* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1 Two ATP molecules each give a phosphate group to a glucose
Survey
Document related concepts
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Biosequestration wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
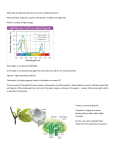
Chlorophyll molecule absorbs light energy Pair of electrons become raised to a higher energy level – excited – and leave the chlorophyll molecule As a result the chlorophyll molecule becomes ionised – photoionisation Electrons are passed along a number of electron carriers in a series of oxidation-reduction reactions The electrons lose energy at each stage and some of this energy is used to move H+ ions (protons) across the thylakoid membrane from the stroma An increase in H+ ions in the thylakoid space produces a concentration gradient. The protons pass through the ATP synthase channels to cause the production of ATP Photolysis of water provides electrons to replace those lost from chlorophyll Photolysis also yields protons which are taken up by NADP to reduce it to NADPH The products of the light-dependent stage are ATP and NADPH, these are then used in the light-independent stage Carbon dioxide from the atmosphere diffuses into the leaf through stomata In the stroma, the carbon dioxide reacts with RuBP (5C) This reaction is catalysed by an enzyme called RuBisCo The reaction between carbon dioxide and RuBP produces two molecules of GP (3C) NADPH is used to reduce GP to TP using energy from ATP Some TP molecules are converted to organic substances such as glucose, starch, amino acids, lipids etc. Most TP molecules are used to regenerate RuBP using energy from ATP Answer – note there are more than one possible correct sequences, this is just one of them. Chlorophyll molecule absorbs light energy Pair of electrons become raised to a higher energy level – excited – and leave the chlorophyll molecule As a result the chlorophyll molecule becomes ionised – photoionisation Electrons are passed along a number of electron carriers in a series of oxidation-reduction reactions The electrons lose energy at each stage and some of this energy is used to move H+ ions (protons) across the thylakoid membrane from the stroma An increase in H+ ions in the thylakoid space produces a concentration gradient. The protons pass through the ATP synthase channels to cause the production of ATP Photolysis of water provides electrons to replace those lost from chlorophyll Photolysis also yields protons which are taken up by NADP to reduce it to NADPH The products of the light-dependent stage are ATP and NADPH, these are then used in the light-independent stage Carbon dioxide from the atmosphere diffuses into the leaf through stomata In the stroma, the carbon dioxide reacts with RuBP (5C) This reaction is catalysed by an enzyme called RuBisCo The reaction between carbon dioxide and RuBP produces two molecules of GP (3C) NADPH is used to reduce GP to TP using energy from ATP Some TP molecules are converted to organic substances such as glucose, starch, amino acids, lipids etc. Most TP molecules are used to regenerate RuBP using energy from ATP