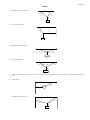
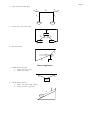
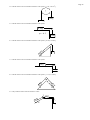
* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Horizontal Kinematics - The Woodlands High School
History of fluid mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Aristotelian physics wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Special relativity wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic mass wikipedia , lookup
Speed of sound wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Negative mass wikipedia , lookup
Time dilation wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Specific impulse wikipedia , lookup
Time in physics wikipedia , lookup
Weightlessness wikipedia , lookup
Anti-gravity wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Mass versus weight wikipedia , lookup
Faster-than-light wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
The Woodlands High School FIZIX PACKET P A P R e v i s e d 2 0 0 9 E d i t i o n Page 2 Table Of Contents Topic Horizontal Kinematics Kinematics Supplement Vertical Motion Projectile Motion Static Equilibrium Gravitational & Fundamental Forces Newton’s Laws of Motion Conservation of Energy Momentum and Impulse Energy Transfer (Heat) Periodic Motion Waves on Strings Light Page Number 3 4 6 8 10 13 16 21 27 30 33 35 38 Page 3 Horizontal Kinematics 1. If continents are drifting apart at the rate of 3.0 cm/yr. and Africa and South America are separated by 6.4 x 10 8 cm, how long have they been drifting apart? [2.1 x 108 yr.] 2. A quarterback throws a football at 40.0 km/hr to a receiver 50.0 yd away. How much time does it take the ball to reach the receiver? 3. While you are driving along westward at 55 mi./hr you doze for 1.5 seconds. How far have you traveled during your snooze? [-36.9 m] 4. Sound caused by an explosion on the ocean's surface travels vertically downward to an underwater mountain and is reflected back to a microphone at the surface. If this takes 11.6 seconds to occur and sound travels at 1450 m/s in water, what is the depth to this mountain? 5. A wombat runs south in a straight line with an average velocity of 5.0 m/s for 4.0 minutes and then with an average velocity of 4.0 m/s for 3.0 minutes in the same direction. a. What is its total displacement? [-1.92 km] b. What is its average velocity during this time? [-4.57 m/s] 6. If one sprinter runs the 400.0 m in 58 seconds and another can run the same distance in 60.0 seconds, by how much distance will the faster person win by if they race? 7. The loser of the above race had to run an extra 1600 m as terms of a bet. She runs the first 800 m at an average speed of 6 m/s and the next 800 m at an average speed of 8 m/s. a. What is her total time needed to run 1600 m? [233 sec] b. What is her average speed? [6.870 m/s] 8. An MR-2 starts from rest and accelerates westward to a speed of 27 m/s in 11.8 sec. a. What is its acceleration? b. What is the displacement it covered? 9. A bowling ball starts from rest and moves 300 m down the gutter in 22.4 sec. a. What is its speed at the end of the track? [27 m/s] b. What is its acceleration? [l.2 m/s2] 10. A falling skydiver slows from a speed of 52 m/s to 8 m/s in 0.8 sec as the parachute opens. a. What is the diver’s acceleration? b. What displacement has she fallen during this time? 11. A car is traveling south at 30 m/s and two seconds later is going 25 m/s in the same direction. What is the car’s acceleration in this time interval? [+2.5m/s2] 12. A spaceship is limited to a maximum speed of 1/10 the speed of light. The ship is also limited to accelerate at only 10m/s 2 to avoid physiological problems to the crew. (The speed of light is 3 x 10 8 m/s) a. How many years does it take the ship to reach this speed? b. How far does it travel in this time? 13. A bicycle traveling at 4 m/s undergoes the same acceleration during 5 seconds as a bus whose velocity changes from 16 m/s to 20 m/s in 8 seconds. What is the bike’s final velocity? [6.5 m/s] 14. A DC-8 has a take-off speed of 80 m/s, which it reaches 35 seconds after starting from rest. a. How much time does the plane spend going from 0-20 m/s? ] b. What distance does it cover doing so? c. How much time does it spend going from 60-80 m/s? [ d. What distance does it cover doing so? e. What is the minimum length of the runway? 15. A giant armadillo moving northward with a constant acceleration covers the distance between two points 60 m apart in 6 seconds. Its velocity as it passes the second point is 15m/s. a. What is the acceleration? [1.7 m/s2] b. What is the velocity at the first point? [5 m/s] Page 4 16. The Tokyo Express accelerates at the rate of 1 m/s2 for one minute. If it begins from rest: a. How far will it have traveled? b. What is its velocity at the end of this time? c. What is its average velocity over this distance? 17. An ultra-light taking off has a 500 m runway. If it starts from rest, constantly accelerates, and travels the 500 m in 30 seconds with what velocity did it take off? [33.4m/s] 18. A taxicab driver forgets to stop at a hotel. As it passes the hotel, he decelerates. Five seconds later the cab is 80 m beyond the hotel and has slowed to 10 m/s. a. What is the speed of the cab as it passed t the stop? b. What is the acceleration of the cab? Kinematics Supplement 1. A sprinter begins from rest and accelerates at the rate of 2 m/s2 for 200 m. a. What is the sprinter’s velocity at the end of the 200 m? [28 m/s] b. How long does it take him to cover it? [14 sec] c. What is his average velocity? [14 m/s] 2. A plane accelerates from 2 m/s at the rate of 3 m/s2 over a 530 m distance. a. How long does it take the plane to cover this distance?] b. What is its velocity at the end of this 530 m distance? 3. A motorcycle travels the first half of a 100 m track with a constant speed of 5 m/s. In the second half of the 100 m, it experiences a flat tire and decelerates at 0.2 m/s2. How long does it take the cycle to travel the 100 m distance? [23.8 sec] 4. A box falls of the tailgate of a truck and slides a distance of 62.5 m before coming to a halt. If friction slows the box at the rate of 5 m/s2: a. What was the speed of the truck when the box fell? b. How long does it take the box to stop? 5. A driver traveling at 90 km/hr sees the lights of a barrier 40 m ahead. It takes the driver 0.75 seconds to apply the brakes. Once braking begins, the car slows at a maximum rate of 10 m/s2. a. Does the car hit the barrier? [yes, at 14m/s, or overshoots by 10m] b. At the moment the driver notices the wall, at what maximum velocity could the car be traveling so that it does not slam into the barrier? [21.76m/s] 6. An engineer decides to design a runway to accommodate flying squirrels. To take off, the squirrels must attain a ground speed of 10 m/s. If they can accelerate at the rate of 1.5 m/s2 a. How long will it take the squirrels to reach this velocity? b..What must be the minimum length of the runway? 7. Tired geese decide to land on the runway described in the problem above. If the geese can slow at the rate of 1.2 m/s 2: c. What is the maximum velocity they can approach the runway? [8.9 m/s] d. How long does it take them to land completely? [7.42 sec] 8 .You are traveling down the highway in a 90 km/hr zone at 100 km/hr when you look up and see a D.P.S. car 300 m ahead. If you can slow at a maximum rate of 3 km/hr/sec: a. Will you have slowed enough to avoid a ticket? b. If you could change your deceleration, what is the minimum deceleration you could have in order to avoid a ticket? 9. The Enterprise is traveling at warp 3 which is three times the speed of light (the speed/of light is 3 x 108 m/s) Capt. James T. Kirk orders the ship to accelerate at the rate of 1.2 x 105 m/s2 for a distance of 250 light-years (a light-year is roughly 1.0 x1013 km) in order to avoid a Klingon battle cruiser. Captain is a chicken. c. What is the Enterprise’s velocity at the end of the acceleration? [7.7 x 10 11 m/s] d. How many years does the Enterprise accelerate? [0.2yr 74 days] e. What is its average velocity? [3.9 x 1011 m/s] 10. A stomper begins from rest and accelerates at 20 cm/s2 for 1.0 m. a. How long does it take the stomper to cover this distance? b. What is its velocity at the end of this acceleration? Page 5 11. A frantic student is running down the hall to her physics class. At 30.0m from the door she begins to decelerate at 1.50 m/s2, but she blows it and ends up passing the door at 1.00 m/s. a. How fast was she traveling 30.0 m from the door when she began to slow down? [9.54 m/s] b. What minimum velocity can she have if she wants to stop at the door instead of passing it? [9.49 m /s] 12. The KLOL running radio is cruising at 2.5m/s when he decides to speed up. He accelerates at the rate of 1.3 m/s 2 for 3.5 m. a. How fast is he moving at the end of his acceleration? b. For how long does he accelerate? 13. A drag racer can accelerate from rest at the rate of 70 km/hr/sec for 400 m. a. What is the car’s velocity at the end of the track? [l 25 m /s] b. How long does it take it to cover this distance? [6.4 sec] 14. The same dragster in the previous problem pops its parachute at the end of the race. If the chute slows it at the rate of 90 km/hr/sec: a. How long of a piece of road will the car need in order to stop? b. How long will it take it to stop? 15. A linebacker gets a running start and crosses the line of scrimmage just as the ball is snapped. He hits the quarterback traveling at 8 m/s at 5.0m behind the line of scrimmage. If the linebacker accelerates at 1.5m/s 2: a. What was his velocity when he crossed the line of scrimmage? [7 m/s] b. How long after the ball was snapped did he hit the Q.B.? [0.67 sec] Honors Supplement 1. A herd of nerds is stampeding at 7m/s. An unsuspecting encyclopedia salesman is 10m in front of this ugly mob. If he begins from rest and accelerates at 3 m/s2, will he get clear of a fate worse than death? [He’s safe] 2. A Volvo moving at a constant speed of 20 m/s passes a Saab waiting at a red light just as the light turns green. If the Saab begins from rest and accelerates at 2 m/s2: a. How far does the Saab travel before drawing even with the Volvo? b. How fast is the Saab traveling at this point? 3. A hockey player stands on the ice as an opposing player skates by with a puck, moving at uniform speed of 12m/s. Three seconds after this, the first player decides to chase him down and body check this guy. If he accelerates at 4 m/s 2: a. How long does it take him to catch his opponent? [8.2 sec] b. How far does he travel to do so? [134 m] 4. A skateboard starts from rest and accelerates at 2 m/s2 for 10 seconds. It then stays at a constant speed for 30 seconds, and then slows down at 4 m/s2 until it finally stops. What is the total distance covered? 5. A bobsled traveling at 24 m/s sees a spectator on the course. a. What is the stopping distance of the sled if her reaction time is 0.75 sec and the sled decelerates at 3.6 m/s? [98 m] b. If the spectator is 92 m away when the brakes are applied, what is the acceleration needed to stop the sled in time? [-3.13 m/s2] 6. A truck accelerates from rest at 1 m/s2. At the same instant that the truck starts, a car is 1000m from the truck and moving toward it head on at 20 m/s. How far from the starting point of the truck are the two when they meet? 7. The driver of a bus traveling at 30 m/s sees a dump truck 200 m ahead on the road. The truck is moving the same direction as the bus at 10 m/s. The bus driver applies his brakes to avoid a collision which slows the bus at the rate of 1m/s2. a. Will there be a collision? [yes, they just touch] b. If yes, where? [400m from where the bus hits the brakes] 8. A brown fruit bat flying toward a wall sends sound waves that travel 330 m/s when the bat is 2 m from the wall. If the bat is flying at 20 m/s, how far will the bat fly during the time required for the sound waves to echo off the wall and reach the bat again? [0.24 and 0.227 are common, but incorrect] 9. The maximum acceleration of a monorail train is 2m/s2 and its maximum speed is 22 m/s. What is the minimum time for it to travel 990 m between stops? [56 sec] 10. A rather quick roach travels 400 m. It starts from rest and accelerates at 1.5 m/s 2 until it reaches a speed of 9m/s. The roach continues at this speed and then finally decelerates at 2m/s2 until it stops. What is the time for the roach to cover this 400 m distance? Page 6 Vertical Motion 1. A robber drops a bag of loot into a 30 m well. If the speed of sound is 340 m/s, how long after dropping the bag does he hear the splash? [2.56 sec] 2. A penny is dropped off a tall building and hits the ground 5 seconds later. How tall is the building? 3. A diver falls from a 10m tower. How fast is she moving when she hits the water? 4. A basketball player has a maximum vertical jump of 0.72 m. What is his speed when he leaves the floor? 5. A stone is thrown down a hole with a speed of 3 m/s and hits the bottom 1.8 sec later. a. How deep is the hole? [21.3 m] b. How fast is the stone traveling when it hits? [-20.61m/s] [- 14 m/s] 6. .A juggler throws a ball upward and catches it 3.5 seconds later. c. What is the ball’s initial velocity? d. What is the ball’s maximum height? 7. A young vandal wishes to hit a truck traveling at a constant speed of 20m/s with a water balloon . If the vandal is in a tree, 40 m from the top of the truck, how far should the truck be from the tree when she releases the balloon so that it hits the truck when it is at a position directly beneath her? [57 m] 8. A jumping bean jumps vertically upward from the edge of a table. It has a speed of 10 m/s when it reaches half of its maximum height. a. How high does it rise? b. What is its velocity and acceleration 1 second after it jumps? c. 3 seconds after? d. What is its average velocity during the first half second? 9. A bomb is dropped from a hovering helicopter. It takes 4 seconds to hit. How high is the copter? [78.4 m] 10. How fast must a bullet be shot to reach a height of 250 m? 11. The acceleration due to gravity on Mars is 8.9 m/s2. If balls on Mars and the Earth are thrown upward simultaneously with a speed of 10m/s, which would return to the ground first and by how much time would it beat the other ball? [the ball on Earth lands 0.2sec before the one on Mars] 12. A bottle is thrown up such that it has a velocity of 19.6 m/s at half of its maximum height. a. What is its maximum height? b. What is its velocity 1 second after it was thrown? 13. A frog jumps vertically upward from a 20m tall building with an initial velocity of 10m/s. a. How high above the ground will the frog reach? [25.1 m] b. What is its velocity as it hits the ground below? [-22.2 m/s] 14. A cat is thrown vertically upward and hits the ground 15 seconds later. a. How high does the cat travel upward? b. What is its velocity when it strikes the ground? 15. David Letterman drops a T.V. from a 5-story building (1 story = 3 m). a. How long does it take the TV to reach the ground? [1.7sec] b. What is its velocity as it impacts? [-17m/s] 16. A construction worker ascending at 6m/s in an open elevator 42 m above the ground drops a hammer. a. How long does it take the hammer to hit the ground? b. How fast is it moving when it hits the ground? 17. A missile is launched upward with an acceleration of 100 m/s2. Eight seconds later, the engine shuts off. a. What height does the missile achieve? [35852 m] b. What is the total time it is in flight? [175 sec] c. What speed does it have when it strikes the ground? [838 m/s] d. What is the greatest speed of the missile? [838m/s upon impact 18. A helicopter drops a care package to stranded climbers as it is ascending at 8m/s. The package hits the ground 4 seconds later. a. How high was the copter when the package dropped? b. How high was the copter when the package hit? Page 7 Honors Supplement 1. If, from a height of 62m, Galileo accidentally dropped one of the cannon balls 0.5sec before the other, with what velocity would the second ball I have to be thrown downward to reach the ground at the same time as the first ball? [-5.3 m/s] 2. A flowerpot is dropped and passes by a window below. It takes 0.15 sec to travel from the top to the bottom of the 1.6 m tall window as it falls to the ground. How far above the window was the pot released? 3. A television is dropped from the top of a cliff, and 1 second later a second television is thrown downward with a velocity of 20 m/s. How far below the cliff will the second television overtake the first? [10.7m] 4. A juggler performs in a room with a 3m ceiling. He bounces the ball off the floor so that it just reaches the ceiling. a. With what velocity does the ball come off the floor? b. How long does it take to go from floor to ceiling'? 5. A second ball is bounced with the same velocity as the first. It leaves the floor at the instant the first ball leaves the ceiling. a. How long after the second ball is bounced do they pass one another? [0.39sec] b. How high above the floor do the two balls pass? [ 2.25m] 6. Lois Lane is dropped off a skyscraper 300m high. Five seconds after she is dropped, Superman dives off the roof to save her. (Assume that Superman has super-human control over his initial velocity but not his acceleration.) a. What is Superman’s initial velocity if he is to save Lois just before she hits? b. What must the height be such that he cannot save Lois? 7. Papa Smurf falls off a 1500m cliff. After 5 seconds of falling, he magically slows his fall so that he lands gently (zero velocity). a. What is the Smurf’s magic acceleration? [0.87m/s2] b. Unable to stop his magic, Papa Smurf is propelled back into the air until 5 seconds later, the magic quits. How high does he reach? [ 11.8m] c. What velocity does he hit the ground with on his return trip? [-15.2m/s] (#4 and #5 go together) Page 8 Projectile Motion 1. A bomber flying horizontally at 120m/s drops a bomb from an elevation of 240 m. How far horizontally does the bomb travel before striking the ground? [840 m] 2. A ball is thrown horizontally off a 35 m tall tower. The ball strikes the ground 80 m from the base of the tower. a. What is the ball's time in flight? b. What is its initial velocity? c. What is its velocity (in i, j) as it strikes the ground? d. What is the magnitude and direction of its velocity as it strikes the ground? 3. A ball rolls off the edge of a table with a velocity of 1 m/s. If the table is 1 m tall: a. How far from the edge of the table does the ball strike the floor? [0.45 m ] b. How long does the ball fall? [0.45 sec] 4. A cannon shoots a projectile horizontally from a 24 m high cliff. The cannon ball lands 100 m from the base of the cliff. a. With what velocity is the projectile fired? b. What is the projectile velocity as it strikes the ground? 5. A DC-8 flying horizontally at an altitude of 20 km and a speed of 250 m/s drops an engine. a. How long after it falls does it take the engine to hit the ground? [63.9 sec] b. How far horizontally has the engine traveled when it hits? [16 km] 6. A BB gun is aim directly at the center of a target 50m away. If the bb is fired horizontally at 350 m/s, how far below the bull's-eye will the BB hit? 7. 7. A life-line is to be thrown from a ship 30 m above sea level to a drowning crew person. If the victim is 30 m horizontally from the ship, with what horizontal speed should the line be thrown? [12m/s] 8. A car loses control and drives off a 3 m high ridge and lands 11 m from the base of the ridge in a river. With what speed was the car traveling when it left the ridge? 9. A football is kicked at an angle of 50o and travels a distance of 20 m before hitting the ground. a. What is the initial speed of the ball? [14.1 m /s] b. How long is it in flight? [2.2 sec] c. How high does it rise? [5.94 m] 10. A cannon's firing angle is varied during a training exercise. If the cannon fires a shell at 700 m/s, find its range, time in flight, and maximum vertica1 height at: a. 45o b. 60o c. 30o 11. A cat is on a 1.5 m high table and jumps at a 37oangle with a speed of 10 m/s. How far horizontally from the edge of the table does the cat land? [11.5m] 12. An arrow is fired at 53o with a velocity of 15 m/s. d. How long is it in the air?] e. What is its range? 13. A cannon fires a shell with a muzzle speed of 600 m/s at 30o. a. What is the cannon's range? [31.8 km] b. How high does the shell rise? [4590 m] 14. If George Washington threw a silver dollar across the Potomac River which is 300m wide, with what speed did be have to throw the coin? Assume a 45o angle. 15. A mortar elevated to 60o scores a hit 15 m up a building 30 m away. a. With what speed was the shell fired? [21.8 m/s] b. What is the velocity of the shell (in i, j) as it strikes the building? [(10.9i - 8.00j) m/s] Page 9 16. A sniper is riding in the back of a pick-up traveling at a constant speed of 20 m/s. If he fires a bullet straight up in the air with a speed of 100 m/s: a. How long is the bullet in flight? b. Where does the bullet land? c. How high does it rise? 17. A long jumper jumps at a 20o angle and attains a maximum altitude of 0.6 m. a. What is her initial speed? [10 m/s] b. How far is her jump? [6.59 m] 18. A bomber is climbing at a 37o angle at a speed of 250 m/s. When it reaches a height of 1000 m, a bomb is released. a. How long is the bomb in flight? b. How high above the ground does the bomb rise? c. How far horizontally from the point it is released does the bomb travel? d. What is the impact velocity of the bomb? 19. As an open elevator rises at a constant speed of 8 m/s, a boy throws an apple with a speed of 10m/s at a 45 o angle (in the reference frame of the elevator) when the elevator is 20 m above the ground. a. How far horizontally from the elevator does the apple strike the ground? [28.8 m] b. How far will the apple rise above the ground? [31 .6 m] c. How long is it in flight? [4.08 sec] d. What is the impact velocity? [25.9 m/s at -74o] 20. You are traveling at a constant speed of 30m/s in a car. You wish to release a water balloon such that it will land in an open manhole. a. If you release the balloon 1.5 m above the ground, how far from the hole should you release the balloon? b. What is the impact velocity of the balloon? 21. What is the minimum speed needed to fire a champagne cork a distance of 11 m? [10.4 m/s] 22. A grasshopper jumps a distance of 5 m. If it left the ground at a 40o angle, what was its initial speed? Honors Supplement 1. A punter wishes his punt to have a hang time of 4 seconds and travel a distance of 50 m. With what velocity (magnitude & direction) must he kick the ball? [23 m/s at 57.5o] 2. At what angle must a rifle be fired if it is to hit a target at the same level 150 m away dead center? The initial speed of the bullet is 450 m/s. 3. Prove that the range of a projectile fired at is the same as one fired at 90o - . 4. A projectile is fire such that its range is equal to three times the vertical height. At what angle is this projectile fired? 5. What effect does doubling the initial velocity have on the range? [the range is quadrupled] 6. A pitcher can throw a ball 40 m vertically upward. What is the maximum horizontal distance that he can throw it? 7. Prove that a projectile fired at 45o will achieve maximum horizontal distance. Page 10 Statics 1. Find the tensions in each string. 40 50 T1 T2 T3 5kg 2. [113 N, 56.6N, 98 N] 60 T1 T2 T3 10kg 3. Find the tension in each string 10 10 200N 4. 44.8N, 36.6N, 50N] T1 T2 45 60 T3 50N 5. A wire is stretched between 2 posts 30 m apart. A 5.0 N bird sits on the center of the wire which sags 6 cm. What is the tension in the wire? 6. [170N, 196N] 30 T2 10kg T1 7. Find the tension in each wire. T1 T2 45 15 T3 6kg Page 11 8. [196N, 169.7N, 196N, 98N, 98N] T1 T3 T2 30 30 T4 T5 10kg 9. 10kg [ 49N, 27.6N, 27.6N, 19.6N, 19.6N] T1 1kg T2 45 45 2kg T3 2kg T4 T5 10. [49N, 84.9N, 49N] 30 60 T2 T3 T1 5kg Honors Supplement 1. Find the tension in the cords a. when = 30o and m = 2 kg b. in terms of , m, and g. T1 T2 2kg 2. Find the tension in the cord. a. when = 60o and m = 50 kg [424 N] b. in terms of and m. [mg sin ] T m Page 12 3. Show that tan = 1 + 2M/m M 45 45 m Page 13 Gravitational Forces (Fundamental Forces) mmoon = 7.36 x 1022 kg mearth = 5.98 x 1024 kg rmoon = 1.74 x 106 m rearth = 6.37 x 106 m rearth-moon = 3.845 x 108 m rearth-sun = 1.50 x 1011 m msun = 1.99 x 1030 kg 1A = 10-10 m rsun = 6.96 x 108 m me = 9.11 x 10-31 kg mp = 1.67 x 10-27 kg G = 6.67 x 10-11 Nm2/kg2 k = 8.99 x 109 N·m2/C2 e = 1.602 x 10-19C 1. Calculate the gravitational force of: a. the sun on the earth [3.5 x 1022 N] b. the earth on the moon [1.99 x 1020 N] 2. Calculate the gravitational attraction between: a. a 50 kg person and a 150 kg file cabinet that are 2 m apart. b. a 50 kg person and the earth if the person is 2 m above the ground. c. Explain why the attraction was apparent in one case and not the other. 3. Find the gravitational force between two 1000 kg lead spheres whose centers are 3m apart? [7.4 x 10 -6N] 4. A 2 kg mass is 1 m away from a 5 kg mass. What is the gravitational force: a. that the 5 kg mass exerts on the 2 kg mass? b. that the 2 kg mass exerts on the 5 kg mass? 5. The mass of the planet Saturn is 5.7 x 1015 kg and that of the sun is 2 x 1030 kg. The average distance between them is 1.4 x 1012 m. What is the gravitational force the sun exerts on Saturn? [3.88 x 10 11 N] 6. Calculate the force of gravity between two bowling balls, each with a mass of 7 kg, when they are 0.5 m apart. 7. Calculate the force of gravity on a spacecraft 12,800 km above the earth’s surface if it has a mass of 700 kg. [760 N] 8. A 50 kg person is standing on Mercury. Mercury’s mass is 0.0553 times the earth's mass and has a radius of 2439 kilometers. a. What is the person’s mass on Mercury? b. What is the person’s weight on Mercury? 9. A person weighing 760 N on earth moves to Saturn. Saturn's radius is 60,000 kilometers and is 17.24 times more massive than the earth. a. What is the person's weight on Saturn? [148 N] b. What is the person's mass on Saturn? [77.55kg] 10. How many times greater is the force exerted by the sun on the moon then the force exerted by the earth on the moon? 11. Calculate the force of the sun on the earth and of the moon on the earth. If the sun is so much more massive than the moon, why does the moon have more of an effect on the tides? [3.53 x 10 22 N, 1.99 x 1020 N] 12. A 30 cm distance separates two identical spheres, each 2 kg in mass. What is the gravitational force between them? 13. A 200 kg mass and a 500 kg mass are 0.40 m apart. Calculate the net force on a 100 kg mass placed midway between them. [5 x 10 -5 Ni] 14. Three 5 kg masses are placed on the corners of a 0.25 m length equilateral triangle. What is the direction and magnitude of the gravitational force on each as a result of the other two masses? 15. A black hole exerts a 50 N gravitational force on a spaceship. The black hole is 1 x 10 14 m from the spaceship. Calculate the force on the ship when it is one-half that distance from the black hole. (Note: one half of 1 x 1014 is not 1 x 107) [200 N] Electric Forces (Fundamental Forces Cont.) 16. 17. Calculate the net charge on an arbitrary substance consisting of a. 5 x 104 electrons b. a combination of 7 x 1013 protons and 4 x 1013 electrons. Two protons are separated in a molecule by a distance of 2.5 Å. What is the electrostatic force exerted by each proton? [3.69 x 10 -9 N] Page 14 18. A 4.5 C charge is located 3.2m from a -2.8 C charge. Find the magnitude of the electrostatic force exerted by one charge on the other. 19. Each of two spheres 6.0 x 10 -2 m apart carries a charge of +2.0 x 10-6 C. a. Calculate the force between them. [10.0 N] b. Is the force attractive or repulsive? [repulsive] 20. A 2.2 C charge is located on the x-axis at x = -1.5 m. A 5.4 C charge is located on the x-axis at x = 2.0m. A 3.5 C charge is at the origin. Find the net force acting on the 3.5 C charge. 21. Three charged particles each having a charge of -4.0 x 10-6 C, form an equilateral triangle with 0.01 m sides. a. What is the magnitude of the net force on each particle? [2490 N] b. In what directions will these three forces act? [outward relative to orientation] 22. Three point charges of 8 C, 3 C, and -5 C, are locate at the top, bottom left, and bottom right corners respectively of an equilateral triangle of side 1Å. Find the magnitude and direction of the net force on the 3 C charge. 23. Two electric charges originally 8cm apart are brought closer together until the force between them is greater by a factor of 16. How far are they apart now? [2cm] 24. Two charges are observed to repel one another with a force of 0.1N when they are 5 cm apart. What will the force be when they are: a. 10 cm apart? b. 50 cm apart? c. 1 cm apart? 25. Two very tiny metal spheres, one with a charge of 2 x 10 -5 C and the other with a charge of -1 x 10-5 C are 10 cm apart. a. What is the force between them? [-180 N] b. If they are allowed to make contact with one another and separate again to I0 cm, what is the force between them now? [22.5 N] 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. What is the magnitude and direction of the electric field needed to balance the gravitational weight of a. an electron? [5.6 X10-11N/C down] b. a proton? [1.02 X 10-7N/C down] c. a neutron? [not possible] . The electric force on a 5 C charge is 3.8 x 10-3 N in the positive x direction. What is the value of the electric field at that point? [+760 N/Ci] A point charge of -2.8 C is located at the origin. Find the electric field at a. x = 2 m b. y = -3 m c. x = 1 m, y = 1 m What is the value of the electric field at a point midway between a -2.5 C and a 6 C charge separated by 1.0m? [3.06 x 1011 N/C towards the negative charge] How many electrons make up a charge of -1 C? 31. What is the total charge on 1 kg of electrons? [-1.76 x 1011 C] 32. A certain raindrop picks up 30 electrons in its fall through the air. a. What is its charge? b. How much has its mass increased? 33. What is the magnitude and direction of the force a +10 C charge exerts on a +3 mC charge 2 m away? [67.5 N away from the other charge] 34. 35. Two charged bodies exert a 420 mN force on one another. What will be the force if the bodies are moved one third the distance apart? How far apart must two electrons be if the force between them is to be 10-12 N? [1.5 x 10-8 m] 36. What is the magnitude of the force between an iron nucleus (26 protons) and its inner-most electron if the distance is 10-2 Å? 37. A force of 2.4 N is exerted on a -1.8 C charge in a downward direction. What is the magnitude and direction of the electric field at this point? [1.3 x 106 N/C up] 38. An electron in an electric field experiences an eastward 8x10-16 N force. What is the magnitude and direction of the electric field? Page 15 39. 40. 41. What is the magnitude of the force on an electron in a 600 N/C electric field? [9.6 x I0 -17 N] A particle with 10 C of charge is placed into a 50 N/C electric field. What is the force exerted on the particles? Find the electric field 40 cm from a 70 C charge? [3.94 x 106 N/Cr] Honors Supplement for Fundamental Forces Gravitational Forces 1. Two stars of masses M and 4M are separated by distance d. Determine the location of a point from M where a third mass may be placed such that it experiences equal forces from M and 4M. [d/3, -d ] 2. At what distance from the center of the earth will a spacecraft experience equal forces from the earth and the moon? [3.46X10 8m. 4.32 X 108m] 3. At what distance from the earth’s surface, in terms of earth radii, r, should a satellite’s orbit be for the gravitational force of the earth on the satellite to be half what it is at the earth's surface? 4. 2 1 r If the mass of both the earth and the moon were doubled, by what factor would a. the radius of the moon’s orbit about the earth change if it had the same linear velocity? [2] b. the linear velocity have to change if it had the same radius? [(2 1/2] Electric Forces 5. An electron traveling at 1 x 108 m/s enters a perpendicular 1 x 106 N/C electric field. The field is 1cm wide. At what angle does the electron emerge from the field? [9.97o] 6. Three point charges are located along the y-axis: q1 = -2C is at y = 2m, and q2 = -3C is at y = -1 m. Where must a third positive charge be placed, relative to the origin if it is to experience equal forces from the other two? Which one of your two answers represents a “stable” position? [0.651m and 15.34m ] Magnetic Forces 7. A proton traveling at 10000 m/si encounters a region which has both an electric field and a magnetic field. The electric field is -200 N/Cj. a. In what direction must the magnetic field be so that the proton travels through the region undeflected? [parallel to the x-z plane, i component can have any value, k component must be negative.] b. How strong must the magnetic field be if it is perpendicular to the electric field? [0.02 T] 8. A particle accelerator needs to accelerate a proton to a speed of 2 x 108 m/s. If the accelerator has a 4 mile diameter, how strong of a magnetic field would be needed? [ 6.48 X 10-4 T] 9. The magnetic field over a region is describe by B = (2i - 3j)T. An electron moving with a velocity v = (i +2j-3k)m/s. What is the force exerted on the electron? [(1.44 x 10-18i + 9.61 x 10-19j + 1.12 x 10-18k)N] 10. A proton moving at 5 x 107 m/s through a magnetic field of 2 T experiences a force of magnitude 3 x 10 -12N. What is the angle between the field and the proton's velocity? [10.8o or 169.2o 11. An electron is projected into a uniform field described by B = (0.2i + 0.5j) T. Find the vector expression for the force on the electron when its velocity is v = 5 x 106j m/s. [1.6 x 10-13k N] Page 16 Newton’s Laws of Motion mmoon = 7.36 x 1022 kg mearth = 5.98 x 1024 kg msun = 1.99 x 1030 kg me = 9.11 x 10-31 kg 1. 2. rmoon = 1.74 x 106 m rearth = 6.37 x 106 m rsun = 6.96 x 108 m mp = 1.67 x 10-27 kg 1A = 10-10 m rearth-moon = 3.845 x 108 m rearth-sun = 1.50 x 1011 m G = 6.67 x 10-11 Nm2/kg2 k = 8.99 x 109 N·m2/C2 e = 1.602 x 10-19C Find the weights of the following masses: a. 10 kg [98 N] b. 2 kg [l 9.6 N] c. 160 kg [1568 N] d. 48 kg [470.4 N] e. 2.2 kg [21.56 N] f. 26.5 kg [259.7N] Find the masses of the following weights on Earth: a. 600 N b. 49 N c. 98 N d. 29.4 N e. 75 N f. 19.6 N 3. What force is needed to give a 25 kg mass an acceleration of 20 m/s 2? [500 N] 4. The acceleration of gravity, on Jupiter, the most massive planet, is 6.47m/s 2, and Jupiter’s radius is 7.1 x 104 kilometers. Calculate Jupiter’s mass. 5. Calculate the acceleration due to gravity on the moon. [-1.62 m/s2] 6. How far above the earth’s surface will the acceleration due to gravity be half what it is on the surface? 7. If you were one earth radius above the surface of the earth, what gravitational acceleration would you experience? 8. A body accelerates at 10 m/s2 when a 5.0 N force is applied to it. What is the body's mass? 9. A 6.0 N force is applied to a 2.0 kg ball. What is the ball's acceleration? [3 m/s 2] [-2.46 m/s2] 10. An object dropped near the earth’s surface falls 4.9 m in the first second. If the moon's gravitational pull is above 1/6 that of earth's, how long would it take the same object to fall the 4.9 m? 11. An 8.0 kg rocket sled is fired and encounters a force of air resistance of 4.9 N. If the sled's engines applied 60.9 N of thrust: a. What is the net force on the sled? [56 N] b. What is the sled's acceleration? [7 m/s2] 12. A 1 kg object can be accelerated at 10 m /s2. If you apply this same force to a 4 kg object, what will its acceleration be? 13. An empty pickup has a mass of 2000kg and has a maximum acceleration of 1 m/s2. What is its acceleration with a 1000 kg load? [0.67 m/s2] 14. A .22 caliber slug moving at 360 m/s hits and embeds in a block of wood to a depth of 0.1 m. If the slug has a mass of 1.8g a. How long does it take the slug to stop? b. What is the average retarding force? 15. A 15kg cart is pushed from rest horizontally by a 30 N force. a. What is the cart's acceleration? [2 m/s2] b. How far will it travel in 10 seconds? [100 m] c. What is its velocity at the end of 10 seconds? [20 m/s] 16. A skate rat and his board have a combined mass of 80 kg. If he is traveling 6 m/s, how much force is needed to stop him in 4 seconds? 17. A driver in a 1,200 kg car shifts to neutral and coasts for 10 seconds. His speed drops from 80 km/hr to 65 km/hr. What is the average drag force? [-500 N] 18. A 1,000 kg cart traveling south at 25 m/s slams into a pile of hay and comes to a stop in 1.5 seconds. a. What is the average stopping force of the hay? b. How far does the car penetrate the hay?] 19. A 20 kg sled is pulled along a frictionless horizontal surface. If the rope is pulling at a 30o angle to the horizontal and the sled accelerates at 2 m/s2, what is the tension in the rope? [46.2N] Page 17 20. A 5 kg block is pulled westward across a frictionless horizontal surface by a 30 N force applied at an 87 o angle above the horizontal. a. What is the block's acceleration? b. What is the normal force? 21. A 10 kg lawn mower is pushed along by a force applied at a 20o angle to the horizontal. If the mower accelerates at 3.4 m/s2, what is this force? [36.2N] 22. A 60 kg skier is pulled across a horizontal surface by a 230 N force exerted at 20o to the horizontal. What is her acceleration'? 23. An 80 kg child jumps from a wall and lands stiff-legged in a sand box. She hits the sand at 6.0 m/s and is stopped after sinking 0.05 m. What is the average stopping force of the sand'? [29, 600 N] 24. A 3.1g penny dropped from the Sear's Tower lands on the head of a passerby 460m below with a speed of 25 m/s. The penny embeds 1.0 mm. a. What is the penny's acceleration? b. What is the retarding force of the head? c. If 900 N ( 200 lbs.) will fracture the skull, will the penny do so? 25. A 60 g golf ball struck by a club acquires a speed of 70 m/s during an impact which lasts 2x 10 -4 seconds. What is the average force of the club on the ball? [2.1 x 104 N] 26. A 100 kg crate slides down a 20o incline. What is its acceleration? 27. A 3 kg block is released and slid down a 45o frictionless incline. a. What are the components of the weight? [Wx = 20.79 N, Wy = -20.79 N] b. What is the block's acceleration'? [6.93 m/s2] 28. A block is given an initial velocity of 5m/s up a smooth 20o incline. How far up the incline does the block slide before coming to rest? 29. A 52 kg skier starting from rest slides down a 30 m 12o incline. a. How long does it take him to reach the bottom? [5.4 sec] b. What is his speed at the bottom of the incline? [11.1m/s] 30. A 20kg crate moves along a surface with a coefficient of kinetic friction of 0.61. The crate is pulled westward by a rope that exerts a 162N force at a 37o angle. What is the crate’s acceleration? 31. A 70 kg mass is sliding up a 12o incline opposed by a 100N frictional force. a. What is its acceleration? [-3.47 m/s2] b. Find the normal forces? [671 N] 32. A 60 kg skier slides down a 12o incline with a surface having a coefficient of kinetic friction of 0.16. What is her acceleration? 33. A 20 kg crate is sitting on a floor with a coefficient of static friction of 0.50. If a rope pulls on the crate at a 37 o angle, what is the least tension that would cause the crate to start moving? [89.2N] 34. A 50kg slab rests on a horizontal surface with coefficients of static and kinetic friction of 0.70 and 0.50 respectively. a. What is the minimum force needed to start the box sliding? b. If the same force continues after the slab is sliding, what is the slab’s acceleration? 35. A block slides down a 10o incline at a constant speed. What is the coefficient of sliding friction between the block’s surface and the incline? [0.176] 36. A 20 kg sled rests on a horizontal surface. If it take 75N to start the sled in motion and 60 N to keep it moving at a constant speed, what are the coefficients of static and kinetic friction respectively? 37. The coefficient of static friction between a 100kg box and a surface is 0.30. What is the maximum force that can be applied to the box horizontally before it will move? [294N] 38. A 5kg block is sliding up a 30o incline. What is the block’s acceleration: a. If the incline is frictionless? b. If it has a coefficient of kinetic friction of 0.20? c. What applied force would be needed to offset the friction and make the block move up the incline at a constant rate? 39. A 10 kg crate moves at a constant speed of 5 m/s across a horizontal surface with a coefficient of kinetic friction of 0.20. a. What is the force required to keep it in motion? [19.6N] b. If the force is removed, how long will it take for the crate to come to rest? [2.55sec] Page 18 Honors Supplement 1. Derive a formula for the mass of a planet in terms of its radius, r, the acceleration due to gravity at its surface, g, and the gravitational constant, G. [mp = gr2/G] 2. A hockey puck leaves a player's stick with a speed of 10m/s and slides 40m before coming to rest. What is the coefficient of friction between the puck and ice? 3. A 2 kg crate is shot up a 30o incline at 22 m/s. If the incline's surface has a coefficient of kinetic friction of 0.30: a. How far up the incline will it slide? [32.5 m] b. How long will it take to do this? [2.96 sec] 4. If F= (6i - 3j) N acts on a 2 kg mass, find the magnitude and direction of the acceleration. 5. A 3 kg mass undergoes an acceleration a = (2i + 5j) m/s2. Find the magnitude and direction of the force that caused this. [16.2 N at 68.2o] 6. A 4 kg object has an initial velocity of 3i m/s and eight seconds later has a new velocity of (8i + 10j) m/s. a. What is the force in (ij) that caused this change? b. What is the magnitude of this force? 7. A shuffleboard puck having an initial speed of 5 m/s slides 8.0 m before coming to rest. What is the coefficient of kinetic friction between the puck and the surface? [0.16] 8. A box starting from rest slides down a 30o incline. After traveling 18m the box has a speed of 3 m/s. a. What is the coefficient of kinetic friction between the box and the incline? b. What is the box's acceleration? 9. For a block sliding on a rough incline with coefficient of kinetic friction k and an angle , show: a. a = g(sin - k cos ) for the block sliding down the incline. b. a = -g(sin + k cos ) for the block sliding up the incline. 10. A 2 kg crate with initial speed of 3 m/s slides 2 m to a stop. a. What is the coefficient of kinetic friction? b. What force would be needed to keep the crate moving at a constant speed? 11. A 900 kg motorcycle traveling at 20 m/s slides to a stop after applying the brakes. If the surface of the road has a coefficient of kinetic friction of 0.40, how far does the motorcycle skid? [51 m] 12. Find the tension in the cord and the acceleration of the system. [2.35N, 3.92 m/s 2] 0.6kg 0.4kg 13. Find the tension in the cord and the acceleration of the system. 20kg 10kg 37 Page 19 14. Find the tension in the cord and the acceleration of the system. [1.31N, 3.27 m/s 2] 0.2kg 0.1kg 15. Find the tension in the cord and the acceleration of the system. 0.5kg k = 0.5 0.5kg 16. Find the tension in the cord and the acceleration of the system. [16.72N, 1.44 m/s2] 2k g 2kg 45 17. Find the tension in the cord and the acceleration of the system. 1kg 1kg 18. Find the tension in the cord and the acceleration of the system. [17.5 N, 3.12 m/s 2] g 2k 7k g 35 35 19. Find k and the tensions if the acceleration is 2 m/s2. T2 3kg 5kg T1 25 10kg Page 20 20. What is the maximum value of M before the 10kg block moves? [2.3 kg] 10kg 30 s = 0.40 M 21. Find the tensions in the cords and the accelerations of each block. (Hint: the correct answers are not 0.336N, 0.1307N, -1.4 m/s2, 4.667 m/s2, -1.867 m/s2.) 40g 10g 20g Page 21 Conservation of Energy 1. A boy pulls a wagon with an 80 N force directed 25o above the horizontal a distance of 30 m. a. How much work does the boy do? [2,175 J] b. How much work does he do if the force is directed parallel to the ground? [2,400 J] 2. A boat pulls a skier 300 m with a 400 N force directed 15o above the centerline of the boat. How much work is done pulling the skier? 3. A fisherman reels in 20 m of line while fighting a fish that exerts an opposing force of 30 N. How much work does the fisherman do? [600 J] 4. A person rolls a 200 kg cart 2 m up a 30o incline at a constant speed. a. What force does the person apply to the cart? b. How much work does the person do? 5. A crane engine exerts a constant 60,000 N force on the other cars for 1 kilometer while bringing them from rest to 50 km/hr. How much work does the engine do? [6 107 J] 6. A car hits a pile of dirt and is stopped in 0.80 m. The work done on the car by the sand is 6.0 105 J. a. What is the average force the sand exerts on the car? b. Explain why the work done by the sand is negative. c. If the stopping distance is doubled, how does this change the stopping force? 7. A dog picks up a 20 kg bone 0.40 m. carries it 30 m down the hall, and sets it back down 0.40 m to the ground. How much work is done in each phase of the trip? [78 J, 0 J, -78 J] 8. 4 kg bucket is pulled at a constant velocity straight up a 5 m well. a. How much work does the puller do? b. How much work is done by the force of gravity on the bucket? c. How much total work is done? 9. A mule tows a barge down a 1.0 kilometer canal. If the mule pulls the barge with a 400 N force at an angle of 20°, how much work does it do? [376,000 J] 10. A 5 N force, parallel to an incline's surface, pushes a crate 5 m up the 15º incline at a constant velocity. a. How much work is done by the force? b. How much total work is done? 11. A 40 kg box is pushed on a horizontal surface for 5 m at a constant speed. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the box and floor is 0.25. a. What is the magnitude of the force pushing the box? [98 N] b. How much work does this force do? [490 J] 12. A 50 kg sack is pushed from rest by a 180 N force across a floor with k = 0.3. a. How much work is done pushing the sack 20 m? b. How much work is done by friction? c. What is the net force and how much work does it do? d. How much total work is done? 13. A log is pushed 2 m by a 2 N force. The opposing frictional force is 0.4 N. a. How much work is done by the 2 N force? [4 J] b. How much work is done by friction? [-0.8 J] 14. What is the kinetic energy of an electron (me = 9.11 10-31 kg) that strikes the screen of a cathode ray tube at 10 7 m/s? 15. What is the kinetic energy of a 2.0 gram rifle bullet with a muzzle velocity of 500.0 m/s? [250 J] 16. Find the kinetic energy of a 150 kg person running at 15 m/s. 17. A 70.0 kg runner covers 400 m in 45 seconds. What is her kinetic energy if we assume that her velocity is constant? [2.77 KJ] Page 22 18. A 2.0 kg and 200 kg body have an equal momentum of 40 kgm/s. How do their kinetic energies compare? 19. A 10.0 gram bullet has a velocity of 1 km/s. a. What is the bullet's kinetic energy? [5000 J] b. If the speed is halved, what is the kinetic energy? [1250 J] 20. What is the change in kinetic energy of a 1,000 kg object that accelerates from: a. 0 to 10 m/s? b. l0 to 20 m/s? 21. A 1500 kg car's kinetic energy changes by 2.6 105 J. If the final speed is 20 m/s, what was the initial speed? [7.3 m/s] 22. A 5 kg cat and a 12 kg dog have the same kinetic energies. If the dog runs at 4 m/s, how fast is the cat moving? 23. A 950 kg cart moving al 22 m/s loses 1.4 l05 J of kinetic energy while slowing to a 35 mph speed zone. Will it be moving slow enough to stay within the law? [yes,Vf = 30.8mph=13.8m/s] 24. A constant 5 N horizontal force hits a stationary 2 kg ball. What is its speed after going 10 m? 25. A 12 kg mass initially moving at 4 m/s is acted upon by a 120 N constant force for 16 m. What is the final speed of the mass? m/s] [18.3 26. A 2 kg mass is pulled 4 m across a frictionless horizontal surface by a 25 N force. If the mass begins from rest, what is its speed after traveling the 4 m? 27. A 5 N force causes a 2 kg body to change speed from 4 m/s to 6 m/s. Over what distance does this force act? [4 m] 28. A 1200 kg cart moving at 24 m/s drives 18 m into a muddy field which exerts a resistive force on the car of 1.7 104 N. What is the car's speed as it leaves the field? 29. A 1500 kg motorcycle moving at 20 m/s is stopped by an 800 N frictional force. How far does it take the bike to slop? [375 m] 30. A 60 kg person stands on a platform 2 m above a 4 m deep pool. a. What is the potential energy of the person with respect to the top surface of the pool? b. With respect to the bottom of the pool? 31. A 5200 kg train is pulled 360m up a 12o incline. What is the change in potential energy of the train? [3.8 106 J] 32. A 2 kg ball hangs 1 m below the ceiling. The height of the room is 3m. What is the gravitational potential energy of the ball relative to the: a. Ceiling b. Floor c. a point at the same level as the ball . 33. What is the potential energy of an 800 kg elevator that is 380m above street level? [2.98 106 J] 34. How much power does a water pump exert lifting 30 kg of water al a constant velocity 20 m each second? 35. How long does it take a 1 h.p. motor to lift a 72 kg mass 16 m at a constant velocity? [15 sec] 36. How much power must an engine have to lift a 10,000 kg safe at a constant velocity to a 20 m height in 5 seconds? 37. A 15 kW motor hoists an 800 kg steel beam at a constant velocity to a height of 90 m. How long will it take the motor to do this job? [47 sec] 38. A weight lifter raises a 150 kg barbell from the floor to a height of 2.2 m in 0.8 seconds at a constant velocity. What is the power output during this lift? 39. At 5 cents per kilowatt hour, what does it cost to operate a 10 h.p. motor for 8 hours? [$ 2.98] 40. A big tree evaporates 500 kg of water per day. If the water has to be raised 8 m at a constant velocity from the roots to the leaves before it can evaporate. a. How much energy must be supplied to do this? b. If this takes half of a day, what is the power needed to provide this energy? Page 23 41. A spring with a 1960 N/m spring constant is to absorb 7.84 J of energy as it is compressed. What distance will the spring be compressed? [0.089 m] 42. A BMW is equipped with a spring loaded bumper designed to compress 0.3 m when it contacts a wall at 9 m/s. The spring must absorb 8 104 J of energy to prevent damage to the car. What should the spring constant be? 43. A spring has a 500 N/m spring constant. What is the spring's potential energy when: a. it is stretched 4 cm from equilibrium? [0.4 J] b. it is not stretched? [0J] c. it is compressed 3 cm from equilibrium? [0.225 J] 44. A spring is stretched 6 cm from equilibrium. If it has a 1.2 104 N/m spring constant: a. what is its change in potential energy? b. what is its change in potential. energy as it moves from 6 cm to 3 cm from equilibrium? c. what is its change in potential energy as it moves from 3 cm to equilibrium? 45. A spring has a spring constant of 150 N/m. a. How much force is needed to stretch the spring 0.25m? b. How much energy is stored in the spring? [4.69J] [37.5 N] 46. A car traveling on a road at 12 m/s. It drives off an embankment and lands in a ditch 6 m below. What is the car's speed as it hits the ditch? 47. A soapbox derby is to be held on a frictionless hill with a 28 m vertical drop. The track is 300m long. a. What is the change in potential energy of a racecar from start to finish if it and the driver have a combined mass of 113 kg? [-31000 J] b. How fast is the car moving at the finish line? [23.4 m/s] 48. A 1 kg mass is released from rest from a height of 5 m on a curved frictionless ramp. The mass slides down the ramp and compresses a spring al the foot of the ramp. If the spring constant is 400 N/m, how far is the spring compressed? 49. A 3 kg mass sliding at 5 m/s on a frictionless horizontal surface encounters a frictionless 30º incline. How far does the mass slide up the incline before stopping? [2.55 m] 50. The same 3 kg body from the previous problem is again moving al 5 m/s on a rough surface 2 m from a 30º incline. All surfaces have a coefficient of kinetic friction of 0.30. a. What is the body's speed when it encounters the incline? b. How far along the incline does the body slide before stopping? 51. A spring with an 8540 N/m spring constant rests at the bottom of a frictionless 37º incline. A 0.60 kg block is placed against the spring, which causes it to compress 0.05 m. Once released, the block moves up the incline. What is the block's speed when it is 1 m from where it started? [4.88 m/s] 52. A 15 gram dart is shot from a spring gun. If the spring constant is 600 N/m and it can be compressed 5 centimeters: a. How high can the dart be shot vertically from its compressed position? b. What is the greatest range possible? (hint: recall which angle provides maximum range and use projectile motion.) 53. A 0.30 kg mass thrown upward reaches a height of 50 m. Calculate: a. its initial speed. [31.3m/s] b. its total energy. [1473] c. the ratio of its kinetic energy to its potential energy at a height of 10 m. [4] 54. A pop-up toy consists of a piece of plastic attached to a spring. The spring is compressed 2 cm and released. If the toy has a mass of 100 grams and reaches a vertical height of 60 cm above its compressed position, what is the spring constant of the spring? 55. A kid slides down a frictionless slide with a height of 4m. (Hint: the answers are independent of the mass.) a. What is the kid's speed at the bottom of the slide? [8.8.5 m/s] b. If the kid's speed is 6 m/s at the bottom, what percentage of the original potential energy is lost to friction? [54.1%] Page 24 56. A 0.4 kg cat is thrown upward at 15 m/s. What is the kinetic, potential, and total energy at: a. its initial position? b. a height of 3.0 m? c. the top of the flight? d. What is the maximum vertical height? 57. A bullet moving at 500 m/s has a 2500 J kinetic energy and a 0.5 J potential energy. a. What is the bullet's mass? [20 g] b. How high above the ground is it? [2.55 m] 58. A 2 kg block is projected up a 30º incline at 3 m/s. If the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.70, what is: a. the distance the block will travel up the incline? b. the amount of energy lost to friction? c. the change in kinetic and potential energy after the block has moved 0.3 m up the incline? 59. A sled travels down a slope that is 100 m high. Its speed at the bottom is 20 m/s. What percentage of its potential energy has been lost? [79.6 %] 60. A 20 kg object falls from a 15 m height and hits the ground 1.9 seconds later. a. If the force of air resistance is constant, find its magnitude. b. What percentage of energy is lost to air resistance? 61. You throw a 1.0 kg rock straight up at a kite resting in a 2.8 m high tree. If the rock hits the kite at 4 m/s, what was the rock's speed when it left your hand? [8.4 m/s] 62. The highest point attained by a 40 kg girl on a swing is 2 m above the ground, while at her lowest point she is 0.8 m above the ground. a. What is her maximum speed? b. What is the maximum speed of a 50 kg boy undergoing the same motion? 63. An 800 kg cart coasts down a 40 m high hill while applying the brakes. The cart's speed at the top of the hill is 6 m/s and 20 m/s at the bottom. How much energy is lost to friction? [168 kJ] 64. A soapbox derby is to be held on a hill with a 28 m vertical drop. The track is 300m long. Friction provides an 80 N opposing force on the car. a. What is the change in potential energy of a racecar from start to finish if it and the driver have a combined mass of 113 kg? b. How fast is the car moving at the finish line? 65. A billiard ball at rest is hit head-on by another ball moving 1.5 m/s in a perfectly elastic collision. What are the final speeds of both balls after the collision? [0 m/s, 1.5 m/s] 66. A 4.0 kg billiard ball moving at 2 m/s has a head-on collision with a stationary l kg ball in a perfectly elastic collision. What are their velocities after the collision? 67. A 1.0 kg block moving at 2 m/s has an elastic collision with a stationary 4 kg block. What are their velocities after the collision? [-1.2 m/s, 0.8 m/s] 68. A 3 kg ball moving at 8 m/s westward overtakes and collides with a 1 kg ball moving at 4 m/s westward. a. What are their speeds afterwards if it is a perfectly elastic collision? b. Is it is an inelastic collision? 69. A 1 a.m.u. neutron moving at velocity V o strikes a 16 a.m.u. oxygen nucleus. What are their velocities after the collision if: a. it is elastic? [(-15/17) Vo , (2/17) Vo] b. it is inelastic? [1/17) Vo] Honors Supplement 1. A 2 kg box slides down a 30º, 10 m long rough incline with k = 0.30. a. Draw and label a force diagram and find the work done by each force. [W g = 98 J, Wf = -50.9 J, WN = 0 J] c. b. Find the net force and the work done by it. [Fnet = 4.71 N, W = 47.1 J] 2. A force F = (6i - 3j) N is applied to a particle over a displacement d = (-3i + 2j) m. How much work does the force do? 3. If Fd = 0 and F = (2i - 3j) N, what can be said about d? Page 25 4. A 15 kg crate, starting from rest, is dragged across a fiat rough surface by a 70 N force acting at a 25º angle, If k = 0.30 and the block is displaced 5m: a. Find the work done by the applied force, the friction force, the normal force, and the gravitational force. b. What is the net work done on the block? 5. A force F = (6i - 2j) N acts on a particle that undergoes a displacement of d = (3i + j) m. a. What is the work done by the force? [16 J] b. What is the angle between F and d'? [36.9º] 6. A 100 kg sled is displaced 2 kilometers at a constant velocity. If k = 0.15, what is: a. the work done by the dogs pulling the sled? b. the work done by friction? 7. After drilling a bottle of Pepsi you want to work off its 110 Calories by lifting a 20 kg dumbbell. If you lift the weight 60cm and your body has 10% efficiency under these circumstances, how many times must you press the weight? (1 Calorie = 4186.8 J) [392 times] 8. A donkey pulls a 100 kg sled for 20 m across a level surface. If the rope pulls at a 30º angle to the horizontal with just enough force to move the sled without acceleration and the coefficient of friction for the sled/surface is 0.30, how much work does the donkey do? 9. A 1200 kg mass must be lifted by a cable, which causes it to go from rest to 4 m/s in 6 m. What tension of cable is needed? 104 N] [1.3 10. A 16 m long rope is pulled to the side 53º from the vertical. A 62 kg person on a balcony swings down on the rope. What is their speed at the bottom of their swing to glory? 11. A 12 kg crate is pushed 20 m up a 37º rough incline with coefficient of friction k = 0.25. If a 120 N force pushes parallel to the plane: a. How much work is done by this force? b. What is the crate’s increase in kinetic energy? [514.9 J] c. What is the crate’s increase in potential energy? [1415 J] d. How much work is done by friction? [-469.6 J] 12. A 2.20 kg egg is dropped from 4 m. a. How fast is the egg moving when it impacts? b. If the egg breaks when subjected to impulsive forces greater than 80 N, over what minimum distance must a force be exerted in order to preserve the egg? 13. A 55 kg woman leaps from a burning building. a. How fast is she moving when she hits a net 8 m below? [12.5 m/s] b. She is stopped in 1.2 m after striking the net. What is the average force of the net on her? [4100 N] 14. A 3 kg particle is moving at 6i m/s along the x-axis at position (3,0) m. A retarding force of -12i N begins to act. a. What are its coordinates when it comes to rest? b. How much work is done by this retarding force as the particle moves from (0,0) to its point of rest? 15. An object of mass m moving at Vo on a horizontal frictionless surface is stopped in distance x by an opposing for F. a. Show that F = (mVo2 )/(2x) b. If x is increased 50%, by what percent does the force change, assuming the same m and Vo? [-33.3%] 16. A rope exerts a 40 N force while lowering a 20 kg crate down a 15º frictionless incline. If its speed is initially 2 m/s, what is its speed after moving 10 m? 17. A rope exerts a 245 N force while pulling a 60 kg sled up a frictionless 25º slope. If the sled begins at rest, what is his speed after going 100 m up the slope? 18. A 900 kg cart initially at rest rolls down a 5º incline opposed by a 400 N frictional force. What is the cart's speed after moving 50 m? 19. The 6 kg block slides down the frictionless curve to position B. At point B, a frictional force opposes the block and brings it to a stop 2.5 m past B. What is the coefficient of kinetic friction of the surface past B. [k = 0.40] A 1m B Page 26 20. A rope exerts a force F displacing an object x in time t. Show that power may be expressed P = F v where v is the object’s velocity. 21. A pile driver drops a 500 kg mass from a 5 m height. If the pile is driven 20 cm into the ground as a result of each impact, what is the average force on the pile? a. [127000 N] 22. A ball is dropped from 1 m and loses 10% of its energy when it bounces. a. To what height will it rise after it bounces? b. How many bounces does it make? 23. A 200 N force lifts a 15 kg object initially at rest to an 8 m height. What is the speed of the object at this height? [7.5 m/s] 24. With what velocity will the 12 kg block strike the ground? 12kg 4kg 25. A ball is swung in a vertical circle of radius 80 cm as slowly as possible without the string going slack. If the total energy remains constant, find the speed of the ball: a. At the top of the circle. [2.8 m/s] b. At the bottom of the circle. [6.28 m/s] c. When the string is horizontal. [4.85 m/s] 26. A 1 kg block is forced against a horizontal spring with spring constant 100 N/m. If the spring is compressed 0.2 m and the block slides 0.8 m after leaving the spring across a rough horizontal surface, what is the coefficient of friction of the surface? 27. An 8kg projectile is shot from a mortar with muzzle velocity of 300 m/s at an angle of 45 o. The angle is then increased to 90o. a. What is the maximum height reached by the projectile in each case? [2296 m. 4592 m] b. Show that the total energy at the top of the trajectory is the same for each. [360,000 J] c. Find the height reached by the projectile fired from a 300 angle. [1148 m] 28. A black ball moving at 30 m/s collides with a white ball of equal mass. The white ball is deflected 450 below the horizontal with some velocity. The black ball is deflected with some velocity 300 above the horizontal. a. What are their respective velocities after the collision? b. Is this a perfectly elastic collision? 29. A 600 g stationary body is struck by a 400 g body moving at 125 cm/s. After the collision, the 400g body is moving at 100cm/s, 370 above the horizontal. a. What is the magnitude and direction of the 600 g body's velocity? [50cm/s at 53.10 below the horizontal] b. Is this a perfectly elastic collision? [No] 30. A ball traveling at a velocity VO impacts elastically with an identical stationary ball. After the impact, the first ball moves with a speed V1 at an angle 1 above the horizontal, while the second ball moves at speed V2 at an angle 2 below the horizontal. Prove that for a perfectly elastic collision: 1 + 2 = 90o 31. A stationary bowling ball is struck by another ball of equal mass traveling at 4 m/s. After the perfectly elastic collision, the incident ball moves off at a 250 angle to its original path. Find the velocity (magnitude and direction) of both balls after the collision. [3.63m/s at 250,1.69m/s at -65o] Page 27 Momentum and Impulse 1. An impulse of 7.5104 Ns stops a car in 0.10 seconds. a. What is the average force stopping the car? [7.5105 N] b. If the time is tripled, what is the new stopping force? [2.5105 N] 2. A loaded eighteen-wheeler is stopped by a frictional force of 2105 N in 50 seconds. a. What force is needed to stop the truck in half that time? b. How much time does it take the truck to stop if the force is only 1105 N? 3. A 0.60 kg basketball strikes the floor at 6 m/s and rebounds at 5.2 m/s. If it is in contact with the floor for 0.12 seconds, what is the average force on the ball? [56 N] 4. A 170 g softball is traveling at 30m/s when caught. If the force of the glove on the ball is 500 N, what is the time it took the ball to stop? 5. A 1.6105 kg aircraft needs to achieve a speed of 870 km/hr. If the engines can provide 3.4105 N of thrust, how long will it take the aircraft to achieve this speed? [113.7 sec] 6. A 1,000 kg motorcycle strikes a parked car at 30 km/hr and comes to a complete stop in 0.15 seconds. What is the average stopping force of the car on the bike? 7. A 0.16 kg baseball thrown at 40 m/s is hit directly back in the opposite direction at 55 m/s. a. What is the impulse imparted to the ball by the bat? [-15.2 kg·m/s] b. If the ball and bat are in contact for 210-3 seconds, what is the average force of the bat on the ball? [-7600 N] 8. An 80 N force accelerates a 5 kg body from 2 m/s to 8 m/s. a. What is the impulse acting? b. What is the time that this force is applied? 9. A person will receive serious chest injury in collisions from shoulder straps if the force exceeds 1.6104 N. If an 80 kg person is initially moving at 16 m/s and stops, find: a. The minimum safe stopping time. [0.08 sec] b. The minimum safe stopping distance. [0.64 m] 10. An impulse of 150 Ns is required to stop a person’s head in a car collision. If the face is in contact with the steering wheel for 0.02 seconds: a. What is the force on the cheekbone? b. If 900 N fractures the cheekbone, how long will it be in contact with the steering wheel in order to fracture? 11. An 80 kg man leaps from a burning building into a net, which stops him over a distance of 1 m. If he entered the net at 24 m/s, what is the average force of the net on him? [23,000 N] 12. A 0.06 kg tennis ball strikes a racket at 10 m/s and rebounds in the opposite direction at 20 m/s. If it is in contact for 0.01 seconds, what is the average force of the racket on the ball? 13. A cheekbone will fracture if subjected to 900 N of force lasting 6 ms or longer. a. What change in velocity is needed for a 0.11 kg hockey puck to provide this force? [49.1 m/s] b. If a goalie’s face mask doubles the impact time, by how much does this change the force? [450 N] 14. A 1.25 g bullet traveling at 300 m/s strikes an apple and exits the opposite side at 290 m/s. If the bullet is contact with the apple for 0.001 seconds, what is the force of the apple on the bullet? 15. An 80 kg person is standing stiff-legged in a free falling elevator. The elevator strikes a shock absorber traveling at 20 m/s. In order to avoid injury, the person should not experience more than 4104 N. What is the minimum stopping time and distance to save this poor soul? [0.04 s, -0.4 m] 16. What is the momentum of a 1104 kg truck moving at 20 m/s? 17. How fast does a 5,000 kg truck need to go to have the same momentum as the truck in the problem above? [40 m/s] 18. A 0.055 kg golf ball leaves the tee at 50 m/s. What is its change in momentum? 19. A 0.145 kg baseball traveling at 35 m/s rebound off a bat at 40 m/s in the opposite direction. What is the ball’s change in momentum? [-10.875 kg·m/s] Page 28 20. A 3 kg gun fires a 5g bullet in 300 m/s. If the gun is mounted on an air-track where the coefficient of friction is zero, what is the rifle’s recoil velocity? 21. A 10 kg sled carries a 30 kg person at 6 m/s northward. This person jumps off the back of the sled and the sled moves in a northern direction at 20 m/s. What is the velocity of the person the instant after leaving the sled? [1.33 m/s] 22. A hunter can fire a 60 g bullet at 900 m/s. If a 40 kg leopard runs at him at 10 m/s, how many bullets will it take to stop him cold in his tracks? (Hint: Integer) 23. A 50 kg girl throws a 7kg medicine ball at 10 m/s to a 40 kg boy. If both are on a frictionless frozen lake, what are both children’s recoil velocities? [-1.4 m/s, 1.49 m/s] 24. A 65 kg boy and a 40 kg girl, both wearing skates, face each other at rest. The boy pushes the girl, sending her off at 4 m/s. What is the boy’s velocity? 25. A 200 kg lifeboat carries two people, 50 kg and 80 kg respectively. If each dive off opposite ends of the boat at 4 m/s, what is the velocity of the boat immediately after? [0.6 m/s in same direction as 50 kg person] 26. If all 240 million people in the US, each having an average mass of 60 kg, all jump up simultaneously at 6m/s, what would be the approximate recoil velocity of the earth? (mearth = 6 1024 kg) 27. An 80 g arrow enters an apple at 50 m/s and exits at 40 m/s. If the apple has a 100 g mass, what is the apple’s final velocity? [8 m/s] 28. A cannon is mounted on the back of an ice sled. Together, the cannon and sled have a mass of 4,000 kg. If a 50 kg shell is now loaded into the cannon and fired horizontally at 150 m/s, what is the speed of the sled after firing the cannon? 29. A 40 kg child, standing on a newly waxed floor, throws a 2 kg stone with a speed of 5 m/s. What is the child’s recoil velocity? [-0.25 m/s] 30. A 1.6 10-27 kg neutron traveling at 105 km/s collides with a 3.34 10-27 kg deuteron and combine to form a triton. What is the speed of this composite particle? 31. A 2,000 kg meteor moving at 80 m/s collides with the earth. a. What is the earth’s recoil speed? [2.67 10-20 m/s] b. What would the recoil speed be if it were the moon hitting at this same speed? [0.973 m/s] 32. A 176 g golf club head strikes a 46 g golf ball at 45 m/s and sends the ball flying at 65 m/s. What is the club head’s final speed? 33. A 0.5 kg object moving at 4 m/s embeds in a 4 kg lump of clay moving in the same direction at 1 m/s. What is the speed of the combined masses? [1.33 m/s] 34. A 500 kg car traveling east at 10 m/s has a head-on inelastic collision with a 200 kg car traveling at 25 m/s. What are their velocities after the collision? 35. A 2 104 kg railroad car moving at 5 m/s collides and couples with three other identical cars moving in the same direction at 2 m/s. What is the speed of the combined masses after the collision? [2.75 m/s] Honors Supplement 1. A BMW is equipped with an impact absorbing bumper designed to stop a car of mass m moving with initial speed V o. If the bumper exerts force F' on the car as it retracts a distance x during a collision, show that these are related by the equation: F = (mVo2) / (2x) 2. A 0.40 kg beach ball, flying east at 8 m/s, is bumped north by a person's hand. This 84 N force acted on the ball for 0.010 seconds. What is the magnitude and direction of the ball after it is bumped? 3. Water, flowing from a hose at the rate of 2 l/s and a speed of 8 m/s, strikes a person. If the water loses all momentum upon impact, what is the force felt by the person? [16 N] 4. A howitzer has a 7.6 m barrel which fires a 65 kg projectile 0.2 m in diameter at 400 m/s. What is the average force on the projectile in the barrel? 5. A 0.3kg ball having a velocity 5i m/s collides with a wall and rebounds with a velocity-3j m/s. a. What is its change in momentum? [-2.4i kg·m/s] b. If the ball is in contact with the wall for 5 10-3 seconds, what is the average force of the wall on the ball? [-480i N] Page 29 6. A 3 kg ball has a velocity (2i - 4j) m/s. What is the magnitude and direction of its momentum? 7. A 3kg sphere moves with velocity 5)m/s. After 5 seconds, it is moving along with velocity 3; m/s. a. What is the impulse given to the sphere? [(9i - 15j) kg·m/s] b. What is the average force exerted over this 5 seconds? [(1.8i - 3j) N] 8. A 20 kg shell, fired at a 60o angle with a speed of 400 m/s, explodes at the highest point of its trajectory into two fragments of equal mass. One of the fragments falls vertically with zero initial speed; how far from the original point of firing does the other fragment strike the ground? 9. A 6 g bullet is fired into a 2 kg block at on the edge of a 1 m high table. if the bullet remains in the block and together they land 2 m horizontally from the edge of the table, what is the initial speed of the bullet? [1.48 103 m/s] 10. A 200 g cart moves on a frictionless air-track at 30 m/s. A 50 g piece of clay is dropped vertically onto the cart where is sticks. a. What is the speed of the system after the collision? b. The clay now has no vertical momentum. Does this violate the law of the conservation of momentum? Why or why not? 11. A stationary bomb explodes into three equal fragments. Two of which have the velocities (3i + 2j) m/s and (-i - 3j) m/s. What is the velocity of the third? [(-2i + j) m/s] 12. A 2kg ball is moving at 5i m/s and collides inelastically with a 3kg ball traveling at -3j m/s. What is the velocity of the new mass? 13. A shell moving al 10 km/s separates into two identical pieces that continue to move in the same direction, if one piece moves at 4 km/s, what is the speed of the other fragment? [16,000 m/s] 14. The same shell in the previous problem again breaks up in to two fragments of equal mass. One fragment travels at 4 km/s in the opposite direction to the initial direction of the shell. What is the velocity of the other fragment? 15. A mortar can fire a shell a maximum distance of 2 km. On one such firing, the shell explodes at the top of its trajectory into two equal fragments, one of which lands on the cannon. How far from the cannon does the other land? [4 km] 16. A black 1 kg billiard ball moving al 3 m/s strikes a pink 1 kg stationary ball. After the collision, the black ball moves at a 37 o angle above the horizontal, and the pink ball moves off at a 53 o angle below the horizontal. Find the magnitude of their velocities. 17. A stationary marble is struck by another identical marble traveling at 5m/s. The incident ball moves off at a 40 o angle above its original path and the other ball moves off at a 30o angle below the original path. Find the magnitude of the velocities for both marbles. [2.66 m/s, 3.42 m/s] 18. A 12 kg clay ball moving north at 3 m/s inelastically collides with an 18 kg clay ball moving east at 2 m/s. What is the magnitude and direction of the velocity of the composite mass? 19. A 3kg mass, moving al a 135o angle towards the origin of a Cartesian axis at 4 m/s, collides inelastically with a 2 kg mass moving at 2 m/s at a 20o angle toward the origin. What is the velocity of the new composite mass? [2.19 m/s at 115 o] Page 30 Energy Transfer (Heat) Substance Solids Aluminum Brass Copper Glass Gold Human Body Ice/steam Iron/Steel Lead Silver Liquids Ammonia Benzene Ethyl Alcohol Glycerin Mercury Nitrogen Oxygen Water Latent heat of Latent heat of fusion Lf vaporization Lv (J/kg) (J/kg) Specific Heat J/(kgoC) Specific Heat Kcal/(kgoC) Melting Point (oC) Boiling point (oC) 900 384 387 840 129 3500 2090/2010 452 128 235 0.215 660.3 900 1083 2467 4X105 2566 2.070X105 47.30 X105 1063 2808 6.28X104 17.20 X105 327.3 1750 2.320X104 8.590X105 -77.8 5.5 -114.4 -33.4 80.1 78.3 3.320X105 1.260 X105 1.080X105 13.70X105 3.940 X105 8.550X105 -38.9 -210 -218.8 0 356.6 -195.8 -183 100 1.140X105 2.570X104 1.390 X104 33.50 X104 2.960 X105 2.000 X105 2.130 X105 22.60 X105 1740 2450 2410 139 2042 1669 4186 0.0924 0.2 0.83 0.478 0.108 0.0305 0.0562 0.415 0.586 0.576 0.0333 1.000 see water 1. A comfortable temperature for most people is 24 oC. What is this temperature in a. Fahrenheit [75C] b. Kelvin? [297C] 2. Dermatologists often remove pre-cancerous skin lesions by freezing them with liquid nitrogen, which has a temperature of 77 oK. a. What is this temperature on the Celsius scale? b. What is this temperature on the Fahrenheit scale? 3. A temperature of absolute zero occurs at –273.15 oC. What is this temperature in degrees Fahrenheit? [-459.67] 4. How much heat must be added to raise 250g of water at 24oC to it’s boiling point? 5. The addition of 1.3x105 J of energy raises the temperature of a block of aluminum from 345 oK to 500 oK. Calculate the mass of the block. [.932kg] 6. If 25g of water at a temperature of 10 oC is mixed with 40g of water at 80 oC, what is the final temperature of the mixture? 7. A piece of brass with a mass of 1750g is heated. The brass is dropped into a 250 g aluminum calorimeter cup containing 600g of water. The temperature goes from 15.0 oC to 80 oC. What was the initial temperature of the brass? [344.7 oC] 8. Determine the specific heat of a material if 5640J of energy will raise the temperature of 50g amount of the material from a temperature of 9.0C to a temperature of 86.0C. Page 31 9. A 350g glass beaker contains 500g of water at a temperature of 10.0C. If 400g of ethyl alcohol at 35C if subsequently poured into the beaker and the water and alcohol mixture is thoroughly stirred, what is its equilibrium temperature? [17.28C] 10. An ice chest at a beach party contains 12 cans of soda at 5.0C. Each can of soda has a mass of 0.35kg and a specific heat capacity of 3800J/kgC. Someone adds a 6.5kg watermelon at 27C to the chest. The specific heat capacity of watermelon is nearly the same as that of water. Ignore the specific heat capacity of the chest and determine the final temperature of T of the soda and the watermelon. 11. Blood can carry excess energy from the interior to the surface of the body, where the energy is dispersed in a number of ways. While a person is exercising, 0.6kg of blood flows to the surface of the body and releases 2000J of energy. The blood arriving at the surface has the temperature of the body interior, 37C. Assuming that blood has the same specific heat capacity as water, determine the temperature of the blood that leaves the surface and returns to the interior. [36.2C] 12. At a fabrication plant, a hot metal forging has a mass of 75kg and a specific heat capacity of 430J/kgC. To harden it, the forging is quenched by immersion in 710kg of oil that has a temperature of 32C and a specific heat capacity of 2700J/kgC. The final temperature of the oil and forging at thermal equilibrium is 47C. Assuming that heat flows only between the forging and the oil, determine the initial temperature of the forging. 13. Heat is supplied to a 0.85kg copper pot at the rate of 203 joules per second. How much time does it take to raise the temperature of the pot from 21C to 95C if the pot: a. is empty [120 sec.] b. contains .200kg of water? [425 sec.] 14. When resting, a person has a metabolic rate of about 4.2 X 10 5 joules per hour. The person is submerged neck-deep into a tub containing 1 EE 3 kg of water at 527C. If the heat from the person goes only into the water, find the water temperature after half and hour. 15. When you take a bath, how many kg of hot water at 49C must you mix with cold water at 13C so that the temperature of the bath id 36C? The total mass of water is 191kg. Ignore any heat flow between the water and its external surroundings. [121kg] 16. An ice cube tray holds 0.39kg of water at 0C. How much heat must a freezer remove to make ice cubes at 0C? 17. To what temperature must a 2270g-iron ball be heated so that it can completely melt a 1150g piece of ice at 0C? [375.47C] 18. A 500g aluminum block is heated to 350C. How many grams of ice at 0C will the aluminum block melt as it cools? 19. How many joules of heat are released by 50g of steam at 100C when it condenses? [1.13x105 J] 20. Calculate the number of joules evolved when 4kg of steam at a temperature of 100C is condensed, cooled, and then changed to ice at 0C. 21. What is the final temperature attained by the addition of 11.4g of steam at 100C to 681g of water at a temperature of 25C in an aluminum calorimeter having a mass of 182g? [34.6C] 22. A calorimeter, specific heat 500J/kgC, mass 200g, contains 300g of water at 40C. If 50g of ice at 0C is dropped into the water and stirred, the temperature of the mixture when the ice has melted is 23.8C. Calculate the heat of fusion of ice. 23. A block of silver, with a mass of 500.0g, temperature 100C, is out in a calorimeter with 300g of water, temperature 30C. The mass of the calorimeter is 50.0g, and its specific heat is 500 J/KgC. A 50.0g mass of ice at –10C is out in the calorimeter. Calculate the final temperature. [20.1C] 24. Heat (5.64x105 J) is added to 1.7 kg of a substance in listed in the table. The substance completely melts without any change in temperature. What is the substance? 25. How much heat is added to 0.45 kg of aluminum to change it from a solid at 130C to a liquid at 660C (its melting point)? [394,650 J] 26. A 10.0kg block of ice has a temperature of -10C. The pressure is one atmosphere. The block absorbs 4.11x10 6 Joules of heat. What is the final temperature of the liquid? 27. Supposed the amount of heat removed when 3.0 kg of water freezes at 0C is removed from ethyl alcohol at its freezing point -114C. How many kilograms of ethyl alcohol would freeze? [9.3kg] 28. A woman finds the front windshield of her car covered with ice at -12C. The ice has a thickness of 4.5x10-4 m, and an area of1.25 m2. The density of is ice 917 kg/m3. How much heat is required to melt the ice? Page 32 29. Liquid nitrogen boils at a chilly –195.8C when the pressure is one atmosphere. A silver coin with a 1.5x10 -2 kg mass at a temperature of 25C is dropped into the liquid. What mass of liquid nitrogen boils off as the coin cools to –195.8C? [3.9x10-3] 30. Ice at -10C and steam at 130C are brought together at atmospheric pressure in a perfectly insulated container. After thermal equilibrium is reached, the liquid phase at 50C is present. Ignoring the container and the equilibrium vapor pressure of the liquid at 50C, find the ratio of the mass of steam to the mass of ice Note: Honors Supplement Honors Supplement 1. A 5.0g lead bullet traveling at 300m/s is stopped by a large tree. IF half the kinetic energy of the bullet is transformed into internal energy and remains with the bullet while the other half is transmitted to the tree, what is the increase in temperature of the bullet? [176 0C] 2. A 1.5kg copper block is given an initial speed of 3.0m/s on a rough horizontal surface. Because of friction, the block finally comes to rest. a. If the block absorbs 85% of its initial kinetic energy as internal energy, calculate its increase in temperature. b. What happens to the remaining energy? 3. A 200g aluminum cup contains 800g of water in thermal equilibrium at 800C. The combination of cup and water is cooled uniformly so that the temperature decreases by 1.50C per minute. At what rate is heat energy being removed? Express your answer in watts. [88.2W] 4. Water at the top of Niagara Falls has a temperature of 100C. If it falls a distance of 50.0m and all of its potential energy goes into heating the water, calculate the temperature of the water at the bottom of the falls. 5. If 200g of water is contained in a 300g aluminum vessel at 100C and an additional 100g of water at 1000C is poured into the container, what is the final equilibrium temperature of the mixture. [35 0C] 6. A 100g aluminum calorimeter contains 250g of water. The two substances are in thermal equilibrium at 10 0C. Two metallic blocks are placed in the water. One is a 50g piece of copper at 80 0C. The other sample has a mass of 70g and is originally at a temperature of 1000C. The entire system stabilizes at a final temperature of 20 0C. Determine the specific heat of the unknown second sample. 7. A 100g cube of ice at 00C is dropped into 1.0kg of water that is originally at 80 0C. What is the final temperature of the water after the ice has melted. [65.50C] 8. How much heat is required to change a 40g ice cube from ice at -100C to steam at 1100C. 9. What mass of steam that is initially at 1200C is needed to warm 350g of water and its 300g aluminum container from 20 0C to500C? [21g] 10. A 75kg cross-country skier moves across snow such that the coefficient of friction between skis and snow is 0.20. Assume all the snow beneath his skis is at 00C and that all the internal energy generated by friction is added to snow which sticks to his skis until melted. How far would he have to ski to melt 1.0kg of snow? 11. A 40g block of ice is cooled to -780C. It is added to 560g of water in an 80g copper calorimeter at a temperature of 25 0C. Determine the final temperature. (if not all the ice melts, determine how much ice is left.) Remember that the ice must first warm to 0 0C, melt, and then continuer warming as water. The specific heat of ice is 2090J/kg0C. [15.60C] 12. A beaker of water sits in the sun until it reaches an equilibrium temperature of 30 0C. The beaker is made of 100g of aluminum and contains 180g of water. In an attempt to cool this system, 100g of ice at 00C is added to the water. a. Determine the final temperature. If Tf = 0, determine how much ice remains.[24g] b. Repeat this for 50g of ice. [8o] 13. Steam at 1000C is added to ice at 00C. a. Find the amount of ice melted and the final temperature when the mass of steam is 10g and the mass of ice is 50g. [40 0C] b. Repeat with steam of mass 1.0g and ice of mass 50g? [8g] 14. An aluminum cup contains 225g of water at 270C. A 400g sample of silver at an initial temperature of 87 0C is placed in the water. A 40g copper stirrer is used to stir the mixture until it reaches its final equilibrium temperature of 32 0C. Calculate the mass of the aluminum cup. 15. Ice at -10C and steam at 130C are brought together at atmospheric pressure in a perfectly insulated container. After thermal equilibrium is reached, the liquid is at 50C. Ignoring the container and the equilibrium vapor pressure of the liquid, find the ratio of the mass of steam to the mass of ice. [.223] Page 33 Periodic Motion 1. A spring with 1200 N/m spring constant has a 55 gram mass at its end. If the total a. energy present in the system is 6J: b. what is the amplitude of vibration? [0.1 m] c. what is the maximum velocity of the mass? [14.8 m/s] d. what is the speed of the mass when it is at a position of one-half the amplitude? [12.8m/s] 2. A 15N force applied to a mass attached to a spring causes the mass to move 0.06m from its equilibrium position. When the force is removed, the mass undergoes simple harmonic motion. a. Find the spring constant of the spring. b. What is the total energy of the system? c. What is the maximum velocity of the 0.5 kg mass? 3. A spring with a 2.5 x 104 N/m spring constant has a 1.4 kg mass at its end. If the amplitude of vibration is 0.03m: a. what is the total energy of the oscillator? [11.25 J] b. what is the maximum speed of the mass? [4 m/s] c. If the energy is tripled, what is the new amplitude? [0.052 m] 4. A harmonic oscillator is made using a body of mass 0.5 kg and a spring. The system is found to have a period of 0.2 seconds. What is the spring constant? 5. A 30N force stretches a spring 15 centimeters. What mass must be attached to the spring so that the system oscillates with a period of 0.785 seconds? [3.13 kg] 6. A body of mass 2 kg is suspended from a spring of negligible mass, and is found to stretch the spring 20 centimeters. a. What is the spring constant? b. What is the period if the mass is pulled and released? c. What is the period if the mass is 4 kg? 7. A 1.6 kg mass attached to a spring undergoes simple harmonic motion of amplitude 0.12 m and has an energy of 72 J. a. What is the spring constant of the spring? [10000N/m] b. What is the frequency of vibration? [12.6 Hz] 8. A 1.2 kg block sliding at 6m/s on a frictionless surface runs into and sticks to a spring. The spring is compressed 0.1 m before stopping the block. a. Find the total energy of the system. b. Find the spring constant of the spring. c. Find frequency of vibration. 9. The Sears Tower in Chicago has a mass of about 5 x 10 8 kg and sways back and forth at a frequency of about 0.1 Hz. a. What is the spring constant of the Tower? [197.4 x 10 6 N/m] b. If a gust of the wind hits the building with a 4 x 10 6 N force, by how much is the top of the building displaced? [0.02m] 10. Find the length of a simple pendulum whose period is exactly 1 second at a point on earth where g = 9.80m/s2. 11. A certain pendulum on earth has a period of 2 seconds. What is its period on the moon, where g = 1.7 m/s2? [4.8 sec] 12. A geologist finds that the frequency of a pendulum is 0.3204 Hz at a location where acceleration due to gravity is 9.80 m/s2. What is the value of g at a location where the frequency is 0.3196 Hz? (Assume the values given are exact, do not round anything.) 13. What is the value of g on a planet where a simple pendulum 40 centimeters long vibrates 100 times in 4 minutes? [2.74 m/s2] Page 34 Honors Supplement 1. A 0.12 kg calculator is to be tested for its ability to withstand vibration and acceleration. It is strapped to a cart of negligible mass at the end of the spring. The vibration amplitude is to be 5 centimeters. When the cart is released, the acceleration is 10 g. a. What is the spring constant of the spring? [470.4 N/m] b. Find the total energy of the system. [0.588 J] 2. A 5 gram bullet traveling horizontally at an unknown speed hits and embeds itself in a 0.195 kg block resting on a frictionless table. The block slides into and compresses a spring with a 180 N/m spring constant a distance of 0.1m before stopping the block and bullet. (HINT: there is an inelastic collision.) 3. A string under tension 1080 N, of mass per unit length 0.003 kg/m, has many resonant frequencies. One is 480 Hz and the next higher frequency is 600 Hz. How long is the string? [2.5 m] 4. A body executing simple harmonic motion has an equation of motion: x = (1/3 m) * cos(8 rad/s * t). a. What is the amplitude? b. What is the angular frequency? c. How long does it take the body to move a position x = 1/2Amplitude? 5. y = -8m + 10m * sin (5( + 6 )) a. Find the period (in degrees). b. Find the amplitude. c. What is the phase displacement? d. What is the vertical displacement? e. Sketch the graph. Label all critical values. 6. (See graph above.) a. Find the period (in degrees). b. Find the amplitude. c. What is the vertical displacement? d. What is the phase displacement? e. Write its equation of motion. 7. By plugging in values for t, graph the following functions, where = b/2m, wo = (k/m) A = 1 m, k = 1 N/m, and m = 1kg. o a. -t 2 2 1/2 x(t) = A((e )/w*sin(wt)), where w = (wo - ) and b = 0.01 kg/s. 1/2 Page 35 Waves on Strings 1. A 2m string is vibrating in 5 segments. a. What is the wavelength? [0.8m] b. How many nodes are present? How many antinodes are present? 2. A physics student observes that a stretched string vibrates with a frequency of 30 Hz. in its are 60 centimeters apart. The string has a mass of 30 grams. a. What is the speed of the wave in the string? b. What is the tension in the string? 3. A cellist tunes the A-string of her instrument to a fundamental frequency of 220 Hz. The vibrating portion of the string is 68 centimeters long and has a mass of 1.29 grams. With what tension must it be stretched? [169.8 N] 4. A clothesline of total mass 0.9 kg is stretched between posts 10 m apart. It is observed that when one pole is struck by a lawnmower, the transverse pulse reaches the other pole in 0.25 seconds. What is the tension of the rope? 5. To what tension must the a violinist adjust his A-string in order to tune its fundamental frequency to 440 Hz? The distance from the bridge to nut is 30 centimeters and the mass of the string is 2 grams. [464.6 N] 6. When the tension is 18N, a string 200 cm long has a fundamental frequency of 150 Hz. a. What is the mass of the string? b. With what tension must the string be stretched so that it vibrates in three segments at the same frequency? 7. A string 10 centimeters long has a mass of 4 x 10 kg and is stretched with the force of 4 N. a. Draw a diagram of the locations of the nodes and the antinodes for the string when it is vibrating in its next-to-the-lowest natural frequency. b. Find the frequency of this mode of vibration. [3162 Hz] 8. How far, and in what direction should a cellist move her finger to adjust and out-of-tune A-string from a fundamental 449 Hz to an intune fundamental 440 Hz? The string is 68 centimeters long and her finger is 20 cm from the nut. 9. A piano tuner stretches a steel piano string 50 centimeters long, of mass 5 grams, with a tension of 400 N. a. What is the frequency of its fundamental mode? [200 Hz] b. What is the number of the highest overtone that could be heard by a person who is capable of hearing frequencies up to 10000 Hz? [49th] fundamental mode when the supports -6 10. A banjo G-string is 0.69m long and has a fundamental frequency of 392 Hz. a. What is the speed of the wave on the string? b. What are the next three resonance frequencies? 11. How far from the end of the banjo string in the problem above must a fret be placed so that the fundamental frequency is increased to 490 Hz when the string is held down at the fret? [0.138 m] 12. A violin A-string 0.33 m long vibrates at a fundamental frequency of 440 Hz. How far from the end should your finger press the string against the finger board so that its decreased length causes it to vibrates at: a. five-fourths times the original frequency? b. four-thirds the original frequency? 13. A 5 m long rope of mass 0.4 kg is secured at one end and stretched with a 120 N tension at the other end. The rope is vibrating in three segments. What is the frequency? [11.6 Hz] 14. A telephone lineman is told to stretch the wire between poles to a tension of about 800 N. Not having a tension scale, the guy thinks back to the good ole’ McC Physics. He decides to measure the speed of a pulse created in the wire when he hits it with a wrench. The pulse travels from one pole 60 m to another pole and back again in 2.6 seconds. The 60 m wire has a mass of 15 kg. Should the wire be tightened or loosened? Explain. Page 36 Open and Closed Pipes (For the following problems use 340 m/s as the speed of sound.) 15. A clarinet (a closed pipe) has an effective bore length of 0.6m. Calculate the first three standing wave frequencies of the clarinet when all the finger holes are closed. [142 Hz, 425 Hz, 708 Hz] 16. Calculate the first three standing wave frequencies of: a. an open pipe 40 centimeters long. b. a closed pipe 40 centimeters long. 17. The 2779 m Brooklyn-Battery Tunnel, connecting Brooklyn and Manhattan, is one of the world’s longest underwater car tunnels. a. Calculate its fundamental frequency of vibration. [0.061 Hz] b. What harmonic must be excited so that it resonates in the audible range of 20 Hz? [327th] 18. A person hums in a well (closed) and finds strong consecutive resonance frequencies of 60 Hz, 100 Hz, and 140 Hz. a. Explain why these cannot possibly be the first three consecutive resonance frequencies. b. What is the fundamental frequency of the well? c. How deep is the well? 19. The lowest three standing wave frequencies of an organ pipe are 120 Hz, 360 Hz, and 600 Hz. a. Is the pipe open or closed? Explain your answer. b. How long is the pipe? [0.708m] c. Calculate the frequencies of the first two harmonics in a pipe of the same length but of the other type than that of part (a). [240 Hz, 480 Hz] 20. A wooden flute, open at both ends, is 0.48 m long. a. Calculate its fundamental vibration frequency. b. How far from one end should a finger hole be placed to produce a sound whose frequency is four-thirds that calculated in part (a)? 21. People can hear sounds ranging in the frequency from about 20 Hz to 20000 Hz. Calculate the wavelengths of these two limits. [17 m, 0.017 m] 5 22. A dolphin has a sonar system that emits sounds having a frequency of 2 x 10 Hz. What is the wavelength of the sound if the speed of sound in sea water is 1530 m/s? 8 23. Radio waves travel at the speed of 1.7 x 10 m/s through the ice. A radio wave pulse sent into the Antarctic ice reflects off the earth at -5 the bottom and returns to the surface in 3.29 x 10 seconds. How deep is the ice? [2796.5 m] 24. A flash of lightening is seen, and 2.4 seconds later thunder is heard coming from the same location. a. Why is there a delay between the lightening and the thunder? b. How far away did the lightening flash occur? Intensity, Intensity Level 2 25. The sound intensity of a gas station next to a turnpike averages 0.001 W/m . The owner decides to collect this energy and convert it to thermal energy for heating his building. a. What is the length of a side of a square sound collector that is needed to provide thermal energy at a rate of 500W. Assume the conversion from sound to thermal energy is 100% efficient. [707 m] b. Is this practical? Explain. 2 26. The sound intensity three miles from the take off point of a Concord supersonic jet is 0.6 W/m . What area sound collector would absorb enough energy to run a 40 Watt light bulb? -8 2 27. In music, a very soft sound called “ triple piano” (ppp) has an intensity of 1 x 10 W/m . A very loud sound called a “triple forte” (fff) -2 2 has an intensity of 1 x 10 W/m . a. What are the intensity levels of these two sounds? [ 40dB, 100dB] b. How many times louder is the triple forte than the triple piano? Page 37 28. Convert the following intensities to intensity levels: -8 2 a. 3 x 10 W/m in a quiet living room.] -5 2 b. 2 x 10 W/m inside a car.] -3 2 c. 6 x 10 W/m near a passing truck. 2 d. 0.5 W/m at a construction site where a jackhammer is operating. 29. Calculate the change in intensity level when a sound intensity is increased by: a. a factor of 8 [9dB] b. a factor of 80 [19dB] c. a factor of 800 [29dB] 30. One violin creates a sound whose intensity level is 60dB. Find the intensity level of 16 violins, each playing at this intensity. 31. A swarm of 10000 locusts causes a sound of intensity level 75dB.[35dB] a. Find the intensity level of one locust. [35 dB] b. How many times louder is the swarm than a single locust?[16X] 32. The average intensity level of a person’s voice is 58 dB. A microphone and amplification system increases the intensity level to 70 dB. By what factor did the system increase the sound intensity? 33. Two separate sounds are incident onto the ear. The intensity level of one sound is 80 dB while the other is 85 dB. What is the intensity level of the two sounds together? [86 dB] 2 34. The average intensity level of sound near a busy intersection is 86 dB. Find the amount of sound energy incident on a person’s 0.2 cm eardrum in 8 hours. 35. What is the difference in the intensity level between the sound from 6 cheerleaders and the sound of 6000 cheering fans? [30dB] a. How many times louder are the fans than the cheerleaders? 2 36. A stereo with the intensity of 40 W/m loses 3 dB when the volume is turned down. What is the new (smaller) intensity? 37. 37. By soundproofing a living room near an airport, a noise reduction of 43 dB is obtained. How many times greater was the intensity before the soundproofing? [19953] Doppler Effect 38. A car horn vibrates at a frequency of 250 Hz. a. Find the frequency that a stationary observer hears as the car approaches at the speed of 20 m/s. b. Find the frequency that a stationary observer hears as the car departs at 20 m/s. If the car is stationary, what frequency is heard by an observer: c. approaching the car at 20 m/s. d. departing form the car at 20 m/s. 39. A car drives at a speed of 25 m/s along a road parallel to a railroad track. A train traveling at 15 m/s sounds a horn that vibrates at 300 Hz. a. If the train and the car are moving toward each other, what frequency of sound is heard by a person in the car? [337 Hz] b. If the train and car are moving away from each other, what frequency of sound is heard in the car? [266 Hz] 40. A whistle with the frequency 400 Hz moves at a speed 20 m/s in a horizontal circle at the end of a rotating string. Find: a. the highest frequency heard by a person riding a bicycle at a speed 10 m/s toward the whistle. b. the lowest frequency heard by that person. 5 41. A bat emits short pulses of sound at a frequency of 3.9 x 10 Hz. As the bat swoops toward a flat wall at a speed of 30 m/s, this sound is reflected from the wall back to the bat. 5 a. What is the frequency of sound incident on the wall? [4.28 x 10 Hz] b. What frequency of sound does the bat hear coming from the wall? Consider the wall as a sound source at the frequency 5 calculated in part (a). [4.7 x 10 Hz] Page 38 Light o 1. Two mirrors are oriented at right angles. A ray strikes the horizontal mirror at a angle of 65 , reflects from it, and then hits the vertical mirror. o a. Find the angle of incidence at the vertical mirror. You must show a correctly labeled diagram for credit. [25 ] b. From your diagram, how do you know that the ray leaving the vertical mirror is parallel to its original direction? 2. Find the index of refraction of a sugar solution through which light travels at 2.06 x 10 8 m/s. 3. Find the speed of light in blood whose refractive index is 1.35. [2.2 x 10 m/s] 4. Light travels 0.7 times as fast in Jell-O as it does in a vacuum. a. Find the index of refraction of Jell-O. b. If the light travels 1.1 times faster in bouillon soup than in Jell-O, what is the index of refraction of the soup? 5. The index of refraction for radio waves passing through ice is 1.305. If the ice is 1860 m thick, how much time is needed for a radio wave pulse to travel for the surface of the ice sheet to the bottom and back to the top again?[1.6X10 -5s] 6. Two light pulses travel side by side one in a vacuum and one in the air. (Note: use the most precise values for velocity that you have.) a. Which pulse travels faster. Explain your answer. b. After the slower one has moved 1600 m, how far ahead of the slower pulse is the faster pulse? 7. A water molecule vibrating at a frequency of 9.66 x 10 Hz in a glass of water emits infrared radiation. -6 a. Find the wavelength of the wave when in the water. [2.328 x 10 m] -6 b. Find the wavelength after it leaves the water and is in the air. [3.106 x 10 m] c. What is the effect on the wavelength of the wave as it passed from water to the air? [lengthened] 8. Light passes from air into a 25% sugar solution (n = 1.3723) at an incident angle of 35 . a. Find the angle of the refracted wave. o b. Light passes from ethyl alcohol (n = 1.3617) to air at an incident angle of 12 . Find the angle of the refracted wave in the air. c. Draw pictures of each situation showing the interface between the media, the normal line, the incident, reflected, and refracted rays, and the angles of these rays relative to the normal line. Be neat and make the diagrams large. 9. Light passes from glass with index of refraction 1.58 into water. The angle of the refracted ray in the water is 58 . o a. Find the angle of the incident ray at the glass-water interface. [45.68 ] o o b. A ray passing from air to cyclohexane is incident at 48 and has an angle of refraction of 31 . Find the index if refraction of the cyclohexane. [1.443] c. Draw pictures of each situation as requested in the above problem. 8 13 o o 10. Sound passes form limestone, where it moves at 4000 m/s, into another unknown material. The angle of incidence at the interface is o o 24 and the angle of refraction in the unknown material is 38 . a. Find the speed of sound in the unknown material. b. Draw a picture of this situation as requested in the above problem. 11. The eyes of a person standing at the edge of a 1.2 m deep swimming pool are 1.6 m above the surface of the water. Light coming from o a silver dollar at the bottom of a pool enters the person’s eyes at an angle of 37 from the horizontal. a. Draw a picture of this situation as requested in the above problem. b. Find the horizontal distance from the person to the dollar. [3 m] 12. Find the critical angle for light inside a diamond ( n = 2.42) incident on the air interface. Page 39 o 13. A scuba diver swimming underwater at night shines a beam of light so that it hits the water-air interface at an incident angle 52 . Will the light be seen by a person above the water? Explain your answer. 14. Find the index of refraction of a sugar solution for which the critical angle for the light traveling in the solution incident on the o interface with air is 42.5 . o o 15. Light is incident on the boundary between two media at an angle of 32 . If the refracted light makes an angle of 42 , what is the o critical angle for light incident on the same boundary. [52.4 ] 16. Rays of light are incident on a glass-air interface (see figure). a. Find the critical angle for total internal reflection if the index of the refraction for glass is 1.58. b. If there is a thin horizontal film of water on the glass (Figure B) will a ray incident on this glass-water interface at the critical angle found in part (a) be able to leave the glass? Explain your answer. c. If there is a thin horizontal film of water on a glass (Figure B) will a ray incident on this glass-water interface at the critical angle found in part (a) be able to leave the water? Explain your answer. 17. A fortuneteller looks into her silver surfaced glass ball whose radius is 10 centimeters and whose focal length is -5 centimeters. a. If her eye is 30 centimeters from the ball, where is the image of her eye? [-0.0429 m] b. If the eye is one centimeter in diameter, what is the height of the image? [0.00143 m] 3 5 18. The diameter of the moon is 3.5 x 10 kilometers and its distance from the earth is 3.8 x 10 kilometers. Find the position and size of the image formed by Hale Observatory reflection concave mirror, whose focal length is 16.5 m. 19. You are going to order a mirror from a scientific supply company. You want to use the mirror for shaving or makeup. The mirror should produce an image that is upright and magnified by a factor of 2 when held 15 centimeters from your face. a. What type of mirror should you buy? Why? (concave) b. What focal length should you buy? (0.3m) 20. You view your face in a converging mirror of focal length 20 centimeters. How far from the mirror should you put your face to form an image that is magnified by a factor of 1.5? 21. A camera with an 8.00 cm focal length lens is used to photograph a person that is 2.00 m tall. The height of the image on the film must be no greater than 3.50 cm. a. Calculate the closest distance the person can stand to the lens. (4.65m) b. For this object distance, where should the film be located from the lens? (0.0814 m) 22. A slide projector produces an inverted image on a screen that is 30 times larger than the view on the slide. The lens has a focal length of 12.0 cm. a. Calculate the distance of the slide from the lens. b. Calculate the distance of the screen from the lens. 23. Use ray diagrams to locate the images of the following objects: a. an object that is 6 cm from a converging lens of +4 cm focal length.[12cm] b. an object that is 8 cm from a diverging lens of -4 cm focal length.[-2.67cm] c. Calculate the image locations for both situations above using the thin lens equation. 24. A concave mirror has a focal length of 10.0 cm. What is its radius of curvature? Page 40 25. If the radius of a curved mirror is 8 cm, what is its focal length? (4 cm) 26. An object is placed 25.0 cm from a concave mirror whose focal length is 5.00 cm. Where is the image located? 27. An object 25.4 cm high is located 91.5 cm from a concave mirror having a focal length of 15.0 cm. a. Where is the image located? [17.94 cm] b. How high is it? [4.98 cm] 28. An object placed 50 cm from a spherical concave mirror gives a real image 33.3 cm from the mirror. a. What is the radius of the curvature of the mirror? b. If the image is 30.5 cm high, what is the height of the object? 29. A converging lens has a focal length of 20 cm. If it is placed 50 cm from an object, at what distance from the lens will the image be? [33.3 cm] 30. When an object 5 cm tall is placed 12 cm from a converging lens, an image is produced on the same side of the lens as the object but 61 cm away from the lens. a. What is the focal length of the lens? b. What is the size of the image? 31. For a lens or mirror of focal length 10 cm plot the following graphs. a. di vs do b. m vs do 32. For the lens (or mirror) of focal length -10 cm plot the graph of a. di vs do b. m vs do