* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cornell Notes Template
Survey
Document related concepts
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Verbascum thapsus wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
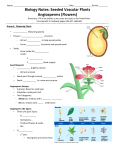
Plant Notes Topic: Seeds, Roots, Flowers, Dispersal Chapter #, Section #: p. 31-50 COMPLETE STAMP Name: Date: Period: Questions / Main Ideas / Vocabulary p. 31 Seeds &Roots Dormant Alive but not active. Seed coat Tough layer that protects embryo Embryo “baby” plant; beginnings of root, stem, and leaves Cotyledon Supply food energy until they photosynthesize Germination Process where dormant seed grows into a plant Root comes out first for water Root Root hairs Xylem Collect water/minerals & anchor/support plant Increase root’s surface area to absorb more water Carries water through roots and stem Fibrous root Monocot root Taproot Dicot root Stems & Leaves p. 35 Stems Holds leaves and flowers in position & carries water to them Leaves Photosynthesis Photosynthesis Inputs water + light + CO2 Outputs oxygen + glucose Chlorophyll Retaining Water Notes / Structure/Function/ Definitions / Examples / Sentences Water Conservation 1. guard cells close stomates 2. stomates in pits to keep out of Wind. 3. leaves have waxy or oily coating 4. thick to concentrate Water. Thin leaves lose water fast! p. 40 Flowers to Seeds Sexual reproduction Petals Sepals Stamens Filament Anther Two parents Showy to attract pollinators Leafy protectors of flower bud; supports petals Male part of flower Holds anther in place to expose to wind or animals Makes/holds pollen Pollen Sperm Small grains that contain sperm Male sex cell Pistil Stigma Ovary Ovules Eggs Fertilized Pollination Pollinators Female part of flower Sticky to collect pollen from wind or animal Protects seeds/ becomes fruit Make/contain eggs Female sex cell Sperm and egg unite Pollen reaches stigma Help pollination; like bees, butterflies, moths, bats, hummingbirds After Pollination Wind Flower does not need to be pretty anymore because it’s already Attracted a pollinator. Focuses on seeds and dispersal. p. 46 Seeds on the Move Wind Dandelions, maple seeds (helicopter), tumbleweed Water Coconuts Animals Seeds stick to fur/feathers or go through digestive system Ejection Flower part explodes…BOOM! A dormant seed germinates. Root comes out and develops first. Stem and leaves emerge to Photosynthesize in the sun, cotyledon falls away. Matures and develops flowers. Gives off Pollen and receives pollen (pollination). Egg is fertilized, seed and fruit develop. Seed is Dispersed and remains dormant until the conditions are right.