* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 4: Newton`s Laws: Explaining Motion
Survey
Document related concepts
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
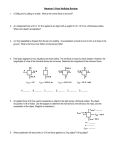
Chapter 4: Newton’s Laws: Explaining Motion 1. All except one of the following require the application of a net force. Which one is the exception? A. to change an object from a state of rest to a state of motion. B. to maintain an object in motion at a constant velocity. C. to change an object’s speed without changing its direction of motion. D. to maintain an object in uniform circular motion. E. to change an object’s direction of motion without changing its speed. 2. The force that accelerates a car on a level road is exerted by which object? A. Motor. B. Gears. C. Rear axle. D. Drive shaft. E. The road. 3. A car rounds a curve while maintaining constant speed. The correct statement is: A. The acceleration of the car is zero. B. The velocity of the car is zero. C. No net force acts on the car. D. The velocity of the car is constant. E. A net force acts upon the car. 4. A book weighing 10 N is held at rest in the palm of the hand. The reaction to the force of the hand on the book is a force of A. 10 N exerted by the Earth on the book. B. 10 N exerted by the book on the Earth. C. 10 N exerted by the book on the hand. D. 0 N. 5. A block of mass 5.0 kg is acted upon by a single force, producing an acceleration of 2.0 m/s². The force has a value of A. 5.0 N. B. 10 N. C. 2.5 N. D. 0.5 N. 6. A crate is acted upon by a net force of 100 N. An acceleration of 5.0 m/s2 results. The weight of the crate is A. 20 N. B. 9.8 N. C. 98 N. D. 196 N. E. 40 N. 7. A parachutist jumping from an airplane reaches a terminal velocity when the force of air resistance is 490 N. The mass of the parachutist is A. 490 kg. B. 9.8 kg. C. 40 kg. D. 50 kg. E. 80 kg. 8. An elevator of mass 500 kg is caused to accelerate upward at 4.0 m/s2 by a force in the cable. What is the force exerted by the cable? A. 2,000 N B. 4,900 N C. 6,900 N D. 2,900 N E. zero 9. A net horizontal force of 200 N acts on a 50-kg cart, which is free to roll on a level surface. 2 A. The cart accelerates at 4 m/s . 2 B. The cart accelerates at 10 m/s . 2 C. The cart accelerates at 10000 m/s . 2 D. The cart accelerates at 0.25 m/s . E. The cart does not accelerate because it pushes back on the person with a force of 200 N. ANSWERS: B E E C B D D C A