* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 6 - Portal UniMAP
Survey
Document related concepts
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Electrostatic generator wikipedia , lookup
History of electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Electroactive polymers wikipedia , lookup
Scanning SQUID microscope wikipedia , lookup
Faraday paradox wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Electromotive force wikipedia , lookup
General Electric wikipedia , lookup
Electric current wikipedia , lookup
Static electricity wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
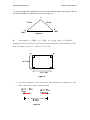
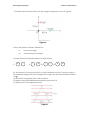
DKT113 Engineering Physics Semester 1 Session 2010/11 TUTORIAL 6 1. (a) What is electric charge? (b) State the principle of law of charges or charge-force law. From Figure below, explain what happened to the two charges given and also the relationship based on law of charges or charge- force law. Figure 1 (c) Name THREE (3) types of electrostatic charging. (d) State Coulomb’s Law with its equation. 2. Figure 2 shows the three charges of q1=+10µC, q2=+5µC and q3=-8µC are fixed along a straight line. Calculate the resultant force on the a) Charge at +5µC b) Charge at +10µC q1=+10µC q2=+5µC 2 cm q3=8µC 2 cm Figure 2 DKT113 Engineering Physics Semester 1 Session 2010/11 3. Find the magnitude and direction of the electric field strength at the point P due to the point charges at A and B as shown in the Figure 3. P 10 cm 10 cm B -8nC A +2nC Figure 3 +2µC 4. The charges q1 20C , q2 15C , q3 15C and q4 10C are arranged as shown in Figure 4. Calculate the resultant electric force and direction which acts on charge q4. [Given o = 8.85 x 10-12C2 / N.m2] q1 q2 q4 q3 a= 4 cm b = 5 cm Figure 4 5. Two point charges of -1.0nC and +2.0nC are separated by a distance of 0.3m, what is the electric force on each particle? q1 = - F12 1nC q2 = F21 +2nC 0.3m Figure 5 DKT113 Engineering Physics Semester 1 Session 2010/11 6. Find the electric field at point O for the charge configuration shown in Figure 6 Figure 6 9. Draw the pattern of electric field line for: (i) Like point charges (ii) Unequal like point charges 10. Draw the electric field line pattern for object below: i) + - ii) - + iii) - - iv) + + 11. An electron is moved from point A to point B and then to point C along two legs of an equilateral triangle with sides of length 0.25 m Figure 8. If the horizontal electric field is 15 V m, (a) what is the magnitude of the work required? (b) What is the potential difference between points A and C? (c) Which point is at a higher potential? Figure 7