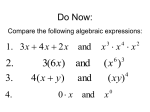* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Grade 7- Chapter 4
Survey
Document related concepts
History of logarithms wikipedia , lookup
Bra–ket notation wikipedia , lookup
Abuse of notation wikipedia , lookup
Musical notation wikipedia , lookup
History of mathematical notation wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Location arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
Big O notation wikipedia , lookup
Proofs of Fermat's little theorem wikipedia , lookup
Real number wikipedia , lookup
Factorization wikipedia , lookup
P-adic number wikipedia , lookup
Large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
Grade 7- Chapter 4 Goals: Key Understandings: Students will understand that… There are equivalent forms for any real number. The results of an operation depend on the types of numbers involved. Multiplying and dividing fractions is sometimes counter-intuitive. Essential Questions: What is the relationship between the position of a number on the number line and the value of the number? How does identifying the types of numbers in an operation help in determining the reasonableness of the result? Students will know that… Students will be able to… One number is divisible by another if it Use the divisibility rules to identify the can be divided evenly by that number factors of a given number. (4-1) with no remainder. List positive factors for various We have divisibility rules that allow us numbers. to tell if a number would be divisible. List factor pairs for various numbers. (pp. 178+179) A factor is a number that can be divided into another evenly. ______________________________________ _______________________________________________ You can use exponents to show repeated multiplication. A power has two parts: a base, the number you will be multiplying, and an exponent, the number of times you will be multiplying the base. Ex: 43 = 4*4*4 You can extend PEMDAS to include simplifying exponents as needed. Ex: (-5)2 = -5* -5 OR +25; while -52 = -( 5*5) OR -25. The exponent affects only that which it is directly adjacent to. Rewrite expressions using exponents instead of repeated multiplication. (4-2) Simplify terms with exponents using PEMDAS. Evaluate terms with exponents using PEMDAS. _________________________________________________ A prime number is a number which can only be multiplied by itself and one. Ex: 13 = 13*1 A composite number has more than two factors. Ex: factors of 24= 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 12, and 24. You can write a composite number as a product of its prime factors. Ex: 24 = 2 * 2* 2* 3 or 23* 3. This is called prime Identify prime and composite numbers and justify. (4-3) Use a factor tree to determine the prime factorization of various numbers then write using exponential notation. Use prime factorization to identify the GCF for two numbers. Venn diagrams can be used to illustrate common factors. Grade 7- Chapter 4 factorization. Greatest common factors or GCF’s are the largest factors that 2 numbers have in common. These can be used to simplify fractions. _____________________________________ Equivalent fractions represent the same portion of the whole, but may be written differently. Ex: 2/4 = ½. You can simplify fractions by dividing the numerator and denominator by the same common factor. Ex: With 10/12 you can divide the numerator and denominator by 2 to get 5/6. You can find equivalent fractions with common denominators for adding or subtracting by multiplying the numerator and denominator by the same number. Ex: With 2/8 + ¾ you can multiply the numerator and denominator in ¾ by 2 to get 6/8. _____________________________________ You can use tree diagrams or nets to account for all possibilities. _____________________________________ A rational number is any number that you can write in the form a/b where a and b are integers and b is not zero. All numbers have a distinct position on the real number line. ____________________________________ When multiplying powers with the same base, just add the exponents. Ex: 23 * 24 = 27 because 23= 2*2*2 and 24= 2*2*2*2; so altogether we are multiplying 2 by itself 7 times, or 27. When raising a power to a power, multiply the exponents. Ex: (23)2 = (2*2*2) *(2*2*2) or 26.because you’re multiplying 2 six times. _________________________________________________ Find equivalent fractions by multiplying (to find common denominators) or dividing (to simplify). (4-4) Simplify fractions by using the divisibility rules. _________________________________________________ Solve problems by accounting for all possibilities using a tree diagram, net, or chart. (4-5) __________________________________________________ Write equivalent fractions using positive and negative integers. (4-6) Find, graph, and position fractions on a number line and in an ordered list. Evaluate fractions containing variables then simplify. Identify rational numbers which lie between two given quantities. _________________________________________________ Simplify exponential expressions containing powers with the same base. (4-7) Simplify powers of powers. Compare exponential expressions. Evaluate exponential expressions using graphing calculators. Grade 7- Chapter 4 _____________________________________ When dividing exponential expressions containing the same base, just subtract the exponents. Ex: 23/ 22 means 2*2*2/ 2*2 which equals 2/1 or 21. Any number to the zero power is equal to 1. Ex: 20= 1; 100 = 1 Any base raised to a negative power is the reciprocal. Ex: 10-2 = 1/100 because it means 1/10* 1/10. While b3 / b9 = b-6 _________________________________________________________ Scientific notation allows you to write very large or very small numbers using powers of ten. Ex: 189,750,000 = 1.8975 * 108; while 0.00001897 = 1.8975* 10-5. Standard notation does not include powers of ten. Ex: 1.5 * 102 = 150 in standard notation. Remember: when multiplying powers with the same base, just add the exponents. Ex: 23 * 24 = 27 because 23= 2*2*2 and 24= 2*2*2*2; so altogether we are multiplying 2 by itself 7 times, or 27. __________________________________________________ Simplify rational expressions with exponents by dividing powers with the same base. (4-8) Simplify expressions with integer exponents (zero or negative). _____________________________________ Translate numbers from scientific notation to standard notation or back again. (4-10) Compare and order numbers written in scientific notation. Multiply numbers written in scientific notation by combining the exponents. Use calculators to multiply numbers written in scientific notation. Learning Plan Day Section / Objectives Q1 Q2 Q3 Capstone Activity- Performance Task (Project) Homework Grade 7- Chapter 4 12 Chapter Review 13 Chapter Test Goals: Key Understandings: Students will understand that… There are equivalent forms for any real number. The results of an operation depend on the types of numbers involved. Multiplying and dividing fractions is sometimes counter-intuitive. Essential Questions: What is the relationship between the position of a number on the number line and the value of the number? How does identifying the types of numbers in an operation help in determining the reasonableness of the result? How can we use a number line to solve problems?