* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Semester Final Review
Survey
Document related concepts
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
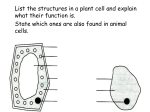
AP Biology Semester Final Study Guide 1. 2. 3. 4. What are the 4 main atoms that make up most life? Define: atomic mass, atomic number, proton, neutron, electron, isotope, cation and anion. Be able to describe the types of bonds. What are the properties of water and why do they display these properties? Example: Why does water exhibit surface tension? 5. What monomers make up each of the following? proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, nucleic acids Describe the properties of each. 6. Be able to recognize and name all the functional groups. 7. What are the definitions to hydrophobic and hydrophilic? 8. What do enzymes do to catalyze a reaction? 9. What are the main differences between a eukaryotic and prokaryotic cell? 10. What are the cell organelles and what are their functions? Describe the structure. 11. Name the first and second laws of thermodynamics. 12. Define: metabolism, catabolism, anabolism, enzymes, oxidation, reduction, glycolysis, citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. 13. What is cellular respiration (including the formula) and what is oxygen’s role? 14. What is photosynthesis (including the formula), and how is it different than respiration? 15. What are the stages of the cell cycle, what happens in each stage, and relatively how long is each? 16. What are the stages of mitosis and meiosis and what happens in each stage? 17. Understand the meanings of the following terms: a. homozygous j. allele b. heterozygous k. Test cross c. genotype l. incomplete domiance d. phenotype m. codominance e. homologous chromosome pair n. epistasis f. diploid o. pleiotropy g. haploid p. sister chromatids h. dihybrid cross q. locus i. monohybrid cross r. polygenic inheritance 18. Use a Punnett square to predict the results of a monohybrid cross, dihybrid cross, and linkage cross and to state the phenotypic and genotypic ratios of the F1 and F2 generations. 19. Explain how a testcross can determine if a dominant phenotype is homozygous or heterozygous. 20. Describe what is meant by the law of segregation and the law of independent assortment. 21. Relate the law of segregation and the law of independent assortment to genetic variation of gametes that arise in the process of meiosis. 22. Explain how the phenotypic expression of the heterozygote is affected by complete dominance, incomplete dominance, and codominance. 23. Define gene linkage and explain why linkage interferes with independent assortment. 24. Distinguish between parent and recombinant phenotypes. 25. Explain how crossing over can unlink genes. 26. Describe sex determination in humans and explain the types of genes located on both chromosomes. 27. Explain why a recessive sex-linked gene is always expressed in males. 28. Be able to read a table of codons and give the sequence of amino acids from an mRNA strand. Ex: What is the sequence of amino acids for the mRNA strand 3’ AUG ACU AAU AGU 5’ 29. What are the enzymes involved in transcription? 30. What are viruses? What is the lytic and lysogenic cycle? What is a vaccination? 31. What is meant by the term fluid mosaic model when talking about cell membranes? How do phospholipids move in a membrane? Be able to name the parts of membranes. 32. Define diffusion and osmosis. 33. What are the stages of cellular respiration? 34. What are the stages of cell signaling? These are the basics for the exam. Be sure to look over your guided reading assignments, notes and the outlines you can find on SWIFT. The more review you do, the better you will do on the exam. Study hard!!