* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 7: Electricity TRUE/FALSE 1. An atom with fewer electrons
Skin effect wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Rechargeable battery wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
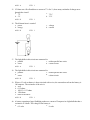
Chapter 7: Electricity TRUE/FALSE 1. An atom with fewer electrons than protons is a negative ion. ANS: F PTS: 1 2. All three types of particles found in atoms are electrically charged. ANS: F PTS: 1 3. An object that has zero resistance is a semiconductor. ANS: F PTS: 1 4. Current is the rate of flow of electric charge. ANS: T PTS: 1 5. The SI unit of electric charge is e, the charge on the electron. ANS: F PTS: 1 6. Electrons are negatively charged. ANS: T PTS: 1 7. Superconductivity is lost when a certain critical temperature is exceeded. ANS: T PTS: 1 8. Voltage is a measure of the energy per unit charge supplied by a battery. ANS: T PTS: 1 9. Voltage can also be called potential. ANS: T PTS: 1 10. Current is the opposition to the flow of charge. ANS: F PTS: 1 11. Voltage is the force on a charged object divided by the charge on the object. ANS: F PTS: 1 12. Larger batteries have higher output voltages. ANS: F PTS: 1 13. Two charged bodies separated by a distance d exert an electrical force on each other. The distance d is doubled. The electrical force on each body is now 1/2 of the original force. ANS: F PTS: 1 14. Two charged bodies separated by a distance d exert a repulsive electrical force on each other. The signs of the charges on the two bodies are + and –. ANS: F PTS: 1 15. The resistance of a conducting material depends on its composition, length, diameter, and temperature. ANS: T PTS: 1 16. If the length of a wire increases, its resistance decreases. ANS: F PTS: 1 17. If the diameter of a wire increases, its resistance decreases. ANS: T PTS: 1 18. The resistance of a wire does not change when its temperature changes. ANS: F PTS: 1 19. Solids that are good conductors of heat tend also to be good conductors of electricity. ANS: T PTS: 1 20. Semiconductor technology has been the basis for many new electronic devices. ANS: T PTS: 1 21. An electrostatic precipitator uses an electric field to remove smoke from the air. ANS: T PTS: 1 22. If the current drawn from a 12 volt car battery is 100 amperes when it is short circuited with a wire, the resistance of the wire is 0.12 ohms. ANS: T PTS: 1 23. A battery operating a large flashlight produces a current of 2 amperes in a light bulb that has a resistance of 4 ohms. The voltage of the battery is 2 volts. ANS: F PTS: 1 24. A battery stores electric charge in the same way that a bottle stores water. ANS: F PTS: 1 25. If an electric toaster operating on 120 volts draws a current of 6 amperes, the resistance of the toaster is 20 ohms. ANS: T PTS: 1 26. In a parallel circuit, the size of the current flowing through each device may be different. ANS: T PTS: 1 27. A light bulb designed for use with AC would still work if hooked up to DC of the proper voltage. ANS: T PTS: 1 A light bulb used in a slide projector draws a current of 6 amperes when operating on 120 volts. 28. The resistance of the light bulb is 20 ohms. ANS: T PTS: 1 29. The power consumed by the light bulb is 20 watts. ANS: F PTS: 1 30. If two slide projectors are connected in parallel across the same 120 volt source, the current drawn from the source remains at 6 amperes. ANS: F PTS: 1 31. If two slide projectors are connected in series across the same 120 volt source, the current drawn from the source remains at 6 amperes. ANS: F PTS: 1 32. The energy used by a 100 watt light bulb in 1 hour is 360,000 joules ANS: T PTS: 1 33. The energy used by a 100 watt light bulb in 1 hour is 100 kilowatt-hours. ANS: F PTS: 1 A heater is rated at 1200 watts for a 120 volt source. 34. The current drawn by the heater is 10 amperes. ANS: T PTS: 1 35. The resistance of the heater is 10 ohms. ANS: F PTS: 1 36. If two heaters are connected in parallel across the 120 volt source, the total power drawn from the source increases to 2400 watts. ANS: T PTS: 1 37. If two heaters are connected in parallel across the 120 volt source, the current drawn from the source is 10 amperes. ANS: F PTS: 1 MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. A positive ion is formed when a. a neutral atom gains an electron b. a neutral atom loses an electron ANS: B c. a negative ion loses an electron d. all of the above PTS: 1 2. An atom with fewer electrons than protons is a a. semiconductor b. superconductor c. positive ion d. negative ion e. none of the above ANS: C PTS: 3. An electric current can consist of a. positive ions flowing in a liquid b. negative ions flowing in a liquid ANS: D PTS: 1 4. An object that has zero resistance is a a. semiconductor b. superconductor c. diode d. transistor e. positive ion ANS: B PTS: 1 5. The rate of flow of electric charge is a. voltage b. current c. resistance d. electric field e. critical temperature 1 c. electrons flowing in a wire d. all of the above ANS: B PTS: 1 6. Suppose current is flowing in a wire from right to left. Which way do the electrons in the wire move? a. right to left b. left to right c. in circles d. It is impossible to tell. ANS: B PTS: 1 7. The SI unit of electric charge is a. e, the charge on the electron b. the coulomb c. the ampere d. the ohm e. the volt ANS: B PTS: 1 8. What is meant by ‘like charges?’ a. charges that are both positive b. equal amounts of charge c. charges that are both negative d. A and C ANS: D PTS: 1 9. What is meant by ‘net charge?’ a. the total amount of positive charge on an object b. the total amount of negative charge on an object c. the total amount of neutral charge on an object d. A minus B ANS: D PTS: 1 10. Superconductivity is lost when a certain ____is exceeded. a. voltage d. electric field b. current e. critical temperature c. resistance ANS: E PTS: 1 11. The energy per unit charge supplied by a battery is its a. voltage b. current c. resistance d. electric field e. critical temperature ANS: A PTS: 1 12. A quantity that is measured in ohms is a. b. c. d. e. voltage current resistance electric field critical temperature ANS: C PTS: 1 13. A quantity that measures the opposition to the flow of charge is a. voltage b. current c. resistance d. electric field e. critical temperature ANS: C PTS: 1 14. Voltage can also be called a. potential b. pressure c. work d. energy e. none of the above ANS: A PTS: 1 15. If you think of a battery as an electric charge ‘pump,’ the battery voltage is analogous to a. rate of fluid flow b. pressure c. flow velocity d. water e. none of the above ANS: B PTS: 1 16. A car headlight and an interior dome light use the same voltage, but the headlight consumes much more power because a. its resistance is lower b. the current in it is larger c. it uses energy faster d. all of the above ANS: D PTS: 1 17. Why do we use fuses? a. to eliminate shock hazards b. to prevent fires c. to save on the cost of electricity d. to store charge ANS: B PTS: 1 18. If three identical bulbs are connected in parallel across a 12V battery, the voltage across each bulb will be a. 12V b. 4V c. different d. none of the above ANS: A PTS: 1 19. If three identical bulbs are connected in series across a 12V battery, the voltage across each bulb will be a. 12V b. 4V c. different d. none of the above ANS: B PTS: 1 20. The force on a charged object divided by the charge on the object is a. voltage b. current c. resistance d. electric field e. critical temperature ANS: D PTS: 1 The electric field shown is produced by a single point charge at the center of the picture. 21. What type of charge produces the electric field shown? a. positive b. negative c. neutral d. impossible to tell ANS: A PTS: 1 22. If a new positive point charge is placed at location A directly to the right of the one pictured, the force on it will a. be zero b. push it to the right c. push it to the left d. be in an unknown direction ANS: B PTS: 1 23. If a new negative point charge is placed at location B directly above the one pictured, the force on it will a. be zero b. push it upward c. push it downward d. be in an unknown direction ANS: C PTS: 1 24. What force will a negative charge placed at location C feel? a. zero b. a force up and to the left c. a force up and to the right d. a force down and to the left e. a force down and to the right ANS: E PTS: 1 25. Suppose both of the new charges from questions 41 and 41 are in their respective positions simultaneously. The forces on each of them are a. still zero b. in the same directions as they were when each was alone c. both in new directions d. the same as before for the positive charge but different for the negative charge ANS: C PTS: 1 26. Two charged bodies separated by a distance d exert an electrical force on each other. The charge on one of the bodies is doubled. The electrical forces on each body now a. double b. decrease by 1/2 c. stay the same d. differ—the force on the other body doubles, but the force on the body whose charge was changed stays the same as before e. increase by a factor of four ANS: A PTS: 1 27. What is the usual symbol used to represent an amount of charge? a. C c. e b. q d. none of the above ANS: B PTS: 1 28. When we say charges are ‘positive’ or ‘negative’ we are speaking of a. two intrinsically different types of charge found in nature b. an excess vs. a deficiency of charge c. charges existing vs. not existing d. none of the above ANS: A PTS: 1 29. Two charged bodies separated by a distance d exert an electrical force on each other. The distance d is doubled. The electrical force on each body now a. decreases by 1/4 b. decreases by 1/2 c. stays the same d. increases by 2 times e. increases by 4 times ANS: A PTS: 1 30. Electrons are a. positively charged b. negatively charged ANS: B c. uncharged d. variably charged PTS: 1 31. The resistance of a conducting material depends on its a. composition b. length c. diameter d. temperature e. all of the above ANS: E PTS: 1 32. If the length of a wire increases, its resistance a. increases b. decreases c. does not change d. will increase or decrease depending on the composition e. will change in a way that can not be determined ANS: A PTS: 1 33. If the diameter of a wire increases, its resistance a. increases b. decreases c. does not change d. will increase or decrease depending on the composition e. will change in a way that can not be determined ANS: B PTS: 1 34. If the temperature of a wire increases, its resistance a. increases b. decreases c. does not change d. will increase or decrease depending on the composition e. will change in a way that can not be determined ANS: A PTS: 1 35. If I short out a D cell and draw a current of 7 A for 5 s, how many coulombs of charge move through the circuit? a. 7 C b. 5 C ANS: D c. 7/5 C d. 35 C PTS: 1 36. The kilowatt-hour is a unit of a. power b. energy ANS: B c. voltage d. current PTS: 1 37. The light bulbs in this circuit are connected in a. parallel c. neither parallel nor series b. series d. a short circuit ANS: A PTS: 1 38. The light bulbs in this circuit are connected in a. parallel. c. neither parallel nor series. b. series. d. a short circuit ANS: B PTS: 1 39. When a 12 volt car battery is short circuited with a wire, the current drawn from the battery is 100 amperes. The resistance of the wire is a. zero b. 0.12 ohms c. 100/12 = 8.33 ohms d. 1200 ohms e. none of the above ANS: B PTS: 1 40. A battery operating a large flashlight produces a current of 2 amperes in a light bulb that has a resistance of 4 ohms. The voltage of the battery is a. 0.5 volts c. 8 volts b. 2 volts ANS: C d. none of the above PTS: 1 41. An electric toaster operating on 120 volts draws a current of 6 amperes. The resistance of the toaster is a. 0.05 ohms b. 20 ohms ANS: B c. 720 ohms d. none of the above PTS: 1 42. In the U.S. AC line voltage oscillates at a frequency of a. 50 Hz c. 120 Hz b. 60 Hz d. none of the above ANS: B PTS: 1 A light bulb used in a slide projector draws a current of 6 amperes when operating on 120 volts. 43. The resistance of the light bulb in ohms is a. 0.05 c. 720 b. 20 d. none of the above ANS: B PTS: 1 44. The power consumed by the light bulb in watts is a. 0.05 c. 720 b. 20 d. none of the above ANS: C PTS: 1 45. If two slide projectors are connected in parallel across the same 120 volt source, the current drawn from the source in amperes is a. 3 b. 6 c. 9 d. 12 e. none of the above ANS: D PTS: 1 46. If two slide projectors are connected in series across the same 120 volt source, the current drawn from the source in amperes is a. 3 b. 6 c. 9 d. 12 e. none of the above ANS: A PTS: 1 47. The energy used by a 100 watt light bulb in 1 hour is a. b. c. d. e. 0.01 J 360,000 J 100 J 6,000 J none of the above ANS: B PTS: 1 A heater is rated at 1200 watts for a 120 volt source. 48. The current in amperes drawn by the heater is a. 0.1 c. 144,000 b. 10 d. none of the above ANS: B PTS: 1 49. The resistance in ohms of the heater is a. 0.1 b. 10 ANS: D c. 144,000 d. none of the above PTS: 1 50. If two heaters are connected in parallel across the 120 volt source, the total power in watts drawn from the source is a. 600 b. 1200 ANS: C c. 2400 d. none of the above PTS: 1 51. If two heaters are connected in parallel across the 120 volt source, the current in amperes drawn from the source is a. 5 b. 10 ANS: C c. 20 d. none of the above PTS: 1 52. Why is most matter electrically neutral? a. It contains no charges. b. There are equal amounts of positive and negative charges present. c. The charge on the electrons and protons in the material is too small to notice. d. none of the above ANS: B PTS: 1 53. Lightning is dangerous to humans because lightning strokes a. carry large currents c. have no resistance b. have high voltages d. fry whatever they hit ANS: A PTS: 1 54. Why do you hear thunder a substantial time after seeing a lightning flash? a. The sound is produced later than the light is. b. Your eyes respond more quickly than your ears. c. The flash and thunder really are simultaneous, but the thunder lasts longer than the flash. d. Sound travels much more slowly than light. ANS: D PTS: 1 55. How come birds can land on overhead power lines without getting electrocuted? a. Their feet are good insulators. b. They are saved by their small size. c. Both their feet are on the same wire, so they don’t complete a circuit. d. They are just lucky, I guess. ANS: C PTS: 1 MULTIPLE RESPONSE 1. A battery supplies a. AC current b. DC current c. resistance d. voltage e. positive ions ANS: B, D PTS: 1 2. What does a neutral atom become if it acquires an extra electron? a. negatively charged b. positively charged c. an ion d. a molecule ANS: A, C PTS: 1 The electric field shown is produced by a single point charge at the center of the picture. 3. What force might a charge placed at location D feel? a. zero b. an upward force c. a downward force d. a force to the right e. a force to the left ANS: D, E D if the charge is positive, E if it is negative PTS: 1 4. Two charged bodies separated by a distance d exert a repulsive electrical force on each other. The signs of the charges on the two bodies might be a. + and + b. – and – c. + and – d. any of the above e. not determinable ANS: A, B PTS: 1 5. Ohmic heating is a. always undesirable b. used in light bulbs ANS: B, C c. what makes fuses “blow” d. all of the above PTS: 1 COMPLETION A heater is rated at 1200 watts for a 120 volt source. 1. If two heaters are connected in parallel across the 120 volt source, the current drawn from the source is __________. ANS: 20 amperes PTS: 1 2. The current drawn by the heater is __________. ANS: 10 amperes PTS: 1 3. The resistance of the heater is __________. ANS: 12 ohms PTS: 1 4. If two heaters are connected in parallel across the 120 volt source, the total power drawn from the source is __________. ANS: 2400 watts PTS: 1 5. Like charges _________, unlike charges __________. ANS: repel, attract PTS: 1 6. An atom with fewer electrons than protons is a __________. ANS: positive ion PTS: 1 7. The type of current supplied by a battery is __________. ANS: DC current PTS: 1 8. In the U.S., AC line voltage oscillates at a frequency of __________. ANS: 60 Hz PTS: 1 9. An object that has zero resistance is a __________. ANS: superconductor PTS: 1 10. The rate of flow of electric charge is __________. ANS: current PTS: 1 11. Superconductivity is lost when a certain __________ is exceeded. ANS: critical temperature PTS: 1 12. A charged particle creates an electric ________ in the space around it. ANS: field PTS: 1 13. Then energy per unit charge supplied by a battery is its __________. ANS: voltage PTS: 1 14. A quantity that measures the opposition to the flow of charge is __________. ANS: resistance PTS: 1 15. The size of the current flowing through a conductor equals the __________ divided by the conductor’s ___________. ANS: voltage, resistance PTS: 1 16. If you think of a battery as an electric charge “pump,” the battery voltage is analogous to __________. ANS: pressure PTS: 1 17. The force on a charged object divided by the charge on the object is __________. ANS: electric field PTS: 1 18. Two charged bodies separated by a distance d exert an electrical force on each other. The distance d is doubled. The electrical force on each body is now __________ times the original force. ANS: 1/4 PTS: 1 19. Two charged bodies separated by a distance d exert an attractive electrical force on each other. The signs of the charges on the two bodies are __________ and __________. ANS: +,– PTS: 1 20. Four things that the resistance of a conducting material depends on are __________, __________, __________ and ___________. ANS: composition, length, diameter, temperature PTS: 1 21. If the length of a wire increases, its resistance __________. ANS: increases PTS: 1 22. If the diameter of a wire increases, its resistance __________. ANS: decreases PTS: 1 23. If the temperature of a wire increases, its resistance __________. ANS: increases PTS: 1 24. If the voltage across the ends of a wire increases, the current in the wire __________. ANS: increases PTS: 1 25. AC voltages can be easily increased or decreased through use of a __________. ANS: transformer PTS: 1 26. When a 12 volt car battery is short circuited with a wire, the current drawn from the battery is 100 amperes. The resistance of the wire is __________. ANS: 0.12 ohms PTS: 1 27. A battery operating a large flashlight produces a current of 2 amperes in a light bulb that has a resistance of 4 ohms. The voltage of the battery is __________. ANS: 8 volts PTS: 1 28. An electric toaster operating on 120 volts draws a current of 6 amperes. The resistance of the toaster is __________. ANS: 20 ohms PTS: 1 A light bulb used in a slide projector draws a current of 6 amperes when operating on 120 volts. 29. The resistance of the light bulb is __________. ANS: 20 ohms PTS: 1 30. The power consumed by the light bulb is __________. ANS: 720 watts PTS: 1 31. If two slide projectors are connected in parallel across the same 120 volt source, the current drawn from the source is __________. ANS: 12 amperes PTS: 1 32. If two slide projectors are connected in series across the same 120 volt source, the current drawn from the source is __________. ANS: 3 amperes PTS: 1 33. The energy used by a 100 watt light bulb in 1 hour is __________. ANS: 360,000 J PTS: 1 MATCHING a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. AC attract critical temperature electric current DC electric field negative ion positive ion i. j. k. l. m. n. o. p. superconductivity is lost when this is exceeded an atom with fewer electrons than protons type of current supplied by a battery employed in toasters and fuses has zero resistance consists of charges flowing back and forth rate of flow of electric charge repel resistance semiconductor transformer superconductor voltage electric charge ohmic heating 8. 9. 10. 11. used to change AC voltages the energy per unit charge supplied by a battery like charges do this it is measured in ohms 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: C H E P M A D L N I J PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 PROBLEM 1. A battery in a large flashlight produces a current of 2 amperes in a light bulb that has a resistance of 3 ohms. What is the voltage of the battery? ANS: 6 volts PTS: 1 2. An electric toaster operating on 120 volts draws a current of 9 amperes. What is the resistance of the toaster? ANS: 13.3 ohms PTS: 1 3. The light bulb used in a slide projector draws a current of 4 amperes when operating on 120 volts. (a) What is the bulb’s resistance? (b) What is the bulb’s power consumption? ANS: (a) 5 amperes, (b) 2.4 ohms PTS: 1 4. How much energy does a 100 watt light bulb use in 1 hour? Express your answer in (a) joules and in (b) kilowatt-hours. (c) Also find how much money it costs if electricity sells for 10 cents per kW-h. ANS: (a) 360,000 J, (b) 0.1 kW-h, (c)1 cent PTS: 1 5. An electric motor on an airplane operates on 24 volts and draws a current of 15 amperes. (a) What is the power consumption of the motor? (b) How much energy does the motor use during a 2 hour flight? ANS: (a) 360 watts, (b) 2,592,000 J PTS: 1