* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Solving Radical Equations
Two-body Dirac equations wikipedia , lookup
BKL singularity wikipedia , lookup
Debye–Hückel equation wikipedia , lookup
Two-body problem in general relativity wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Calculus of variations wikipedia , lookup
Itô diffusion wikipedia , lookup
Navier–Stokes equations wikipedia , lookup
Euler equations (fluid dynamics) wikipedia , lookup
Equation of state wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Computational electromagnetics wikipedia , lookup
Derivation of the Navier–Stokes equations wikipedia , lookup
Differential equation wikipedia , lookup
Schwarzschild geodesics wikipedia , lookup
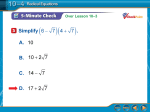
Solving Radical Equations 1 Name:________________________________ A "radical" equation is an equation in which there is a variable inside the radical sign. x 26 x 4 1) Here are four steps to solve equations with radicals Step 1: Isolate the radicals to left side of the equal sign. Step 2: Square each side of the equation (If the radical is not a square root, raise each side to a power equal to the index of the root.) Step 3: Solve the resulting equation Step 4: Check all solutions x 2 2) x 1 2 2 3 4x 9 5 4 16 4) 16 2 6 4 2 6 CHECK x2 3 3 2 3) x Solve these equations. Be sure to check for extraneous solutions! 1 4 x 8 5 3 x 9 3 6 2x 1 5 7 7 3 2 x 1 10 8 2x 1 7 4