* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download file - Athens Academy
Survey
Document related concepts
Post-classical history wikipedia , lookup
Myth of the flat Earth wikipedia , lookup
England in the High Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Medieval Inquisition wikipedia , lookup
England in the Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Scotland in the Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Scotland in the High Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Wales in the Early Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
European science in the Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Medievalism wikipedia , lookup
History of the Czech lands in the High Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Dark Ages (historiography) wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
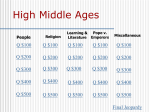
Name: Honors World History- Mr. Snead Athens Academy- Spring 2008 Study Guide: High Middle Ages Reading Assignments: (found in Chapters 8&9) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Read pp. 215-225. Read pp. 225-229. Read pp. 229-235. Read pp. 235-238. Read pp. 238-245. Read pp. 251-263. Read pp. 263-272. Read pp. 272-276. Terms: Feudalism Vassal Homage Fealty Manorialism Primogeniture Knights Song of Roland Demesne Glebe Land Serf/Serfdom Week Work Boon Work Guild Magna Carta Friars 4th Lateran Council Norman Conquest Duke William (Conqueror) Edward the Confessor Harold Godwinson Harold Hardrada Battle of Hastings Doomsday Book Curia Regis Henry I (England) William Rufus Exchequer Capetians Otto I Henry IV (Germany) John I St. Dominic Franciscan Order Cluny Leo IX Nicholas II College of Cardinals Gregory VII Investiture Controversy Concordat of Worms Canon Law Papal Curia Universities St. Anselm Thomas Aquinas Gothic Common Law Frederick Barbarossa St. Francis of Assisi Town vs. Gown Mendicants Cistercians Pax Dei Innocent III Heresy Sacraments Relics Cathars Indulgences Inquisition Abelard Romanesque Henry II Richard I Frederick II Crusades Questions: 1. Explain the significance of the Feudal “Pyramid” in European politics during the High Middle Ages. 2. Discuss how the Agricultural Revolution of the Middle Ages impacted Europe from 1050-1350. (Be sure to mention what were the elements that brought about agricultural revolution? 3. What was chivalry? How did it affect medieval society? 4. How did the Norman Conquest change England? 5. How and why did trade emerge/flourish during the High Middle Ages? 6. Access the following changes to the church which occurred during the High Middle Ages: monastic changes, rise of the papacy, and the impact of religion on popular culture. 7. Explain, in your own words, what factors led to the growing strength/influence of the church during the High Middle Ages. 8. Describe the factors which allowed Feudalism to emerge. What this a successful system of governing? Explain your answer with examples from England, France, and Germany. 9. List and explain the factors which led to the reemergence of cities and towns during the High Middle Ages. 10. Did life improve for the typical person during the High Middle Ages? Explain your answer. 11. Which did more to change the papacy during the High Middle Ages: the Investiture Controversy or the Papal Curia? Explain. 12. How and why was the church allowed to get so powerful during the High Middle Ages? 13. Discuss the roots of the doctrine of the separation of church and state as they emerged in the Middle Ages. What forces and events contributed to this development? 14. What role did guilds play in the economic life of towns and cities during the High Middle Ages? 15. Assess the following in terms of impact on the church: Leo IX, Nicholas II, Gregory VII, Urban II, and Innocent III. 16. How did the rise of universities impact life during the High Middle Ages? (hint: causes & consequences of their founding) 17. Compare and contrast Romanesque and Gothic architecture. 18. The Crusades have been called “successful failures.” In your opinion, why is this statement true? 19. Briefly explain intolerance in the thirteenth century. What groups were singled out for attack? Why were they attacked? 20. Discuss the background of the Crusades. What key events precipitated these ventures of European knights toward the Holy Land? What were the underlying reasons/principal motivations for them?