* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ARABIAN PENINSULA and ISLAM – KEY -
International reactions to Fitna wikipedia , lookup
Imamah (Shia) wikipedia , lookup
Political aspects of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Islamism wikipedia , lookup
Sources of sharia wikipedia , lookup
Islam and violence wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Twelver Shia Islam wikipedia , lookup
War against Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Mormonism wikipedia , lookup
Succession to Muhammad wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
The Jewel of Medina wikipedia , lookup
Islamic–Jewish relations wikipedia , lookup
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
Islamic culture wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
Soviet Orientalist studies in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Muhammad and the Bible wikipedia , lookup
Islamic schools and branches wikipedia , lookup
Satanic Verses wikipedia , lookup
Islam and other religions wikipedia , lookup
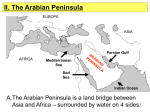
ARABIAN PENINSULA and ISLAM – KEY --Review for Quiz 1 1. Which continents surround the Arabian Peninsula? Asia, Africa and Europe 2. Locate the Arabian Peninsula and describe its diverse geography. Most important: deserts, mountains, coastal plains and oases influence life there. Deserts: harsh climate, powerful winds – Arab nomads moved through the desert with their camels, sheep and goats, which provided them with food and hair, wool and hides for clothing, blankets and tents. Oases: areas of water in the desert which also provide plant life and shade— Nomads moved from oasis to oasis. Some people settled there towns developed around the oasis became trading centers Coastal plains: better land for farming – people could build dams and wells to irrigate ( give water to) the land—ports on the coastal plain increased trade with other lands Mountains: limit movement and make communication difficult, however, some people settled there and created terraces (steps) to farm the land and grow fruit trees 3. Describe Bedouin culture. Nomads constantly traveling in camel caravans in search of water and land for vegetation for animals Became strong and resourceful in order to survive in those conditions Had a social hierarchy or class system: Leader—Shaykh Warriors and their families Slaves Were excellent warriors 4. Who was Muhammad? How did he become the voice of Islam? Muhammad was a trader in the Arabian Peninsula. The angel Gabriel appeared to him in a cave and called him the “Prophet” or the messenger of God. 5. Describe the reason for Muhammad’s hejira (flight/escape) to Medina in 622 CE. What makes this important? Arabs asked Muhammad to go to Medina to bring peace to warring tribes. **Very important because Muhammad’s followers went there with him. People were bound together by faith, not blood. 6. Why did Muhammad return to Mecca in 630? 624 - Fighting broke out between Muslims and Meccans. The Meccans broke their agreement that would allow Muslims to make their pilgrimage to Mecca. In 630, Muhammad returned with an army to capture the city of Mecca. 7. What did he do when he returned to the city? In Mecca, Muhammad destroyed all the idols at the Ka’ba and rededicated it to one god, Allah. 8. Why was this action so important? This was the true beginning of Islam. Also, this event marked the change from polytheism to monotheism in this part of the world. 9. Name and describe the 5 Pillars of Islam. (Study the Teachings of Islam page from Mrs. Gil) (#10 not on test) 11. Define monotheism and polytheism. Why were Muhammad’s ideas not accepted by many people? monotheism – belief in one god polytheism – belief in many gods Many people… did not like Muslim idea of sharing wealth did not want to give up polytheistic beliefs did not accept breakdown of their heritage (their culture and customs)