Physics Today
... energy dependence of the fragmentation cross section σ in the zero-energy limit. In most cases the threshold law assumes the simple form σ ~ Eκ, E → +0, and the problem reduces to evaluating the exponent κ, which need not be a real number. In deriving his threshold law, Wannier made use of two impor ...
... energy dependence of the fragmentation cross section σ in the zero-energy limit. In most cases the threshold law assumes the simple form σ ~ Eκ, E → +0, and the problem reduces to evaluating the exponent κ, which need not be a real number. In deriving his threshold law, Wannier made use of two impor ...
1014 Sec. 4.4 Notes
... An exponential equation is an equation containing a variable in an exponent. B. Solving Exponential Equations by Expressing Each Side as a Power of the Same Base ...
... An exponential equation is an equation containing a variable in an exponent. B. Solving Exponential Equations by Expressing Each Side as a Power of the Same Base ...
On the Explanation for Quantum Statistics
... Ehrenfest and Trkal considered the equilibrium condition for molecules subject to disassociation into a total N of atoms, whose number is conserved, with recombination into di¤erent possible numbers N; N 0 ; N 00 ::: of molecules of various types. The upshot: a contribution k log(N !=N !N 0 !:::) to ...
... Ehrenfest and Trkal considered the equilibrium condition for molecules subject to disassociation into a total N of atoms, whose number is conserved, with recombination into di¤erent possible numbers N; N 0 ; N 00 ::: of molecules of various types. The upshot: a contribution k log(N !=N !N 0 !:::) to ...
13.1 - Newton`s Law of Motion
... Tangential and Normal Forces. • Determination of the resultant force components ΣFr, ΣFθ, ΣFz causing a particle to move with a known acceleration. • If acceleration is not specified at given instant, directions or magnitudes of the forces acting on the particle must be known or computed to solve. • ...
... Tangential and Normal Forces. • Determination of the resultant force components ΣFr, ΣFθ, ΣFz causing a particle to move with a known acceleration. • If acceleration is not specified at given instant, directions or magnitudes of the forces acting on the particle must be known or computed to solve. • ...
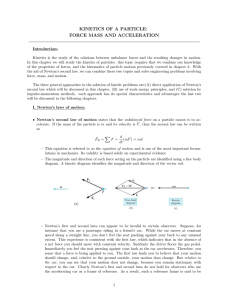
KINETICS OF A PARTICLE: FORCE MASS AND ACCELERATION
... In this chapter we will study the kinetics of particles. this topic requires that we combine our knowledge of the properties of forces, and the kinematics of particle motion previously covered in chapter 2. With the aid of Newton’s second law, we can combine these two topics and solve engineering pr ...
... In this chapter we will study the kinetics of particles. this topic requires that we combine our knowledge of the properties of forces, and the kinematics of particle motion previously covered in chapter 2. With the aid of Newton’s second law, we can combine these two topics and solve engineering pr ...
A brief introduction to Quantum computer Alri Moore`s law the
... ——- Gordon E. Moore, the co-founder of Intel ...
... ——- Gordon E. Moore, the co-founder of Intel ...
Quantum Information and Quantum Computation
... Over the last half century, the components of computers have gotten smaller by a factor of two every year and a half, the phenomenon known as Moore's law. In current computers, the smallest wires and transistors are coming close to a size of one hundred nanometers across, a thousand times the diamet ...
... Over the last half century, the components of computers have gotten smaller by a factor of two every year and a half, the phenomenon known as Moore's law. In current computers, the smallest wires and transistors are coming close to a size of one hundred nanometers across, a thousand times the diamet ...
Solutions HW # 3 Physics 122 Problem 1 The total potential at P due
... The potential difference between (0,0,0) and (x1,y1,z1) can be found by integrating the electric field over the path connecting (0,0,0) and (x1,y1,z1). The path integral of the electric field is path independent, and we thus can choose the most convenient path for us to bring us from (0,0,0) to (x1, ...
... The potential difference between (0,0,0) and (x1,y1,z1) can be found by integrating the electric field over the path connecting (0,0,0) and (x1,y1,z1). The path integral of the electric field is path independent, and we thus can choose the most convenient path for us to bring us from (0,0,0) to (x1, ...
E2-2004-4 M. I. Shirokov* DECAY LAW OF MOVING UNSTABLE
... with time not only because of the decay but also because of the packet diffusion. Besides, the corresponding amplitude of moving particles changes due to the initial packet displacement at the vector vt, v being the packet average velocity (under the displacement our Ψp does not change up to an unes ...
... with time not only because of the decay but also because of the packet diffusion. Besides, the corresponding amplitude of moving particles changes due to the initial packet displacement at the vector vt, v being the packet average velocity (under the displacement our Ψp does not change up to an unes ...
Chap17_Sec3
... Choose any point (x1, y) in the disk with x1 < x. Then, let C consist of any path C1 from (a, b) to (x1, y) followed by ...
... Choose any point (x1, y) in the disk with x1 < x. Then, let C consist of any path C1 from (a, b) to (x1, y) followed by ...
An Introduction to Quantum Control
... The Postulates of Quantum Mechanics. The basic quantum mechanical model is specified in terms of the following: Observables. Physical quantities like position, momentum, spin, etc., are represented by self-adjoint operators on the Hilbert space H and are called observables. These are the noncommuta ...
... The Postulates of Quantum Mechanics. The basic quantum mechanical model is specified in terms of the following: Observables. Physical quantities like position, momentum, spin, etc., are represented by self-adjoint operators on the Hilbert space H and are called observables. These are the noncommuta ...
Basic mathematical concepts from probability and information theory.
... Suppose we have a process (referred to as a random variable) where there are a finite number of possible outcomes {xi : i = 1, . . . , N } to each trial of the system. If the system is observed for a large number of trials then the frequency of occurrence of each outcome will be approximately fixed ...
... Suppose we have a process (referred to as a random variable) where there are a finite number of possible outcomes {xi : i = 1, . . . , N } to each trial of the system. If the system is observed for a large number of trials then the frequency of occurrence of each outcome will be approximately fixed ...
Entropy and temperature of a quantum Carnot engine
... In the analysis above we have considered only the square-well potential model, which can be interpreted as the quantum analogue of the classical ideal gas. A natural extension of this work would be to consider other Hamiltonians. For example, for a harmonic potential whose energy eigenvalues are En ...
... In the analysis above we have considered only the square-well potential model, which can be interpreted as the quantum analogue of the classical ideal gas. A natural extension of this work would be to consider other Hamiltonians. For example, for a harmonic potential whose energy eigenvalues are En ...
Noisy Storage talk
... in every layer of recursion, there is a constant probability of success. invariant: except for the last teleportation step, Bob can completely trace back and correct previous errors. using an exponential amount of EPR pairs, players succeed with probability arbitrarily close to 1 scheme generalizes ...
... in every layer of recursion, there is a constant probability of success. invariant: except for the last teleportation step, Bob can completely trace back and correct previous errors. using an exponential amount of EPR pairs, players succeed with probability arbitrarily close to 1 scheme generalizes ...
Effects of Decoherence in Quantum Control and Computing
... The architecture of quantum walks quantum computer could be simpler than that of standard quantum computer We have developed and applied a new approach to evaluation of the effect of decoherence on quantum walks. The density matrix is approximated by explicit formula ...
... The architecture of quantum walks quantum computer could be simpler than that of standard quantum computer We have developed and applied a new approach to evaluation of the effect of decoherence on quantum walks. The density matrix is approximated by explicit formula ...