* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 3rd Six Weeks Review
Survey
Document related concepts
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Faster-than-light wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Mass versus weight wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Length contraction wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
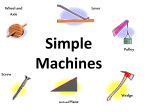
Force, Motion, and Speed Unit Guide What is force? a) b)example: What are balanced forces? Give an example. a) What are unbalanced forces? Give 2 examples. a) b)example: b) examples: How does mass effect force? What are 3 things that can happen when an object is affected by force? How is force affected when a simple machine is used? What is a pulley and why is it used? a) b) c) a) b) example: a) b) examples: c) Illustrate: What is an inclined plane and why is it used? Give an example of an object continually changing (transforming) from kinetic to potential energy. Give an example of an object gaining potential energy. What is motion? a) b)example: Explain this statement: “An object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion unless acted upon by an outside force.” Explain how to calculate speed. Give an example. How do you calculate average speed from a graph? Explain what a graph would look like for a car in constant motion. Explain what a graph would look like of a student walking at different speeds. Describe 3 ways you can tell the motion of an object is changing by looking at a motion line graph. Describe two types of constant motion that can be represented on a motion graph. What does the slope of the line in a speed graph tell? What does a horizontal straight line in a speed graph tell? What equipment would you need to measure the speed of a runner? Why? a) b)example: a) b) example: a) b) example: a) b) c) a) b) a) b) In your spiral define the following words for a spiral check on test day!!!! Frayer Model for: balanced force, unbalanced force, motion, potential energy, kinetic energy, inclined plane, pulley, speed, inertia, velocity, acceleration, deceleration Force, Motion, and Speed Study Guide ANSWERS What is force? What are balanced forces? Give an example. What are unbalanced forces? Give 2 examples. a) a push or a pull exerted on an object b)examples: gravity, a boy pulling a wagon a) are balanced on all sides and do not change the object’s motion or position b)example: pushing on both sides of a toy car a) When forces are not balanced on all sides of an object. Unbalanced forces change the position of an object and b) examples: winning a tug-of-war game, someone pushing another person over How does mass effect force? What are 3 things that can happen when an object is affected by force? How is force affected when a simple machine is used? The greater the mass of an object, the greater the object's force What is a pulley and why is it used? a) A pulley system changes the direction of the force a) speed up b) slow down c) change direction a) It increases the force that we apply to a task. b) example: we pull down on a pulley and this makes the object easier to lift (uses less effort on our part) we apply. Rather than pulling up, we pull down. This makes it easier to lift an object. b) examples: A pulley helps us lift objects – raising a flag on a flag pole, raising or lowering window blinds, construction crane c) Illustrate: What is an inclined plane and why is it used? An inclined plane is a slanted surface used to raise an object. When an object is moved up an inclined plane, a) What is potential energy? b) Give 3 examples less effort is needed than if you were to lift it straight up, but, you must move the object over a greater distance. Example: ramp a) Energy of position b) stretched rubber band stacked dominoes charged battery a) What is kinetic energy? b) Give 3 examples. a) energy of motion b) flying rubber band Give an example of an object continually changing (transforming) from kinetic to potential energy. Give an example of an object gaining potential energy. What is motion? Roller coaster – potential at the top of the hills and kinetic going down the hills falling dominoes driving a car Stretching a rubber band A roller coaster getting to the top of the highest hill. a) the change in location of an object b)example: Explain this statement: “An object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion unless acted upon by an outside force.” Explain how to calculate speed. Give an example. How do you calculate average speed from a graph? Explain what a graph would look like for a car in constant motion. a car going down the street It means that a object will stay in the same place unless a force moves it OR an object will keep moving unless a force stops it (or slows it down) Example – wear your seat belt to become “part of the car” so you’ll stop when it stops. a) speed = distance traveled divided by time passed b)example: A car moving 60 meters in one hour = 60m divided by 1 hour = 60mph (meters per hour) Average speed = total distance traveled divided by total time traveled. a) The motion of the car would be shown by a straight line. b) example: Explain what a graph would look like of a student walking at different speeds. Describe 3 ways you can tell the motion of an object is changing by looking at a motion line graph. Describe two types of constant motion that can be represented on a motion graph. Write a “speed calculation” question. What does the slope of the line in a speed graph tell? What does a horizontal straight line in a speed graph tell? What equipment would you need to measure the speed of a runner? Why? a) 2 or more straight lines at different slopes. b) example: a) the line turns left b) the line turns right c) the object stops and the line goes “flat” or parallel to the x axis. a) a straight line going “up,” a straight line going “down,” b) or a straight line running parallel to the x axis How fast is an airplane traveling it is moves 500 meters in 2 hours? 500/2 = 250 mph The steeper the slope is rising, the faster the motion. A flat line means zero motion. The object is not moving. a) Metric tape measure and Stop watch. b) Speed is determined by measuring distance traveled over time so you need the tape measure to measure the distance and the stop watch to measure the time.