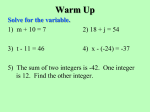* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch. 6 Benchmark Assessment Tuesday, February 19th 6
Survey
Document related concepts
Vincent's theorem wikipedia , lookup
List of important publications in mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Georg Cantor's first set theory article wikipedia , lookup
History of logarithms wikipedia , lookup
Large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Surreal number wikipedia , lookup
Real number wikipedia , lookup
Elementary arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
Positional notation wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Location arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
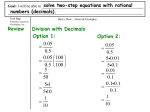
Ch. 6 Benchmark Assessment Tuesday, February 19th 6-1 Estimating Fractions - Use the benchmarks 0, ½, and 1 to round fractions - Round mixed numbers to the nearest whole number Examples: Estimate. 4 7 1 +2 . 8 3 Estimate 3 9 + . 8 10 7 1 4 2 5 2 7 8 3 3 1 9 is about , and is about 1. 8 2 10 3 9 1 1 So, 1 1 8 10 2 2 The sum is about 7. The sum is about 1 1 . 2 Practice: 1 19 = 6 7 5 = 9 6 11 1 - = 12 8 6-2 Adding and Subtracting Fractions - Like fractions have a common denominator - Unlike fractions have do not have a common denominator - When adding/subtracting like fractions add or subtract the numerators and put it over the denominator. - When adding/subtracting unlike fractions, find a common denominator, rename the fractions with a common denominator, add or subtract the numerators and put it over the denominator. Examples: Subtract 11 4 . Write in simplest form. 12 12 11 4 11 4 12 12 12 = Add 7 12 Subtract the numerators. Write the difference over the denominator. 1 1 + . Write in simplest form. 4 12 The least common denominator of 4 and 12 is 12. 1 1 3 3 4 4 3 12 1 Rename 4 using the LCD. 3 1 4 1 or + = 12 12 12 3 Practice: 2 1 = 3 4 3 1 + 8 8 MAGAZINES In Monday’s mail, Dave received a stack of magazines measuring Tuesday, he received magazines measuring 5 inch in height. On 8 2 inch in height. What is the total height of the stack of 3 magazines Dave received on Monday and Tuesday? 6-3 Adding and Subtracting Mixed Numbers - To add mixed numbers, add the fractions and whole numbers separately. Rename the fractions if necessary and simplify. - To subtract mixed numbers, make sure the first fraction is larger than the second fraction. If it is not, rename the fraction by writing an improper fraction using the whole number. Examples: 7 1 + 3 . Write in simplest form. 12 12 7 1 8 2 6 3 9 or 9 Add the whole numbers and fractions separately. Simplify.\ 12 12 12 3 1 3 Find 5 2 . 4 4 1 Rename 5 before subtracting. 4 1 4 1 5 1 5 Rename 5 as 4 . 5 4 or 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 5 3 2 1 4 2 2 or 2 First subtract the whole numbers and then the fractions. Simplify. 4 4 4 2 1 3 1 So, 5 2 2 . 4 4 2 Add 6 Practice: 1 1 8 6 = 5 2 Danielle needs 3 7 3 7 3 8 4 2 3 feet of trim to complete the blouse she is making and 1 feet of the same trim to 3 4 complete the matching skirt. What is the total amount of trim Danielle needs to complete the outfit? 6-4 Multiplying Fractions and Mixed Numbers - To multiply fractions, multiply the numerators and multiply the denominators. Then simplify. - To multiply mixed numbers, rewrite your mixed number as an improper fraction then multiply. Examples: 1 1 . Write in simplest form. 4 5 1 1 1 1 Multiply the numerators and multiply the denominators. 4 5 45 1 = Simplify. 20 1 2 Find 2 . Write in simplest form. 3 5 Multiply 4 1 2 1 12 2 3 5 3 5 Rename 2 2 12 as an improper fraction, . 5 5 1 1 4 = 1 5 4 = 5 Multiply. Simplify. Practice: 3 2 = 5 James uses he need? 3 2 4 7 2 × ×4 cups flour to make one pie. If he is making four pies for a bake sale, how much flour will 6-5 Solving Equations with Fractions - Two numbers whose product is 1 are called multiplicative inverses or reciprocals - Multiplication Property of Equality: If you multiply each side of an equation by the same nonzero number, the two sides remain equal. Examples: 3 . 8 3 8 3 8 Multiply by to get the product 1. 1 8 3 8 3 3 8 2 The multiplicative inverse of is , or 2 . 8 3 3 Find the multiplicative inverse of d Solve 6 = 4. Check your solution. d 4 6 d 6 46 6 d = 24 The solution is 24. Write the equation. Multiply each side of the equation by 6. Simplify. Practice: Solve. 5 x = −10 8 =2 =3