* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2013 Taxonomy Notes ppt
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Cambrian explosion wikipedia , lookup
Natural environment wikipedia , lookup
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
History of biology wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Symbiogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Soil microbiology wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Precambrian body plans wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Bacterial taxonomy wikipedia , lookup
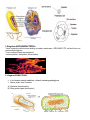
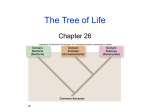
Classification Notes * Classification provides scientists and students a way to sort and group organisms for easier study. * There are millions of organisms on the earth! (approximately 1.5 million have been already named) Organisms are classified by their: * physical structure (how they look) * evolutionary relationships * embryonic similarities (embryos) * genetic similarities (DNA) * biochemical similarities UNITY AND DIVERSITY All living things carry out the life functions. There are many different types of organisms. In one classification system, there are 2 main groups. In others, there are 3. In the one used by most of the world's scientists, which we will also use, there are 6 main groups. All living things are placed in one of the six KINGDOMS...which are the most general group. They are then broken down into smaller groups, then smaller groups, then smaller and so on until there is just one... SPECIES is the most specific group... Domain DKPCOFGS Can you make a sentence using the first letter of each classification subgroup? NOMENCLATURE--a system for naming things In biology there is a two-word system that is used to name organisms. It is called BINOMIAL NOMENCLATURE (a two named--naming system). Carolus Linnaeus devised this in the 1800's using these two subgroups for the name: GENUS & SPECIES (more general) (more specific) Humans are known as Homo sapiens The Six Kingdoms ARCHAEBACTERIA EUBACTERIA PROTISTA FUNGI PLANT ANIMAL A E P F P A Can you make a sentence using the first letter of each kingdom? Alice Eats Preferably Fat Prairie Animals I. Kingdom ARCHAEBACTERIA-* have a primitive cell structure lacking a nuclear membrane—PROKARYOTE, cell wall does not contain peptidoglycan * live in extreme harsh environments * extremophiles—halophiles, thermophiles II. Kingdom EUBACTERIA Live in more neutral conditions, cell wall contains peptidoglycan Know as the “true” bacteria A) Bacteria (heterotrophic) B) Blue-green algae (autotrophic) II. Kingdom PROTISTA-* has a membrane around the nucleus of the cell--EUKARYOTIC * predominantly unicellular * two main phyla A) Protozoa--animal like nutrition (heterotrophic) ex. paramecia, ameba B) Algae--plant like nutrition (autotrophic) ex. spirogyra III. Kingdom FUNGI-* has a membrane around the nucleus of the cell--EUKARYOTIC * absorbs food from its environment (heterotrophic), does NOT ingest it! * organized into branched, multinucleated filaments ex. bread molds (multicellular) mushrooms (multicellular) yeast (unicellular) IV. Kingdom PLANTS-* has a membrane around the nucleus of the cell--EUKARYOTIC * multicellular organism * photosynthetic organisms (autotrophic) (photo=light) (synthesis=to make) PHOTOSYNTHESIS=TO MAKE FROM LIGHT V. Kingdom ANIMAL-* largest of 5 kingdoms * has a membrane around the nucleus of the cell--EUKARYOTIC * multicellular * ingests their food (heterotrophic) * four main phyla A) Coelenterates (soul-en-ter-ates) 1) has only two layers of cells 2) has a hollow body cavity ex. hydra, jellyfish B) Annelids 1) has segmented body walls (rings) ex. earthworm, sandworm C) Arthropods 1) has an exoskeleton (exo=outside) 2) has jointed appendages ex. grasshopper, lobster, spiders, insects D) Chordates 1) have a dorsal (back) nerve cord 2) have a notochord at some point in their development 3) have a post anal tail at some point in their development 4) have gill slits at some point in their development ex. sharks, frogs, humans, cats **Chordates have many CLASSES (the next subgroup)** Pisces (ex. fish) Amphibians (ex. frogs) Reptiles (ex. lizards) Aves (ex. birds) Mammalia (ex. humans, cats, dogs, whales)