* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Physics: Principles and Applications, 6e Giancoli
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Tensor operator wikipedia , lookup
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Bra–ket notation wikipedia , lookup
Derivations of the Lorentz transformations wikipedia , lookup
Faster-than-light wikipedia , lookup
Laplace–Runge–Lenz vector wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic angular momentum wikipedia , lookup
Velocity-addition formula wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
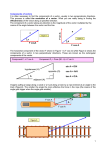
Name: Date: Mr. Rodriguez Physics is Life Chapter 3: Problem Set #5 1) Which one of the following is an example of a vector quantity? A) distance B) velocity C) mass D) area 2) The resultant of two vectors is the smallest when the angle between them is A) 0°. B) 45°. C) 90°. D) 180°. 3) Two displacement vectors have magnitudes of 5.0 m and 7.0 m, respectively. When these two vectors are added, the magnitude of the sum A) is 2.0 m. B) could be as small as 2.0 m, or as large as 12 m. C) is 12 m. D) is larger than 12 m. 4) Two vectors, of magnitudes 20 and 50, are added. Which one of the following is a possible answer for the magnitude of the resultant? A) 10 B) 20 C) 40 D) 80 5) Three forces, each having a magnitude of 30 N, pull on an object in directions that are 120° apart from each other. Make a statement concerning the resultant force. A) The resultant force is zero. B) The resultant force is greater than 30 N. C) The resultant force is equal to 30 N. D) The resultant force is less than 30 N. 6) Ignoring air resistance, the horizontal component of a projectile's velocity A) is zero. B) remains constant. C) continuously increases. D) continuously decreases. 7) A ball is thrown with a velocity of 20 m/s at an angle of 60° above the horizontal. What is the horizontal component of its instantaneous velocity at the exact top of its trajectory? A) 10 m/s B) 17 m/s C) 20 m/s D) zero 8) Ignoring air resistance, the horizontal component of a projectile's acceleration A) is zero. B) remains a non-zero constant. C) continuously increases. 1 D) continuously decreases. 9) A soccer ball is kicked with a velocity of 25 m/s at an angle of 45° above the horizontal. What is the vertical component of its acceleration as it travels along its trajectory? A) 9.80 m/s2 downward B) (9.80 m/s2) × sin (45°) downward C) (9.80 m/s2) × sin (45°) upward D) (9.80 m/s2) upward 10) If the acceleration vector of an object is directed anti-parallel to the velocity vector, A) the object is turning. B) the object is speeding up. C) the object is slowing down. D) the object is moving in the negative x-direction. 11) At what angle should a water-gun be aimed in order for the water to land with the greatest horizontal range? A) 0° B) 30° C) 45° D) 60° 12) When a football in a field goal attempt reaches its maximum height, how does its speed compare to its initial speed? A) It is zero. B) It is less than its initial speed. C) It is equal to its initial speed. D) It is greater than its initial speed. 13) A stone is thrown horizontally from the top of a tower at the same instant a ball is dropped vertically. Which object is traveling faster when it hits the level ground below? A) It is impossible to tell from the information given. B) the stone C) the ball D) Neither, since both are traveling at the same speed. 14) A bullet is fired horizontally, and at the same instant a second bullet is dropped from the same height. Ignore air resistance. Compare the times of fall of the two bullets. A) The fired bullet hits first. B) The dropped bullet hits first. C) They hit at the same time. D) cannot tell without knowing the masses 15) You are traveling at 55 mi/h in the +x axis relative to a straight, level road and pass a car traveling at 45 mi/h. The relative velocity of your car to the other car is A) -10 mi/h. B) 10 mi/h. C) 65 mi/h. D) 35 mi/h. Quantitative Problems 1) Vector A has magnitude 8.0 m at an angle of 30 degrees below the +x axis. The y component of A is A) 6.9 m. 2 B) -6.9 m. C) 4.0 m. D) -4.0 m. 2) If a ball is thrown with a velocity of 25 m/s at an angle of 37° above the horizontal, what is the vertical component of the velocity? A) 12 m/s B) 15 m/s C) 19 m/s D) 25 m/s 4) A butterfly moves with a speed of 12.0 m/s. The x component of its velocity is 8.00 m/s. The angle between the direction of its motion and the x axis must be A) 30.0°. B) 41.8°. C) 48.2°. D) 53.0°. 5) A car travels 20 km west, then 20 km south. What is the magnitude of its displacement? A) 0 km B) 20 km C) 28 km D) 40 km 6) Three vectors, expressed in Cartesian coordinates, are x comp -3.5 y comp +4.5 _T 0 -6.5 _U +5.5 -2.5 _S What is the magnitude of the resultant vector S + T + U? A) 4.9 B) 24 C) 16 D) 18 7) A runner runs halfway around a circular path of radius 10 m. What is the displacement of the jogger? A) 0 B) 5 m C) 10 m D) 20 m 3 FIGURE 3-1 8) Two forces are acting on an object as shown in Fig. 3-1. What is the magnitude of the resultant force? A) 47.5 N B) 185 N C) 198 N D) 200 N 9) Two forces are acting on an object as shown in Fig. 3-1. What is the direction of the resultant force? A) 12° above -x B) 78° above -x C) 12° above +x D) 78° above +x 10) Vector A is 5.5 cm long and points along the x axis. Vector B is 7.5 cm long and points at +30° to the negative x axis. (a) Determine the x and y components of Vector A. (b) Determine the x and y components of Vector B. (c) Determine the sum of these two vectors in terms of components. (d) Determine the sum of these two vectors in terms of magnitude and direction. 11) Vector A is 75.0 cm long and points at 30° above the positive x axis. Vector B is 25.0 cm long and points along the negative x axis. Vector C is 40.0 cm long and points at 45° below the negative x axis. (a) Determine the x and y components of Vector A. (b) Determine the x and y components of Vector B. (c) Determine the x and y components of Vector C. (d) Determine the sum of these three vectors in terms of components. (e) Determine the sum of these three vectors in terms of magnitude and direction. PROJECTILE MOTION/RELATIVE VELOCITY PROBLEMS 1) A stone is thrown horizontally with an initial speed of 10 m/s from the edge of a cliff. A stop watch measures the stone's trajectory time from the top of the cliff to the bottom to be 4.3 s. What is the height of the cliff? A) 22 m B) 43 m C) 77 m D) 91 m 2) A girl throws a rock horizontally, with a velocity of 10 m/s, from a bridge. It falls 20 m to the water below. How far does the rock travel horizontally before striking the water? 4 A) 14 m B) 16 m C) 20 m D) 24 m 3) A ball thrown horizontally from a point 24 m above the ground, strikes the ground after traveling horizontally a distance of 18 m. With what speed was it thrown? A) 6.1 m/s B) 7.4 m/s C) 8.1 m/s D) 8.9 m/s 3) A jumper in the long-jump goes into the jump with a speed of 12 m/s at an angle of 20° above the horizontal. How long is the jumper in the air before returning to the Earth? A) 0.21 s B) 0.42 s C) 0.84 s D) 1.3 s 4) A jumper in the long-jump goes into the jump with a speed of 12 m/s at an angle of 20° above the horizontal. How far does the jumper jump? A) 3.4 m B) 6.2 m C) 9.4 m D) 15 m 5) A projectile is launched with an initial velocity of 60.0 m/s at an angle of 30.0° above the horizontal. How far does it travel? A) 152 m B) 160 m C) 184 m D) 318 m 6) A projectile is launched with an initial velocity of 60.0 m/s at an angle of 30.0° above the horizontal. What is the maximum height reached by the projectile? A) 23 m B) 46 m C) 69 m D) 92 m 7) A projectile is shot horizontally at 23.4 m/s from the roof of a building 55.0 m tall. (a) Determine the time necessary for the projectile to reach the ground below. (b) Determine the distance from the base of the building that the projectile lands. (c) Determine the horizontal and vertical components of the velocity just before the projectile reaches the ground. 8) A projectile is fired from ground level with an initial speed of 55.6 m/s at an angle of 41.2° above the horizontal. (a) Determine the time necessary for the projectile to reach its maximum height. (b) Determine the maximum height reached by the projectile. (c) Determine the horizontal and vertical components of the velocity vector at the maximum height. (d) Determine the horizontal and vertical components of the acceleration vector at the maximum height. 5