* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 13
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Cultivated plant taxonomy wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Fertilisation wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Embryophyte wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
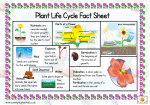
Chapter 13 Plant Processes SECTION 1 Reproduction of Flowering Plants Remember: Flowers are the structure for angiosperms to carry out sexual reproduction. The main role of the flower is to produce sperm and egg cells for reproduction. How does it happen? Recall the male structures of the flower (anthers that produce pollen) and the female structure (stigma, style and ovary that contains the ovules). If a pollen grain from an anther lands on the stigma, a pollen tube forms down through the style. The sperm cells travel down the pollen tube and enter the ovary. Inside the ovary, there are the ovules that contain the eggs. The sperm travel down the pollen tube and fertilize an egg. The ovules develop into seeds and the ovary surrounding the ovules develops into a fruit. Example: A watermelon plant will bloom with flowers. When the pollen is formed, an insect often serves as a pollinator and transfers the pollen onto the stigma. A pollen tube grows down through the style and into the ovary. The sperm travel down the pollen tube and fertilize the egg. The fertilized egg turns into a seed or seeds if more than one egg is fertilized and the ovary turns into the fruit we call a watermelon. This is the same process for tomatoes, squash, beans, peas, apples, pears, and any other flowering plants you may want to write down. SEEDS Seeds contain the young plant that is capable of producing more flowers and fruit. When a seed becomes mature in fruit, the seed becomes dormant. In other words the seed does not develop any further until conditions are “good” again. Many seeds require cold temperatures, some require freezing, and some may require extreme heat like a fire to break their dormant period. When a seed ends up in a suitable location to grow (proper temperature, moisture and oxygen) it germinates or undergoes germination. Germination is when the young plant begins to grow. Experiment at home: Take a small bowl with moist paper towels and line the bottom, place 5-10 dry pinto beans into the bowl and cover with a few more moist paper towels. Keep the towels moist but not wet. Check the beans daily, but be careful not to allow them to dry out. As you watch them for 7-10 days you will see the beans germinate (begin to grow). There are other methods of reproduction that are asexual. Some plants may send out rootlike structures from the main plant called runners. These runners will form new plants. Strawberries are an example of a plant that will send out runners to make new plants. Potatoes can also reproduce asexually. Have you ever seen an “eye” of a potato? You can cut the potato eye leaving some of the potato flesh with it and plant the eye and a new potato plant will grow. The new plant will be a clone genetically to the potato the eye was removed from. Some other plants may have “pieces” of vegetation fall from the plant that will grow into a new plant. The Food Making Process Plants make food in the form of a sugar (glucose). They do this through photosynthesis. Plants will take in carbon dioxide and water and capture the light energy from the sun and produce glucose and oxygen. The formula for photosynthesis should be a review for you. Formula for photosynthesis: 6CO2 + 6H2O --------light energy C6H12O6 + 6O2 Six Carbon Dioxides + Six Waters captured sunlight energy Yields Glucose + Oxygen The chemical that enables plants to capture the light energy is chlorophyll. It appears green because it absorbs all colors of the light spectrum except green light. It reflects the green light and that is why plants look green to us. Photosynthesis occurs mainly in the leaves of plants, but some plants also have stems that contain chlorophyll and photosynthesis can occur here also. The plants can use the glucose for their energy needs and when they do this they carry out cellular respiration like we discussed humans and other animals do. When they need to repair structures, they will use the glucose and oxygen and give off carbon dioxide and water. RECALL: If we look at the layers of a leaf, we know that the lower epidermis and cuticle have guard cells that regulate gas exchange into and out of the leaf. This is where carbon dioxide enters and oxygen and water will leave the plant. If there is more water leaving the plant than the root system is taking into the plant, the plant will wilt. To prevent total drying out at times, the guard cells may “close” off the opening. The opening the guard cells surround is called the stoma (singular) or stomata (plural). When water is lost through the leaves of plants it is called transpiration. SECTION 3 Plant Responses to the Environment Recall: anything that causes a reaction in a tissue is a stimulus. Plants also have stimuli, which we call tropisms. The two main tropisms are gravitropism and phototropism. Phototropism is the tendency for plants to grow toward the available sunlight. If you place a plant near a window, it will “bend” toward the light from the window. It is bending, but the side away from the light tends to grow a little faster and it appears the plant bends toward the light. It does grow toward the light. In gravitropism, the roots of plants grow toward gravity, which is a positive tropism and the shoot system grows away from the center of gravity and we call this a negative tropism. Some plants respond to seasonal changes. Many may change the colors of their leaves based on the length of the night. Some may flower when the length of day and night fall into a specific range. Some may flower when the days are longer than the nights (long day plants like lettuce and clover), and vise versa like poinsettias. During long nights, their green leaves will turn red, and so individuals that grow them for Christmas sales, use artificial light and control when the leaves are red. Recall: Some trees stay green all yearlong, these are evergreen trees. Evergreen trees include conifers, cedars, spruces, hemlocks and Southern Magnolias in our area. The trees with leaves that change color in the fall are called deciduous trees because they lose their leaves during the winter. As the days get shorter in the fall, the chlorophyll that reflects the green we see begins to break down and we begin to see the chlorophyll types that reflect reds, yellows, and scarlet shades. This is considered one of the prettiest times of the year in the southeastern United States. So it is not the color of the chlorophyll we see, but the colors that are not absorbed. Your clothing is the same way. A red shirt is red because it reflects the red wavelength of light and absorbs all other colors. Structures that are white reflect ALL wavelengths and those that are black absorb ALL wavelengths. SECTION 1 STUDY GUIDE 1. The ____________________ contain the male and female reproductive parts of Angiosperm plants. 2. The _______________________ make the pollen grains which contain the ______________________ cells in Angiosperms. 3. Pollen grains must land on the _______________________ and grow pollen tubes to allow sperms to enter the ovary of a flower. 4. A sperm cell unites with an _____________________ in order for fertilization to occur in an angiosperm. 5. The colorful portions of a flower make up the ________________. 6. The _______________________ develops into a fruit and the ______________ develops into seeds. 7. If there are six fertilized ovules in an ovary, how many seeds will form and how many fruit will develop. 8. When seeds are inactive (not growing), we say they are ____________________. 9. When seeds ______________________ they begin to grow and the young plant will emerge. 10. Some flowering plants can also reproduce by ______________________ reproduction. An example of this is the eye of a potato. SECTION 2 STUDY GUIDE 1. _____________________________ is the chemical that captures sunlight energy in plants for photosynthesis. 2. Explain why we see plants as being green. 3. 6CO2 + 6H2O --------light energy C6H12O6 + 6O2 is the chemical equation for ___________________________________. 4. C6H12O6 is the chemical formula for what sugar? _____________________ 5. Organisms that break down C6H12O6 for the use of carrying out life activities are carrying out ________________________ respiration. This will release carbon dioxide and water. 6. _______________________ is the process in which plants lose water out their stoma. 7. The size of stoma in a plant leaf is controlled by the ___________________ ____________________ that surround the stoma. 8. When plants grow in response to a stimulus like light or gravity, we say the stimulus is a _____________________. 9. __________________________ is the growth stimulus that results due to gravity. 10. __________________________ is the growth stimulus plants have in response to light. 11. The length of ________________ and _________________ often triggers growth responses in plants. 12. _________________________ have their leaves year round. They may lose some leaves, but they will be replaced. 13. ___________________________ trees lose their leaves during some portion of the year. This allows trees to slow transpiration and survive during extreme periods of the year. Some places the trees may lose their leaves during a drought and others may lose their leaves during cold temperatures.