* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Blank Final Exam from 2004 - Department of Chemistry | Oregon
Survey
Document related concepts
Kinetic resolution wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Hofmann–Löffler reaction wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Baylis–Hillman reaction wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Enantioselective synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
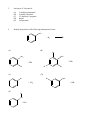
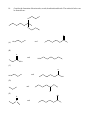
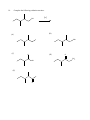
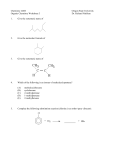
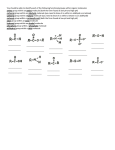
Chemistry 130 Final Exam Spring 2004 June 9, 2004 Oregon State University Dr. Richard Nafshun Mr. Peter Ruiz-Haas Fill in the front page of the Scantron answer sheet with your last name, first name, middle initial, and student identification number. Leave the class section number and the test form number blank. This exam consists of 22 multiple-choice questions. Each multiple-choice question has five points associated with it. Select the best multiple-choice answer by filling in the corresponding circle on the rear page of the answer sheet. 1. What is the name of the following structure? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) 2. 2, 2 diethylpentane 2-ethyl-4-methylhexane 3,5-dimethylheptane 3,5-dimethylnonane 3,5-dimethylcycloheptane The molecular formula of (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) is C4H10. is C6H14. is C6H12. is C6H10. is C6H8. 3. An isomer of 3-hexanol is: (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) 4. 3-methylcyclopentanol. 2-methyl-3-hexanol. 2,3-dimethyl-2-propanol. phenol. cyclohexanol. Identify the products of the following substitution reaction: NO 2 + Br2 (A) (B) Br NO 2 NO 2 + HBr + HBr Br Br (C) Br (D) Br Br + NO2- (E) Br NH + H2O NO 2 + HBr Questions 5 and 6 refer to the following reaction: Fe3+ + HS- → Fe2+ + S 0 + H+ The oxidation number for S in HS- is: 5. (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) 6. Which of the following statements is TRUE: (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) 7. +2 0 -1 +1 -2 Iron is being reduced and Sulfur is being oxidized Hydrogen is being reduced and Iron is being oxidized Sulfur is being reduced and iron is being oxidized Sulfur is the oxidizing agent and iron is the reducing agent Hydrogen is being oxidized and sulfur is being reduced Complete the following heated elimination reaction: 8. Drugs A and B below (Sertraline, the active ingredient in Zoloft) were synthesized in a lab. The amine group in compound A was neutralized with HCl to produce structure B, an ammonium salt. Cl NH Cl and Cl N + - +Cl Cl A B Which of the following are most likely to be actually employed as medicines and for which correct reason? (A) Structure A because it has a higher boiling point (B) Structure A because structure B has been treated with hydrochloric acid which is toxic (C) Structure B because it is more soluble (D) Structure B because the amine group has been denatured (E) Both structure A and B have the same properties so it doesn’t matter. 9. When a carboxylic acid and an alcohol react in a condensation reaction: (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) an ether is produced. a hemiacetal is produced. an acetal is produced. an amide is produced. an ester is produced. 10. Consider the formation of hemiacetals, acetals, hemiketals and ketals. The molecule below can be formed from: O O O and (A) HO (B) O and HO CH 3 (C) O and HO OH (D) O and O (E) OH O and C H 11. Complete the following addition reaction: + HBr (A) (B) Br Br (D) (C) 12. Br Br Br Identify the functional groups in the following molecule: O NH2 O O OH (A) aldehyde, alcohol, ester, amine (B) aldehyde, alcohol, ether, amine (C) carboxylic acid, amine, ether, alcohol (D) ketone, alcohol, ester, amine (E) ester, carboxylic acid, alcohol, amine 13. Chymotrypsinogen is a globular protein and is a precursor of the digestive enzyme trypsin. In this context, “globular” refers to what? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) primary structure quaternary structure size tertiary structure viscosity 14. Complete the following oxidation reaction: OH [o] (B) (A) CH 3 O (C) (D) O O CH 3 OH (E) O O 15. The pH of a soda is found to be 3.2. Therefore, the soda is: (A) (B) (C) 16. basic neutral acidic Identify the number of chiral carbons in the molecule below. O H C OH CH H 3C CH C H2 OH CH Cl (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) 17. A scientist accidentally left a vial with some enzymes in the sun and realized that the enzymes did not work as anticipated after being exposed to the heat. The enzymes were: (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) 18. 1 2 3 4 5 burned denatured catalyzed evaporated liquefied Which of the following statements is false? (A) Alanine (Ala) and Glycine (Gly) are amino acids both of which have 1 chiral carbon (B) a chiral molecule is not superimposable on its mirror image (C) the following molecule is chiral: O OH HO (D) a chiral carbon has 3 different groups bound to it (E) m-chlorotoluene is not chiral 19. The following is the structure of galactose. Which of the following statements is false: (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) 20. The structure shows D- galactose Galactose is an aldohexose Galactose has 5 chiral carbons It can form hemiacetals with alcohols It is an aldehyde Consider the fat molecule below. Which of the following is false? O H O H O C O H C O H C H (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) O It is an omega-3 fat it is saturated it contains cis bonds it contains trans bonds could undergo hydrogenation 21. In DNA, the base pairs are G and C; A and T. It can be said that this selective pairing is due to: (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) 22. the aldohexose. omega-3 fats. enzyme liquidizing. carbon monoxide. hydrogen bonding. The structure of DNA is: (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) cyclic. a beta sheet. an alpha helix. a double helix. tetrahedral.