* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download White Dwarf star. Are
Chinese astronomy wikipedia , lookup
History of supernova observation wikipedia , lookup
Corona Borealis wikipedia , lookup
Spitzer Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Chronology of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Star of Bethlehem wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
H II region wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
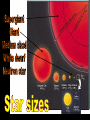
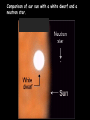
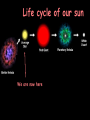
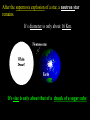
The Universe Pictures by the Hubble Space Telescope Notice the individual stars in the picture. They are not part of the galaxy in the picture but part of our own Milky Way Galaxy. We think! This is not really a picture of our galaxy – just one that looks like what we think our galaxy is like! Top view Side view Every star we see in the night sky is in our own galaxy. The Milky Way is estimated to have 200 billion stars. Current estimate of the age of the universe is 13.7 billion years. The solar system is 4.6 billion years old. The solar system is not the same age as the entire universe. They seem to form a picture in the sky. People use them to find their way around the sky like someone using objects to get from place to place. To measure the distances in space, astronomers use a light year. A light year is the DISTANCE light travels in one year. One light year is equal to a little under 6 trillion miles! (6,000,000,000,000) Proxima Centauri is the closest star to our solar system. It is about 4 light years away. Going the speed of light it would take us 4 years to get there. Traveling as fast as the average spaceship, it would take between 70,000 and 100,000 years to get there! https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ewGsiUPeBD4 Types of Stars Comparison of our sun with a white dwarf and a neutron star. Star color Determined by surface temperature. Hottest are blue – coolest are red. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IurFmd8xDe0 Protostars Gravity pulls huge nebulas of hydrogen gas and dust into a single spinning cloud. The particles crash into each other H H Matter heats up to about 15 million degrees. The mass begins to shine brightly. Fusion begins….. A star is born! This is when a star forms and it begins its “life.” https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tnzRUYSiCnc Medium-Sized Stars H Hydrogen fuel is fused into helium at the star’s core until the hydrogen is used up. H He The core shrinks, heats up, & releases energy. H The star heats, expands, reddens and becomes a …… Red Giant These drifting gases form a nebula ring around the star. The star is dying. It grows fainter and fainter. Gravity causes its matter to collapse inward. The star is squeezed into a…… …….a White Dwarf star. o Are super dense stars with a carbon core. o size of our (Our sun’s) sun has been squeezed into the size of the earth. When a star runs out of fuel, it dies. So a star has a life similar to a battery that cannot be recharged. When the battery runs out of energy, it is finished. Our sun will run out of energy and it will be finished too. But this will not happen for another 5 billion years! Life cycle of our sun We are now here Massive Stars Has about 6 times as much mass as our sun. Burn hydrogen at first. Redden as their helium core forms. Become Red supergiants. Start expanding. A Supernova happens ! The entire sky lit up for weeks. http://www.maniacworld.com/Crab-SupernovaExplosion.html After the supernova explosion of a star, a neutron star remains.. It’s diameter is only about 16 Km. It’s size is only about that of a chunk of a sugar cube The core’s gravity is so strong that even light can’t escape. The core has become ……a….. A Black Hole This diagram follows the life of both large and average stars. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hoLvOvGW3Tk