* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Name MEASURING AND USING ELECTRICITY from the series
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Power over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Standby power wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Power factor wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Amtrak's 25 Hz traction power system wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
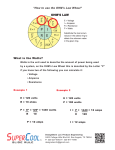
Name ____________________ MEASURING AND USING ELECTRICITY from the series Electricity and Magnetism Electric power is the amount of electric energy that flows through a circuit in a given amount of time. Electric power is measured in units called watts. The amount of wattage used by an electrical device is determined by multiplying the voltage of the circuit times the current. The current is measured in amperes. Here is a formula for calculating electric power. Power = voltage x current (amps) EXAMPLE: A hair dryer needs 10 amperes of current in a 120-volt circuit. How much power does it use? SOLUTION: Power = voltage x current 120 volts x 10 amps = 1,200 watts The hair dryer uses 1,200 watts of power every hour. A kilowatt is used to measure large amounts of electrical power. A kilowatt is equal to 1,000 watts, so the hair dryer uses 1,200 watts or 1.2 kilowatts of power. Directions: Try these problems using the information and formula from the top part of this sheet. (Give your answers in watts or kilowatts.) 1. A washing machine uses six amperes of current in a 120-volt circuit. How much power does it use? 2. A color television needs to be plugged into a 120-volt circuit. It uses 2.5 amperes. What is the television’s wattage? 3. The wattage of a vacuum cleaner is calculated to be 1,080 watts. If it is in a 120-volt circuit, how many amperes of current does the vacuum cleaner draw? 4. A clothes dryer has a wattage of 2.4 kilowatts. If it is in a 120-volt circuit, what is the amperes it needs to run? © 2004 Colgren Communications Published and Distributed by United Learning All rights to print materials cleared for classroom duplication and distribution.