* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download HW #5
Survey
Document related concepts
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization group wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Center of mass wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
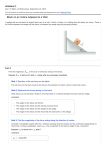
PHYSICS 1500 FS 2013 Homework #5 (due Friday, September 27, 2013 at the beginning of class) For these problems, please use the Newton’s Laws Problem Solving Scheme! 1. A 65 kg person stands on a bathroom scale in an elevator moving downward. If the scale reads 720 N, what are the magnitude and direction of the elevator's acceleration? (Hint: A scale reads the value of the upward normal force it is exerting.) 2. James Bond jumps from the top of a building 4.2 m tall. Being in top shape, he bends his knees in order to decelerate his torso on impact over a distance of 60cm. Bond’s torso’s mass is 45 kg. a. Calculate Bond’s velocity just before impact. b. Find the average acceleration [added later: and the average force on the torso due to the legs] during deceleration. (Hint: Draw that free-body diagram!) 3. A block on a smooth horizontal surface is connected by a thin rope passing over a pulley to a block of different mass hanging vertically without further support. Ignore friction and masses of pulley and rope. a. Sketch the physical situation and draw a free body diagram for each block showing all forces acting on that block. b. Using Newton’s second law, find the acceleration of the system. c. Determine the tension in the cord. 4. A right triangular wedge of mass M and angle θ rests on a horizontal table. A block of mass m rests on the wedge. The contacts between wedge and table and between wedge and block are frictionless. a. What horizontal acceleration must the wedge have relative to the table so that the block stays stationary on the wedge? b. What horizontal force should be applied to the wedge to produce this result? c. Suppose no horizontal force is applied to the wedge. Describe the resulting motion. 5. Consider three boxes of different masses on a frictionless tabletop in contact with each other. Some force F is applied to the leftmost box, pushing it to the right. It thus will push on box 2 which in turn will exert a force on box 3. a. Draw a free-body diagram for each of the boxes. b. Calculate the acceleration of the system. c. Determine the net force on each block. d. Find the force of contact that each block exerts on its neighbor. e. Assume now that all boxes have a mass of 8kg and the force F is 76 N to evaluate the results of b,c,d numerically.