* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Name - Manhasset Public Schools
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
Weightlessness wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to gauge theory wikipedia , lookup
Electron mobility wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear physics wikipedia , lookup
Field (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Speed of gravity wikipedia , lookup
Casimir effect wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistivity and conductivity wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear force wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Anti-gravity wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
Atomic nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
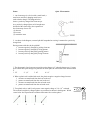
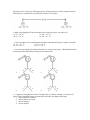
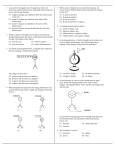
Name: Quiz: Electrostatics 1. An electroscope is a device with a metal knob, a metal stem, and freely hanging metal leaves used to detect charges. The diagram below shows a positively charged leaf electroscope. As a positively charged glass rod is brought near the knob of the electroscope, the separation of the electroscope leaves will (1) decrease (2) increase (3) remain the same 2. As shown in the diagram, a neutral pith ball suspended on a string is attracted to a positively charged rod. During contact with the rod, the pith ball 1. become negatively charged by gaining electrons 2. become negatively charged by losing protons 3. become positively charged by gaining protons 4. become positively charged by losing electrons 3. The electrostatic force between two positive point charges is F when the charges are 0.1 meter apart. When these point charges are placed 0.05 meter apart, the electrostatic force between them is 1. 2F 2. ½ F 3. 4F 4. ¼ F 4. When a plastic rod is rubbed with wool, the plastic acquires a negative charge because 1. electrons are transferred from the wool to the rod 2. protons are transferred from the wool to the rod 3. electrons are transferred from the rod to the wool 4. protons are transferred from the rod to the wool 5. Two plastic rods, A and B, each possess a net negative charge of 1.0 × 10-3 coulomb. The rods and a negatively charged sphere are positioned as shown in the diagram. Which vector below best represents the resultant electrostatic force on the sphere? 1. 2. 3. 4. Questions 6 and 7 refer to the following diagram which represents two small, charged, identical metal spheres, A and B that are separated by a distance of 2.0 meters. 6. What is the magnitude of the electrostatic force exerted by sphere A on sphere B? (1) 7.2 × 10−3 N (3) 8.0 × 10−13 N −3 (2) 3.6 × 10 N (4) 4.0 × 10−13 N 7. If the two spheres were touched together and then separated, the charge on sphere A would be (1) −3.0 × 10−7 C (3) −1.3 × 10−6 C −7 (2) −6.0 × 10 C (4) −2.6 × 10−6 C 8. A positively charged rod is held near the knob of a neutral electroscope. Which diagram below best represents the distribution of charge on the electroscope? 1. 3. 2. 4. 9. A negatively charged plastic comb is brought close to, but does not touch, a small piece of paper. If the comb and the paper are attracted to each other, the charge on the paper 1. may be negative or neutral 2. may be positive or neutral 3. must be negative 4. must be positive 10. Gravitational forces differ from electrostatic forces in that gravitational forces are (1) attractive, only (2) repulsive, only (3) neither attractive nor repulsive (4) both attractive and repulsive 11. During a lightning storm, most cars can provide safe shelter because cars 1. have rubber tires. 2. repel static charges. 3. are metal containers. 4. have antennas. 12. Moving 4.0 coulombs of charge through a circuit requires 48 joules of electric energy. What is the potential difference across this circuit? (1) 190 V (3) 12 V (2) 48 V (4) 4.0 V 13. The electronvolt is a unit of (1) energy (3) electric field strength (2) charge (4) electric potential difference Free Response 14. Two similar metal spheres, A and B, have charges of +2.0 × 10-6 coulomb and +1.0 × 10-6 coulomb, respectively, as shown in the diagram below. The magnitude of the electrostatic force on A due to B is 2.4 newtons. [a] What is the magnitude of the electrostatic force on B due to A? [b] Calculate the distance between spheres A and B? Show equation and substitution with units. [2] [c] If A and B are connected with a metal wire, what will be the magnitude of the charge left on sphere B? 15. Two conducting parallel plates 5.0 × 10−3 meter apart are charged with a 12-volt potential difference. An electron is located midway between the plates. The magnitude of the electrostatic force on the electron is 3.8 × 10−16 newton. a. On the diagram above, draw at least three field lines to represent the direction of the electric field in the space between the charged plates. b. Identify the direction of the electrostatic force that the electric field exerts on the electron. c. Calculate the magnitude of the electric field strength between the plates, in newtons per coulomb. [Show all work, including the equation and substitution with units.] [2] d. Describe what happens to the magnitude of the net electrostatic force on the electron as the electron is moved toward the positive plate. 16. Which diagram represents the electric field between two oppositely charged conducting spheres?