* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Math 11 - BigEngine
Survey
Document related concepts
Unification (computer science) wikipedia , lookup
Two-body problem in general relativity wikipedia , lookup
BKL singularity wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Equation of state wikipedia , lookup
Derivation of the Navier–Stokes equations wikipedia , lookup
Itô diffusion wikipedia , lookup
Euler equations (fluid dynamics) wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Navier–Stokes equations wikipedia , lookup
Calculus of variations wikipedia , lookup
Schwarzschild geodesics wikipedia , lookup
Differential equation wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
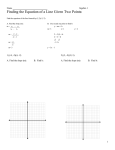
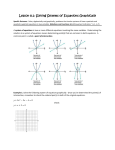
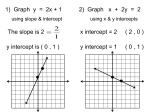
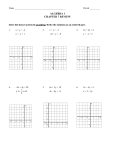
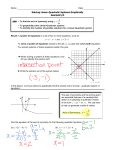
Name: ____________________ Date: ___________ Math 11 Principles Section 5.1: Solving Systems of Linear Equations by GRAPHING When you are asked to solve a system of equations, you are being asked to determine all the ordered pairs (x, y) that satisfy EACH equation in the system. For example: Is (5, -2) a solution to either of the following systems? a) b) x – y = 7 2x + y = 5 x+y=3 x – 2y = 9 In general, the solution to a system of equations (i.e. the ordered pairs) may be determined by graphing each equation on the same grid. Consider the following examples: Example 1: A tornado is following a path plotted by the weather office as given by the equation x – 2y = -8. At the same time, the centre of a thunderstorm is on the path given by y = 7 – x. At which point might the tornado and thunderstorm meet? Graph both linear equations and find the _________________ y=7–x slope = x – 2y = -8 slope = y int = y int = Solution ____________________ Example 2: Solve the following linear system graphically. 4x y 8 x 2 y 7 Solution ____________________ Example 3 : Solve the linear system graphically, then check the result. (1) 3x y 11 (2) x 2 y 6 Example 4 : Solve this non-linear system graphically. (1) y x 2 (2) y x 2 Textbook – page 306 #2, 6ab, 8 and page 315 #1