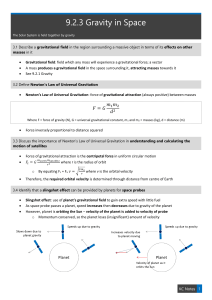
... The force of Gravity, FG is one of the fundamental forces of nature. It is incredibly important in understanding the universe. It is a vector, and it has magnitude and direction. ...
... The force of Gravity, FG is one of the fundamental forces of nature. It is incredibly important in understanding the universe. It is a vector, and it has magnitude and direction. ...
Gravity - barransclass
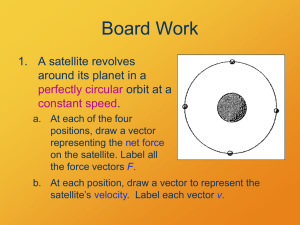
... positions, draw a vector representing the net force on the satellite. Label all the force vectors F. b. At each position, draw a vector to represent the satellite’s velocity. Label each vector v. ...
... positions, draw a vector representing the net force on the satellite. Label all the force vectors F. b. At each position, draw a vector to represent the satellite’s velocity. Label each vector v. ...
Escape Velocity and Newton`s Laws
... (then adding his own), Newton deduced three laws of motion which: – describe any moving object (from automobiles to galaxies colliding). – were the underpinnings for Newton’s understanding of gravity. • Published in “Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy” – 1687. ...
... (then adding his own), Newton deduced three laws of motion which: – describe any moving object (from automobiles to galaxies colliding). – were the underpinnings for Newton’s understanding of gravity. • Published in “Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy” – 1687. ...
File
... actually an acceleration of the entire reference frame, they are necessarily proportional to mass. Why? Examples: “Centrifugal force” in rotating systems ...
... actually an acceleration of the entire reference frame, they are necessarily proportional to mass. Why? Examples: “Centrifugal force” in rotating systems ...
Mass Wasting
... moves weathered particles down a slope to produce features like piles of rock debris. Mass wasting is a process defined as the downhill movement of weathered materials resulting from the pull of gravity. Mass Wasting: The energy exerted by gravity on a load is determined by the following factors: ...
... moves weathered particles down a slope to produce features like piles of rock debris. Mass wasting is a process defined as the downhill movement of weathered materials resulting from the pull of gravity. Mass Wasting: The energy exerted by gravity on a load is determined by the following factors: ...
Gravity Equation
... F = force of gravity G = gravitational constant (6*10-11) 0.00000000006 M1 = mass of body 1 M2 = mass of body 2 S2 = distance between M1 & M2 squared ...
... F = force of gravity G = gravitational constant (6*10-11) 0.00000000006 M1 = mass of body 1 M2 = mass of body 2 S2 = distance between M1 & M2 squared ...
The Force of Gravity
... from a building, which one will hit the ground first? • Air resistance- a type of fluid friction – Is an upward force – More surface area=more air resistance – Increases with velocity (as objects speed up, air resistance increases) ...
... from a building, which one will hit the ground first? • Air resistance- a type of fluid friction – Is an upward force – More surface area=more air resistance – Increases with velocity (as objects speed up, air resistance increases) ...
Forces and Energy Summary Sheet File
... kilograms (kg). Know that weight is the force of gravity acting on an object and is measured in Newtons (N). The formula linking mass and weight is: ...
... kilograms (kg). Know that weight is the force of gravity acting on an object and is measured in Newtons (N). The formula linking mass and weight is: ...
F=ma(5) - University of Michigan
... 5. (8 points) In introductory physics one learns the formula F = ma, connecting the force on an object, F , with the mass of the object and the acceleration that the object experiences under the force. One also learns the formula p = mv where p is the momentum of an object, m is the mass, and v is t ...
... 5. (8 points) In introductory physics one learns the formula F = ma, connecting the force on an object, F , with the mass of the object and the acceleration that the object experiences under the force. One also learns the formula p = mv where p is the momentum of an object, m is the mass, and v is t ...