* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Variation and selection
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Haplogroup G-P303 wikipedia , lookup
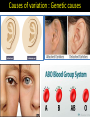
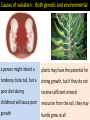
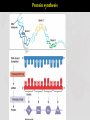
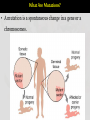
Variation and selection What do you mean by variation..? Differences between species Differences within a species VARIATIONS: SPECIES : A species is a group of organisms that are able to interbreed and produce fertile offspring. Causes of variation : Genetic causes Causes of variation : Environmental causes 1.Climate, 2.Diet, 3.Accidents, 4.Culture and 5.Lifestyle. Causes of variation : Both genetic and environmental a person might inherit a plants may have the potential for tendency to be tall, but a strong growth, but if they do not poor diet during receive sufficient mineral childhood will cause poor resources from the soil, they may growth hardly grow at all CONTINUOUS VS DISCONTINUOUS VARIATION Variation, the small differences that exist between individuals, can be described as being either discontinuous or continuous. Continuous variation 1. Continuous variation shows a complete range of the characteristics within a population. Example: a) Height is an of continuous variation - individuals can have a complete range of heights, for example, 1.6, 1.61, 1.62, 1.625 etc meters high. b) Weight; c) Hand span d) Shoe size Continuous variation is the combined effect of many genes (known as polygenic inheritance) and is often significantly affected by environmental influences. Discontinuous variation Discontinuous variation 1. This is where individuals fall into a number of distinct classes or categories, and is based on features that cannot be measured across a complete range. 2. There are no intermediates between categories. 3. You either have the characteristic or you don't. Examples: a) Blood groups are a good example: you are either one blood group or another - you can't be in between. Such data is called discrete (or categorical) data. 1. Discontinuous variation is controlled by alleles of a single gene or a small number of genes. 2. The environment has little effect on this type of variation. 17.2 MUTATION Protein synthesis What Are Mutations? • A mutation is a spontaneous change in a gene or a chromosomes. Types of mutation 1. Gene Mutation • Change in the nucleotide sequence of a gene • May only involve a single nucleotide. Gene Mutation Examples 1. Gene mutation in drosophila 2. Albino 3. Sickle cell anemia Describe the features of sickle cell anaemia. 1. fewer red blood cells 2. less elastic / less flexible / sickle-shaped, red blood cells 3. haemoglobin is abnormal shape 4. haemoglobin / blood, less efficient at transporting oxygen 5. less respiration 6. less energy / fatigues / exhaustion / less active / 7. feeling faint / breathlessness 8. death of tissues linked to oxygen supply 9. capillaries are blocked 10. ‘sickle cell crisis’ 11. slow / poor, growth 12. susceptible to infections 13. reduced life span Example : Sickle cell anaemia Sickle cell Sickle cell anaemia & its incidence in relation to that of malaria Explain why HbS is more common in parts of tropical Africa Chromosome : Structure TypesMutation of mutation 2. Chromosome Mutation : Structural and numerical The loss or gain of part of a chromosome Changing the structure or number of a chromosome 2. Chromosome Mutation : Number Causes of mutation • Mutagens such as: 1. Naturally: DNA replication error 2. X-rays 3. UV rays 4. Chemicals (tobacco smoke) Are Mutations Helpful or Harmful? • Often mutation can be harmful. • Some mutation are beneficial . • Some mutation have no effect at all.