* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download EC210Course_File_Summary
Survey
Document related concepts
Eigenstate thermalization hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Marcus theory wikipedia , lookup
Degenerate matter wikipedia , lookup
Spinodal decomposition wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Molecular Hamiltonian wikipedia , lookup
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
Electron configuration wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
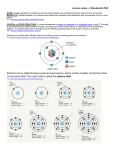
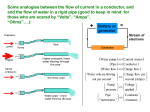
EC 210- Solid State Electronics Required Syllabus COURSE DESCRIPTION: Elementary materials science concepts: Atomic structure, Bonding and types of solids, The crystalline state. Lattice vibrations. The hall effect and hall devices. Quantum mechanics: photons, particles and waves, the electron as a wave, infinite potential well, Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle, Tunneling phenomenon (potential barrier). The band theory of solids: .E-K diagram, energy bands diagram, Electrons and holes, effective mass Semiconductors: Intrinsic semiconductors, Extrinsic semiconductors (n-type doping, p-type doping, compensation doping), Electron and holes Concentrations, Fermi energy level position, Conductivity of a semiconductor, Diffusion and conduction currents equations. Definitions for dielectric and magnetic materials and superconductivity. PREREQUISITE: BA114, BA118 TEXT BOOK: S. O. Kasap, Principles of Electronic Materials and Devices, 2nd Edition, McGraw-Hill COURSE OBJECTIVE: The knowledge of the fundamental principles is described in this course; the student will be able to follow the theoretical details of the advanced-level courses. COURSE OUTLINE: Week Number 1: General introduction for the course contents and the grading system. Week Number 2: Atomic structure, Molecules and general bonding principles. Week Number 3: Types of crystals models. Week Number 4: Covalent Bond, Metallic Bond, Ionic Bond Week Number 5: Miller indices: crystal directions and planes. Week Number 6: The dispersion relationship of a mono atomic lattice vibrations, phase and group velocities. Week Number 7: Particles and waves Week Number 8: De Broglie relationship, time Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle. Week Number 9: Application on Schrödinger equation (Infinite potential well: A confined electron) independent Schrödinger equation, Week Number 10: Application on Schrödinger equation (Tunneling phenomenon: Quantum leak) Week Number 11: Energy Band theory of solids: (energy bands, effective mass, concept of a hole) Week Number 12: (Semiconductors) Intrinsic semiconductors (Si crystal and energy band diagram, electrons and holes, conduction in semiconductors, electrons and holes concentrations). Week Number 13: (Semiconductors ) Extrinsic semiconductor: (n-type doping, p-type doping, compensation doping) and carriers concentrations. Fermi energy level position. Week Number 14: Semiconductor conductivity and resistivity. Week Number 15: Semiconductors (Diffusion and conduction current equations). Week Number 16: Final Exam. CLASS SCHEDULE: Lecture: 2 Tutorial: 2 OR Practical: 1 CONTRIBUTION OF COURSE TO MEET THE REQUIREMSNTS OF CRITERION 5: Math and Basic Sciences Professional Component Content Engineering General Topics Education Engineering Design RELATIONSHIP OF COURSE TO PROGRAM OUTCOMES: Course Title Outcomes Assessed Assessment Method(s)(per outcome) a. An ability to apply PC1: Local Developed Exams knowledge of PC2:Software Report mathematics, science, PC3: and engineering. EC 210 c. An ability to design a PC1:Ability to design among local developed exams system, component, or PC2: process to meet desired PC3: needs. f. An understanding of professional and ethical responsibility. i. A recognition of the need for, and an ability to engage in life-long learning. PC1: Behavioral Observation"sec" PC2: PC3: PC1:Work shop PC2:Focus Group"lab" PC3: Grades PREPARED BY:Dr.Iman Morsi