* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapters 12-16 Cumulative Test
Survey
Document related concepts
Event symmetry wikipedia , lookup
Penrose tiling wikipedia , lookup
Mirror symmetry (string theory) wikipedia , lookup
Rotation formalisms in three dimensions wikipedia , lookup
Coxeter notation wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
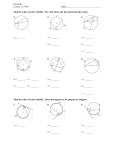
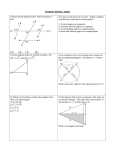
Chapters 12-16 Cumulative Test 1. True or False a. SAS, SSS, ASA, and SSA are triangle congruence properties. b. SAS, SSS, and AA are triangle similarity properties. c. All squares are congruent to each other. d. Translations and rotations are the only isometries that do not change the orientation of a figure. e. All isometries preserve angle measure. f. If A' B' is the image of AB under a reflection, then A' B' AB . 2. Sketch the following and include proper labeling to illustrate the size or congruence of sides and angles. a. A trapezoid that is not isosceles. b. A right isosceles triangle. 3. For each of the following name and sketch a type of quadrilateral that has the stated properties? Sketch the lines of symmetry and/or describe the angles of rotation. a. Rotational symmetry but not reflexive symmetry b. Reflexive but not rotational symmetry c. Neither reflexive nor rotational symmetry 4. a. In the following diagrams let one circle represent the set of acute triangles and the other circle represent the set of isosceles triangles. Which of the diagrams best represents the relationship between acute triangles and isosceles? b. In the following diagrams, let one circle represent the set of kites and the other circle represent the set of squares. Which of the diagrams best represents the relationship between kites and squares? i ii iii 5. In the following figure, l m . Given the measures of angles indicated in the figure, find the measures of the angles identified by a, b, c, d, e, and f. f l e d 48 m 58 c a 85 6. The formula for computing the measure of the vertex angle of a regular n-gon can be (n 2) 180 n 180 360 written as or . Select one of the forms of the equation and n n explain how it was derived. 7. The van Hiele levels are levels of reasoning used in learning geometry. Name the first three van Hiele levels and explain each. 8. Choose the most realistic measures for the following objects. Circle the best answer. a. The weight of a baseball b. The height of a desk c. The volume of a cup of water 10 kg 10 cm 100 kg 1m 200 mL 2 L 100 g 1 km 2 mL 9. Sketch two different rectangles with the same area. What do you notice about their perimeters? (Be sure to label the dimensions of your rectangles.) 10. Perform each of the following conversions a. 247 mm2 = cm2 b. 36 mm = m c. 2.39 g = mg d. 108 ft3 = yd3 e. 247 cm3 = m3 f. 72 in yd = g. 463 cm3 = mL h. 2 gal = quarts 11. The number is equal to 3.14159… What does represent? 12. Given the top view of a stack of blocks where the numbers tell you how high each stack of blocks should be. Which picture below represents the same stack? 13. Find the perimeter of the figure below and leave the answer in exact form. 14. How far will a wheel with radius of 5 feet roll in two revolutions? 15. Explain why the area of the triangle below can be found by using the following formula. 1 A bh 2 16. Betty’s yard is shaped as shown in the following figure. If she has a bag of fertilizer that will cover 450 yd2 of grass, exactly how much of the bag should she spread on her yard? Justify your answer. (Note: 18’ in the figure means 18 feet.) 17. a. A can of soda has a diameter of 8 cm and a height of 12 cm. What is the volume? b. What is the volume in milliliters? c. If 6 cans are packed in a rectangular box so that the cans touch each other and the sides of the box in a perfect fit, what is the surface area of the box? 18. Explain what in means for two triangles to be congruent by the SAS congruence property. B 19. Given that ABCD in the following figure is a parallelogram A E C D a. Prove that AED CED. b. Use the result of part (a) to show that the diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other. 20. a. Use a compass and straightedge to construct the angle bisector of an angle. b. Explain how the properties of the diagonals of a rhombus are related to the construction done in part (a). 21. Given the lengths and angles indicated in the following figure, find CE and AD. E 9 4 A 75 ° C 75 ° 6 5 D 22. Given ABC ~ XYZ and ABC ? AB 3 . If the area of XYZ is 8 in2, what is the area of XY 23. In ABC let l be the perpendicular bisector of side AB and m is the perpendicular bisector of BC . If l and m intersect at point O, what property does O have in relation to the vertices of the triangle? For problems 24-27, let A(0,0), B(5,0), C(8,4), and D(3,4) be the vertices of quadrilateral ABCD. 24. a. Find the slopes of AB, BC, CD, and DA . b. Based on the information in part (a), we can conclude ABCD is what type of quadrilateral? 25. a. Find the lengths of AB, BC, CD, and DA . b. Based on the information in part (a), we can conclude ABCD is what type of quadrilateral? 26. a. Find the slopes of diagonals AC and BD . b. Find the midpoints of AC and BD . c. Based on parts a. and b. what properties do the diagonals of a rhombus have? 27. Let l be the line that passes through D and is perpendicular to side BC . a. Find the equation of l. b. Find the point of intersection of l and BC . 28. Find the following points on the following square lattice. a. TAB(P) A b. RO,-90 (P) c. MBD (P) F d. SE, 3 (P) B 0 P E C D 29. In each of the following cases, ABC A' B' C' . Identify the type of isometry that maps ABC to A' B' C' as either a rotation, translation, reflection, glide reflection or none and justify your conclusion. B B A B A A C C B' C C' C' A' B' A' A' C' B' a. b. c.