* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 10 Notes
Malay grammar wikipedia , lookup
Compound (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old Irish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lexical semantics wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Udmurt grammar wikipedia , lookup
Antisymmetry wikipedia , lookup
Navajo grammar wikipedia , lookup
Arabic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Georgian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Icelandic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Zulu grammar wikipedia , lookup
Romanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Preposition and postposition wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Kannada grammar wikipedia , lookup
Determiner phrase wikipedia , lookup
Vietnamese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Turkish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Polish grammar wikipedia , lookup
English clause syntax wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
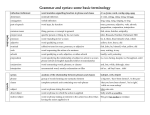
Nominals
Rhetorical Grammar (7ed)
Chapter 10--Choosing Nominals
chart--page 140
Form
Word
noun
verb
adjective
adverb
Phrase
noun phrase
verb phrase
o gerund
o infinitive
o participle
prepositional phrase
Clause
independent clause (sentence)
dependent clause
o adverbial clause
o adjectival clause
o nominal clause
Function
Adverbial
modifier of verb (time, location,
manner, reason)
Adjectival
subject complement
object complement
modifier of noun
Nominal
subject
subject complement
direct object
indirect object
object complement
object of preposition
appositive
Appositives (noun in "apposition"=adjacent structures filling the same
position)
appositives provide more information about the noun and rename the noun phrase
My brother, Kirk, lives in Connecticut.
An income tax lawyer, he handles the taxes for large veterinary clinics.
Group Discussion (p. 193)
The Colon (or Comma or Dash)
use a colon to signal an appositive that renames the noun ("namely. . . .")
Fornes will be teaching two new courses this fall: Writing in the Workplace and
the Nonfiction Workshop.
Fornes will be teaching two new courses this fall-- Writing in the Workplace and
the Nonfiction Workshop.
Fornes will be teaching two new courses this fall, Writing in the Workplace and
the Nonfiction Workshop.
Nominals
Use a dash or comma when the appositive appears in the middle of the sentence.
Fornes's two new courses-- Writing in the Workplace and the Nonfiction
Workshop--promise to be exciting and rewarding.
Fornes's two new courses, Writing in the Workplace and the Nonfiction
Workshop, promise to be exciting and rewarding.
Use a dash when the series has commas (more than two items)
All of Fornes's classes this fall--College Composition, Critical Inquiry, and the
Nonfiction Workshop--will be 75-minutes long.
Regardless, colons and dashes need to be preceded by independent clauses.
Fornes's two new courses are: Critical Inquiry and the Nonfiction Workshop.
(wrong)
Fornes's two new courses are as follows: Critical Inquiry and the Nonfiction
Workshop. (kinda icky, compare emphasis to the first exampe above)
Sentence appositives can add drama.
The USCA Pacers were behind by 24 points before rallying to win. That
comeback was amazing.
The USCA Pacers were behind by 24 points before rallying to win--an amazing
comeback.
Joe bought a gas guzzler, a decision that surprised me.
Exercise #33 (p. 184)
Nominal Verb Phrases
Gerunds/Infinitives
Gerunds=the -ing form (progressive) of a verb without auxiliary (name actions--not
persons, places or things--and can be replaced by it)
Infinitives=the to + form a verb
Both gerund and infinitive nominals can serve in any slot a noun phrase fills.
(see above)
o Jogging in the early morning is an activity I enjoy. (gerund phrase as
subject)
o To jog in the early morning is an activity I enjoy. (infinitive phrase as
subject)
When any phrase with a verb form opens a sentence, the subject of the verb must
correspond to the subject of the sentence. It also requires a comma.
Jogging in the early morning, a car almost ran me down. (dangling)
Jogging in the early morning, I was almost struck by a car.
page 188-89, Exercise #34
The best thing would be to tell the truth.
To ignore the judge's order would be foolhardy.
Nominals
This invitation thwarted his latest plan, to buy up a controlling number of
stocks.
Raising the company's national profile was the new owner's long-term goal.
I appreciate your proofreading this final version for me.
Nominal Clauses
that as the nominalizer
Step 1--take a declarative sentence ("The final portfolio is due April 27.")
Step 2--add that ("that the final portfolio is due April 27")
Step 3--use it as a noun phrase
"Fornes announced that the final portfolio is due April 27."
"That the final portfolio is due April 27 should come as no surprise."
interrogatives (question words)
Fornes cannot understand how students misunderstood the due date.
Why some students are afraid of the rain is a mystery.
Ex 35, p. 191