* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Earth Crust in Motion Vocbaulary (Aca).doc
Survey
Document related concepts
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Mantle plume wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
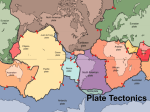
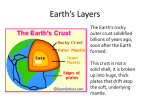
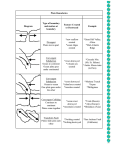
Name Period Earth’s Crust in Motion Vocabulary Geology – the study of the solid Earth Convection – the transfer of thermal energy by movements of fluid Convection Currents – the movement of fluid, caused by differences in temperature, that transfers thermal energy from one part of the fluid to another Conduction – the transfer of thermal energy through direct contact between particles of matter Radiation – the transfer of energy of electromagnetic waves Plasticity – the semi-solid, semi-liquid property of the mantle that allows for movement of the plates Crust – the layer of rock that forms Earth’s outer surface Mantle – the layer of hot, solid materials between Earth’s crust and core Outer core – a layer of molten iron and nickel that surrounds the inner core of the Earth Inner core – a dense ball of solid metal at the center of the Earth Lithosphere – a rigid layer made up of the uppermost part of the mantle and the crust Asthenosphere – the soft layer of the mantle on which the lithosphere floats Seafloor Spreading – the process by which molten material adds new oceanic crust to the ocean floor Subduction – the process by which oceanic crust sinks beneath a deep-ocean trench and back into the mantle at a convergent plate boundary Deep Ocean Trench – a deep valley along the ocean floor through which oceanic crust slowly sinks towards the mantle; a convergent plate boundary Mid-Ocean Ridge – the undersea mountain chain where new ocean floor is produced; a divergent plate boundary Fossil – a trace of an organism that has been preserved in rock Divergent Boundary – a plate boundary where two plates move away from each other Convergent Boundary – a plate boundary where two plates move toward each other Transform Boundary – a plate boundary where two plates move past each other in opposite directions Continental Drift – the hypothesis that all continents were once joined together in a single landmass and have since drifted to their current locations Fault – breaks in Earth’s crust where rocks have slipped past each other Shearing – the lateral movement of one rock surface against another; caused by intense pressure along plate boundaries Folded Mountains – mountains formed when two plates hit each other straight on, causing them to rise out of the earth; formed at a convergent boundary Science 8 – Earth’s Crust in Motion Pangaea – large ancient landmass that was composed of all the continents joined together Plate Boundary – the line where the edges of the plates meet Plate Tectonics – the theory that Earth's crust and upper mantle are broken into plates that float and move around on a plastic like layer of the mantle Plates – the large sections of the Earth's crust and upper mantle Rift Valley – deep valley that forms when two plates diverge or move apart Hot Spot – an area where magma from deep within the mantle melts through the crust above it Volcano – a weak spot in the crust where magma has come to the surface Science 8 – Earth’s Crust in Motion