* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Honors Physics S2 Final Exam Review 2013
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Relational approach to quantum physics wikipedia , lookup
Sagnac effect wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Wave packet wikipedia , lookup
Velocity-addition formula wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Surface wave inversion wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic spectrum wikipedia , lookup
Faster-than-light wikipedia , lookup
Variable speed of light wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Matter wave wikipedia , lookup
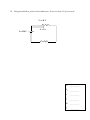
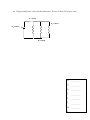
Name: _____________________________ Date _______________ Class Period ______ HONORS Physics: 2nd Semester Final Exam Review NEWTON’S LAWS 1. State Newton’s 1st Law: (remember to address both states of motion!) 2. What is inertia? 3. How is inertia related to mass? 4. Rank the following objects from least to greatest inertia. a. _______a 3kg golf ball moving at 2 m/s d. _______a 10,000 kg truck that is at rest b. _______a 100kg jogger walking at 3 m/s e. _______a .003kg fly moving at 10m/s c. _______a 4000 kg boat at rest f. _______a 0.2kg mouse running at 9 m/s 5. Explain using Newton’s 1st law what will happen to unsecured cargo in a truck if the truck suddenly stops. 6. Newton’s 3rd law says force occur in _________. 7. In the pair of forces, Newton’s 3rd law says the amount of the action force is ________to the amount of the reaction force. 8. In the pair of forces, Newton’s 3rd law says the direction of the action force is ________of the direction of the reaction force. 9. A person pulls on a door handle with 5N of force. Use a complete sentence to describe the reaction force (include direction and amount). 1 10. What is the equation for Newton’s second law of motion? 11. As the force on an object increases, the acceleration _______________________. 12. As the mass on an object increases, the acceleration _______________________. 13. An object will only accelerate if the net force is not equal to ___________. 14. Between which two points on the graph shown below is the Fnet on the object zero? How do you know? Fnet is zero between points ________and ________ because _________________________________________. 15. If a 9 kg bowling ball accelerates at 4 m/s2, what is the net force acting on the bowling ball? Show ALL work! 16. A net force of 180 N acts on a crate of books and causes it to accelerate at a rate of 3.4 m/s2. What is the mass of the crate? Show ALL work! 17. A net force of 250 N is applied to a 0.3 kg hockey puck. Determine the acceleration of the hockey puck. Show ALL work! 2 18. Find the acceleration of the 40kg object below. Show ALL work! 50 N 20 N 70 N 140 N 19. The acceleration of the object below is 4.5 m/s². Determine the mass of the object. Show ALL work! 200 N 25° 135 N 100 N 20. A force scale is placed onto a single cable that is part of a pulley system used to lift a crate. This cable suspends a 315 kg crate. The crate is accelerated straight upwards. During the acceleration, the force scale reads 5,400 N. Determine the acceleration of the crate. Show ALL work! 3 21. A 62 kg high jumper accelerates upward at 8 m/s2 to jump over the bar. For b and c you must show ALL work! a. Draw a free-body diagram. b. Determine the net force c. 22. Calculate the applied force from the athlete’s legs. A 100 kg block (A) rests on a frictionless table; a cord attached to the block extends horizontally to a pulley at the edge of the table. A 30 kg mass (B) hangs at the end of the cord. a. Clearly draw free body diagrams for blocks A and B. FBD-Block A b. c. FBD-Block B Calculate the acceleration of the whole system. Show ALL work! Calculate the tension in the cord. Show ALL work! 4 MOMENTUM 1. Two objects, A & B, have identical velocities. Object A has 3 times the mass of object B. Compare the momentum of each object. Justify your answer. 2. Two other objects, C and D, have identical masses. Object C has twice the velocity of object D. Compare the momentum of each object. Justify your answer. 3. Rank the following objects from least to greatest momentum. _____a. a parked 1430 kilogram car _____b. a 0.015 kilogram fly moving at 7 meters per second _____c. a 52 kilogram sprinter running at 9 meters per second _____d. a 1.4 kilogram ball rolling down a hill at 0.67 meters per second 4. Calculate the momentum of the following objects. Show ALL work! a. A 30kg cart moving at a constant 9 m/s. b. A 10kg object that begins at rest and accelerates to a speed of 6m/s. c. A 5kg object that begins at rest and accelerates at a rate of 4 meters per second for 3s. d. A 15kg object that starts from rest and is pushed with a net force of 30N for 4s. 5 5. In an elastic collision between two objects, the two objects______________________. 6. In an inelastic collision between two objects, the two objects ____________________. 7. A 3 kg ball moving east at 5 m/s collides elastically with a 4kg ball moving west at 5.0 m/s. After the collision, the 3kg ball is moving west at 8 m/s. What is the speed of the 4kg ball? Show ALL work! 8. A 35 kg child is running at 10 m/s when she jumps on a stationary, 5 kg sled. What is the speed of the sled and the child after the child jumps on board? Show ALL work! 9. A 5 kg cart and a 2 kg cart are placed with a spring between them so that both carts are free to move when the spring is released. Both carts begin at rest. The 5 kg cart moves off to the west with a speed of 1.4 m/s when the spring is released. What will the speed of the 2 kg cart be after the spring is released? Show ALL work! 6 ENERGY 1. Two cars (Car #A----1500kg and Car #B----mass of 3500kg) are driving with the same velocity. Which one has more Ek? Explain to conceptually support your answer. 2. A 5000kg school bus is stopped at a bus stop. Another school bus with the same mass is zooming along with a velocity of 34m/s. Which one has more Ek? Explain to conceptually support your answer. 3. A truck with a mass of 1900kg is driving with a velocity of 40m/s. What is the Ek of the truck? Show ALL work! 4. When do you have more Eg? On the 2nd floor of the building OR on the ground floor? Explain to conceptually support your answer. 5. Two snowboarders are at the top of a hill that is 38m tall. Snowboarder #1 has a mass of 62kg. Snowboarder #2 has a mass of 53kg. Who has more Eg? Explain to conceptually support your answer. 6. A 70 kg student is standing at on top of a 5m tall balcony. What is her gravitational energy? Show all work! 7 7. Use the graph shown below to answer the following questions. Read the graph carefully and show ALL work! a) Find the k-value for each spring. b) Find the force required to stretch spring B spring 1m. c) How much energy is stored in each spring when they are stretched to 0.4m? d) How much energy is stored in each spring when they are stretched 0.8m? e) Which spring is hardest to stretch? How do you know? 8 8. What does it mean to say the energy is conserved? Explain using a complete sentence. 9. A spring with a k-value of 400N/m is compressed 0.75m. a. How much Ee is stored in the spring? Show ALL work! b. How much velocity could it give to a 0.3kg ball? Show ALL work! 10. A 85 kg stuntman jumps from the 12 meter tall building into a safety net (at ground level) below. Show ALL work! a. Determine the stuntman’s Eg at the top of the building. b. How much Ek does the stuntman possess the moment before impact? c. What is his velocity the moment before impact with the net? 11. A 90 kg person slides down a 15 m high water slide and reaches the surface of the water (h=0m) with a speed of 4 m/s. a. What is the person’s initial gravitational energy? b. What is the person’s kinetic energy at the bottom of the slide? c. How much energy was dissipated due to friction in the process? 9 12. A boat with a mass of 3000kg is moving through the water with a velocity of 8m/s in the beginning. It slows down and at the end is only moving with a velocity of 4m/s. v = 4m/s. v = 8m/s. Initial a) Final Draw the bar charts (qualitatively) to show the energy transfer and conservation. b) Write the energy conservation equation for this situation. c) Determine the amount of dissipated energy that is present in the final situation. Show ALL work! 10 CIRCULAR MOTION 1. Joey drives his car around a circular section of a road having a radius of 80m at a constant speed of 20 m/s. What is the centripetal acceleration of Joey's car? Show ALL work! 2. Julia twirls a stone attached to a string 1.5 meters long in a horizontal circle. At what velocity must the stone move for its centripetal acceleration to be equal to the acceleration due to gravity? Show ALL work! 3. What centripetal force is needed to keep a 1.9 kg object moving at a constant speed of 4 m/s in a circle having a radius of 8m? Show ALL work! 4. A car of mass 1200 kg is travelling 8.33 m/s around a bend of radius 100 m. a. What is its centripetal acceleration? Show ALL work! b. What will be its centripetal acceleration if it travels, at the same speed, around a bend of radius 70 m? Show ALL work! 11 5. A truck with a mass of 5500kg travels at 14 m/s around a bend of radius 22 m. a. Determine the centripetal acceleration of the truck. Show ALL work! b. Calculate the centripetal force acting on the truck. Show ALL work! 6. James applies a force of 10 N to one end of a string to a bag of tied to the other end moving at a speed of 2.0 m/s in a horizontal circle of radius 3.0 m. What is the mass of the bag? Show ALL work! 7. Two motorcyclists are riding identical motorcycles around a curve in the road at the same speed. Chris has a mass 90kg and Bobby has a mass 70 kg. a. Which person has the greater centripetal acceleration acting on him? How do you know? b. Which one has the greater force acting on him? How do you know? 12 WAVES and SOUND 1. Identify the following: _____ =Trough _____ =Crest _____ =Wavelength _____ =Amplitude _____ =Line of Equilibrium 2. How do you measure wavelength? 3. What is a transverse wave? 4. An example of a transverse wave is __________________________. 5. What is a longitudinal wave? 6. An example of a longitudinal wave is _______________________________. 7. What is a compression? 8. What is a rarefaction? 9. Explain how amplitude and intensity (loudness) of a sound wave are related. 10. Explain how frequency and pitch of a sound wave are related. 11. What is The Doppler Effect? 12. When an object is forced to vibrate at its natural frequency this is called______________. 13. List the three major factors that affect the natural frequency of an object. a. _______________ b._______________ c._______________ 14. Explain why we are unable to hear sounds in space (in a vacuum). 13 15. Sound travels faster through materials that are more ___________________. 16. List these three mediums (water, air, steel) in order, from fastest to slowest, at which the speed of sound travels through them. 1st _____________ 2nd _____________ 3rd _____________ 17. When you whisper quietly and then yell louder, you are changing the ________________of the sound wave you are making. 18. Superposition is a result of _________________________. 19. What is constructive interference? Draw a diagram to illustrate it. 20. What is destructive interference? Draw a diagram to illustrate it. 21. What are “beats?” 22. Explain how these two sounds waves are different. 14 23. A surfer sits by the ocean and watches 28 waves pass by in 60 seconds. a. What is the frequency of the waves? b. What is the period of the ocean wave? 24. If the period of a wave is 19 s what is the frequency? 25. Calculate the wave speed of a wave with a frequency of 150 Hz if the wavelength is 2.5 m. 26. Calculate the wavelength of a wave with a frequency of 68 Hz and a wave speed of 170 m/s. 27. Calculate the frequency of a wave with a wavelength of 9 m and a wave speed of 343 m/s. 28. You move towards a stationary 300 Hz siren at 35 m/s. What frequency do you hear? 29. You run away from a 2,500 Hz siren at 10 m/s. The siren is traveling away from you at 40 m/s. What frequency do you hear? 30. You drive towards from a 300 Hz siren at 15 m/s. The siren is headed towards you at 30 m/s. What frequency do you hear? 31. A 485 Hz siren moves away from you at 25 m/s. You are stationary. What frequency do you hear? 15 THE EM SPECTRUM and LIGHT 1. What is the speed of light? _________________________ 2. All waves from the electromagnetic spectrum are what type of wave?_______________________ 3. Does visible light contain frequencies that make up a majority of electromagnetic spectrum? ______ 4. Do gamma rays travel faster than microwaves? _________ 5. As the frequency of a wave in the EM spectrum increases, it’s wavelength __________________ 6. What causes electromagnetic waves to form? 7. What electromagnetic wave has the highest frequency?___________ Lowest frequency?_______________ 8. What are the types of waves in the EM Spectrum that have a frequency just higher than visible light? 9. Write out the law of reflection. 10. A ray of light strikes an object with an angle of incidence of 29 degrees. What will be the angle of reflection? 11. Draw the refracted light rays below. Fast Slow Slow Fast 12. Explain why refraction occurs. 16 13. As light travels from air to water, what happens to its speed? 14. What are the colors represented by the acronym ROY G BIV? List them in order from 15. Which color of light has the highest frequency? __________ 16. Which color of light has the lowest frequency? __________ 17. The three primary colors of light are __________, ___________ and ____________. 18. The three secondary colors of light are _________, __________ and ____________. 19. Blue + Green Light = _____________ light Blue + Red Light = _____________ light Red + Green Light = _____________ light Red + Green + Blue Light = _____________ light 20. A white object ______________ all light to an observer’s eyes. 21. A black object ________________ all light that is shined upon it. 22. Red light + cyan light creates _____________ light 23. Two colors of light that combine to form white light (like the problem above) are called ____________________ colors. 24. Joe looks at Frank’s shirt and sees that it is a green color. Describe and draw a diagram of how and why Frank’s shirt appears green to Joe. 25. If a t-shirt appears yellow it is because it is reflecting ____________ and _________ light and ______________ all other colors of light. 17 26. What is the difference between a luminous source and an illuminated source? 27. Give two examples of a luminous source and two examples of illuminated objects. 28. Define the following and provide one example of each: Opaque – Transparent – Translucent - 30. What is a plane mirror? How is the image different than the actual object that is being viewed in the mirror? 31. A mirrors can make virtual images. What does this mean? 32. Write whether the following descriptions apply to concave or convex mirrors: A. Curves Inward B. Curves Outward C. Always produced smaller images D. Can produce images that are upside-down E. Always produces images that are right side up F. Provides viewers with a larger field of view 32. Draw a picture to represent a concave mirror. 33. Draw a picture to represent a convex mirror. 18 ELECTRICITY 1. How is an open loop different from a closed loop? 2. Describe a “test” you could perform to determine if an object is an insulator or a conductor. Explain or diagram how you would arrange the circuit components and what you would look for. 3. An example of a conductor is ____________________. 4. An example of an insulator is _____________________ 5. Name the 3 conducting parts of a light bulb. 6. What causes the charge in a circuit to move? 7. When charge flows, it is called __________________. 8. According to conventional charge flow, charge moves away from the ______________ end of a battery. 9. How does increasing resistance affect the amount of current in a circuit? 10. Draw a circuit, using schematic symbols, which contains a battery with 3 resistors in series. 11. Draw a circuit, using schematic symbols, which contains a battery and 3 resistors in parallel. 19 12. Of the two circuits you have drawn in problems 10 and 11which would have: a. brighter bulbs? ____________ b. the most resistance? __________ Solve the following problems using the Ohm’s Law equation. 13. A certain light bulb has a resistance of 120 Ω. If a current of 1.2 A is going through it, calculate the voltage applied. 14. A voltage of 200 volts is applied to a 1000 Ω resistor. Calculate the current through the resistor. 15. A voltage of 90 volts is applied to a resistor and the current going through it is found to be 0.04A. Calculate the resistance. 16. A toaster operates from a 120 V outlet. It has a heating element with a resistance of 6.0 Ω. Calculate the current going through the heating element. 17. In a small Mp3 player, the current going through a 1500 Ω resistor is 0.165 A. Calculate the voltage across the resistor. 20 18. Using circuit below, solve for the unknowns. Be sure to show ALL of your work! V1 = 20 V VT =150 V IT = 5A V1 ________________ V2 ________________ I1 ________________ I2 ________________ RT ________________ IT ________________ 21 19. Using circuit below, solve for the unknowns. Be sure to show ALL of your work! R1 = 20 kΩ R3 = 40 kΩ VT =10 kV R2 = 40 kΩ V1 ________________ V2 ________________ V3 ________________ I1 ________________ I2 ________________ I3 ________________ RT ________________ IT ________________ 22 20. See the Combination Circuit that is drawn below. Solve for all of the unknowns. Be sure to show ALL of your work! R1 = 3Ω R2 = 4 Ω R3 = 12 Ω R4 = 5 Ω V1 ________________ V2 ________________ V3 ________________ V4 _______________ I1 ________________ I2 ________________ I3 ________________ I4 ____________ RT ________________ IT ________________ 23