* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sharing-Lives-Lesson
Persecution of Muslims wikipedia , lookup
Islam and secularism wikipedia , lookup
The Satanic Verses controversy wikipedia , lookup
Satanic Verses wikipedia , lookup
Soviet Orientalist studies in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Political aspects of Islam wikipedia , lookup
The Jewel of Medina wikipedia , lookup
LGBT in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Sources of sharia wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Islamism wikipedia , lookup
International reactions to Fitna wikipedia , lookup
Islam in South Africa wikipedia , lookup
Violence in the Quran wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
Islam and violence wikipedia , lookup
Islam in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Islam in the Netherlands wikipedia , lookup
Morality in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
Islamic culture wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Mormonism wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Bangladesh wikipedia , lookup
War against Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Indonesia wikipedia , lookup
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
Hindu–Islamic relations wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Europe wikipedia , lookup
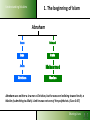
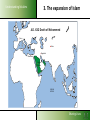
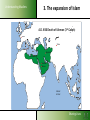
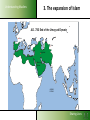
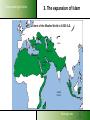
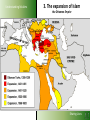
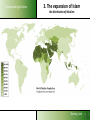
Understanding Muslims LESSON 3: Understanding Muslims Sharing Lives Understanding Muslims Mosul, 400 km from Bagdad, is where Nineveh used to be. On the Jonah hill was the Joenoes mosque, which attracted many pilgrims. The mosque was built over an Assyrian temple, that later was turned into a fire temple for Ahura Mazda werd, later a monastery and later a church. In one of the rooms one could find the grave of Nabi Joenoes, decorated with whale bones. The mosque was bombed in July 2014 by IS Muslim extremists. Jonah in Islam Joenoes mosque in Mosul, before and after destruction by Muslim extremists in July 2014 Sharing Lives Understanding Muslims References to Jonah in the Qur'an Sura 4:163; Sura 10: 98-100 - Sura 10 bears his name Sura 21:87-9 - “Fishman” Sura 37:138-148; Sura 68: 48- 50 -”man in the whale” If you want to pass for an exam or something, then read the prayer of Jonah, when he was in the whale. Sharing Lives Understanding Muslims Jonah (Yunus) in the Qur’an Discuss: 1. What do you find significant when you compare the Biblical narrative of Jonah with that found in the Qur’an and the Islamic traditions? 2. How do you explain the similarities and differences? Sharing Lives Understanding Muslims 1. The beginning of Islam Abraham Isaac Ishmael Jews Arabs Jesus Muhammad Christians Muslims Abraham was neither a Jew nor a Christian, but he was one inclining toward truth, a Muslim (submitting to Allah). And he was not one of the polytheists. (Sura 3:67) Sharing Lives Understanding Muslims 2. The person Muhammad 570 AD Born in Mecca of the Hashemite branch of the Quraish Tribe Father died before his birth 576 His mother died. Cared for by his grandfather for two years, then by his uncle - Abu Talib 582 Began helping with trading caravans to Syria 593 Led trading caravans of a wealthy widow, Khadija, to Syria 595 Married Khadija. Began contacts with Hanifs. 610 First recitation (surah 96:1-3) in a cave on Mt. Hira 612 Resumption of recitations (the Meccan suras) Years of 616 Persecution by the Quraish at its height persecution 621 Abu Talib and Khadija die 622 Flight from Mecca to Yathrib (Medina) 623 Establishment of Islamic state; start Islamic calendar Years of war 630 Subjugation of Mecca 632 Died and buried in Medina According to the Qur’an: an excellent example to follow Sharing Lives Understanding Muslims 3. The expansion of Islam A.D. 632 Death of Mohammed Tours Talas Tunis Baghdad Alexandria Medina Mecca INDIAN OCEAN Sharing Lives Understanding Muslims 3. The expansion of Islam A.D. 656 Death of Uthman (3rd Caliph) Tours Talas Tunis Baghdad Alexandria Medina Mecca INDIAN OCEAN Sharing Lives Understanding Muslims 3. The expansion of Islam A.D. 750 End of the Umayyad Dynasty Tours Talas Tunis Baghdad Alexandria Medina Mecca INDIAN OCEAN Sharing Lives Understanding Muslims 3. The expansion of Islam Extent of the Muslim World in 1500 A.D. Tours Talas Tunis Baghdad Alexandria Medina Mecca INDIAN OCEAN Sharing Lives Understanding Muslims 3. The expansion of Islam the Ottoman Empire Sharing Lives Understanding Muslims 3. The expansion of Islam the distribution of Muslims Sharing Lives Understanding Muslims 3. The expansion of Islam the distribution of Muslims Sharing Lives 3. The expansion of Islam Understanding Muslims Muslims in Europe Total Muslims in Europe: Russia 13% 20,000,000 France 8,3% 5,000,000 Germany 6% 45,700,000 4,9% 4,000,000 Albania 70% 2,400,000 Serbia-Mont 19% 2,020,000 Ukraine 4% 2,000,000 U.K. 2,7%1,600,000 Bosnia 40% 1,600,000 Spain 2,5% Italy 1,8% 1,000,000 Bulgaria 1,000,000 12% 986,0000 Netherlands 5,7% Macedonia 30% Greece 4,1 Belgium 3.5 Sweden 4 Austria 4.2 944,000 613,000 450.000 364.000 360,000 350,000 Switzerland Cyprus Denmark Norway Romania Croatia Slovenia Portugal Norway Slovakia Finland Hungary Czech Rep 4.4% 26 3.0 1.6 0.3 1.0 2.4 0.4 1.0 1.5 0.4 2 0.2 330,000 200,000 170,000 144,000 68,000 50,000 48,000 35,000 46,000 30,000 20,000 20,000 20,000 Sharing Lives Understanding Muslims 4. What Muslims Believe The three fundamental Islamic beliefs Tawhid (the oneness of God) Risalah (prophethood) Akhirah (life after death) Sharing Lives Understanding Muslims 4. What Muslims Believe Tawhid (the oneness of God) The most important Islamic belief. Everything in existence originates from the one and only Creator, who is the Sustainer and sole Source of Guidance. This belief governs all aspects of life. Recognition of this truth brings a unified view of life which rejects any division into religious and secular. Muslims stress the unity of God. The emphasis is on the majesty, transcendence and sovereignty of God. Sharing Lives Understanding Muslims What Muslims Believe Risalah (prophethood) 1. God has not left man without guidance for the conduct of his life. Since the creation of the first man, God has revealed His guidance to mankind through his prophets. Prophets who received books from God are called messengers. 2. All the prophets and messengers came with the same message: they urged the people of their time to obey and worship God alone and none other. Sharing Lives Understanding Muslims What Muslims Believe Risalah (prophethood) 3. Whenever the teachings of a prophet were distorted by people, God sent another prophet to bring them back to the Straight Path. 4. The chain of prophethood started began with Adam and ended with Muhammad, who is considered the final messenger of God to mankind. Sharing Lives Understanding Muslims What Muslims Believe Risalah (Prophethood) The revealed books from God are: • The Torah (Tawrah) • The Psalms (Zabur) • The Gospel (Injil) • The Qur’an, which is considered the final book of Guidance. Sharing Lives Understanding Muslims 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. Adam Idris (Enoch) Nuh (Noah) Hud Salih Ibrahim (Abraham) Isma'il (Ismael) Ishaq (Isaac) Lut (Lot) Ya'qub (Jacob) Yusuf (Joseph) Shu'aib Ayyub (Job) The Prophets of Allah 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. Musa (Moses) Harun (Aaron) Dhu'l-kifl (Ezekiel) Dawud (David) Sulaiman (Solomon) Ilias (Elijah) Al-Yasa (Elisha) Yunus (Jonah) Zakariyya (Zechariah) Yahya (John) Isa (Jesus) Muhammad Sharing Lives Understanding Muslims What Muslims Believe Akhirah (life after death) Everyone accountable to God on Day of Judgment; People judged on how they lived, by their actions; Who obeys and worships God will be receive a place in Paradise; A person who does not, will be sent to Hell, a place of punishment & suffering Angels record all actions of mankind; Sharing Lives Understanding Muslims The Five Pillars of Islam (The Basic duties of a Muslim) Hajj Prayer Sawm Salat Creed Zakat Shahada The 5 Pillars of Islam Fasting Sharing Lives Understanding Muslims The Five Pillars of Islam (The Basic duties of a Muslim) 1. Confessing the faith (shahadah) “There is no God except Allah. Muhammad is the messenger of Allah.” This declaration contains the two basic concepts of Tawhid (oneness of God) and Risalah (prophethood) and is the basis of all actions in Islam. Sharing Lives Understanding Muslims The Five Pillars of Islam (The Basic duties of a Muslim) 2. Compulsory Prayer (salah) • Performed 5 times a day, either in congregation or individually • • • • • Between dawn and sunrise Between midday and mid afternoon Between mid afternoon and sunset Just after sunset Between nightfall and dawn • Preceded by ceremonial ablutions • Requires proscribed postures and genuflections • Consists of memorised prayer – recitation of the first surah – the Fatiha • Each prayer takes a few minutes to complete “It is a system of spiritual, moral and physical training that makes a Muslim truly obedient to his Creator.” Islam: a brief guide, MET Sharing Lives Understanding Muslims The Five Pillars of Islam (The Basic duties of a Muslim) 3. Zakah (welfare contribution) Compulsory payment from one’s savings 2,5% of the value of cash, jewellery and precious metals, separate rate applies to animals, crops and mineral wealth. Can only be spent on helping the poor and needy, the disabled, the oppressed, debtors and other welfare purposes Considered an act of worship, to express that our wealth and property belong to God and that we are trustees. Sharing Lives Understanding Muslims The Five Pillars of Islam (The Basic duties of a Muslim) 4. Fasting (sawm) Obligatory fast during the month of Ramadan, the ninth month in the Islamic calender. Refrain from eating, drinking, smoking and from sex with marital partner from dawn to sunset every day. “Sawm is an annual training programme which increases a Muslim’s determination to fulfil his obligations to the Creator and Sustainer.” (Islam: a brief guide, MET) Sharing Lives Understanding Muslims The Five Pillars of Islam (The Basic duties of a Muslim) 5. Pilgrimage (hajj) A journey to the Ka’aba in Mecca, in the 12th month of Islamic calendar; Annual event; Obligatory at least once in a lifetime for those who can afford it; Symbolizes the unity of mankind as Muslims from every race and nationality assemble in equality and humility to worship God; Sharing Lives Sources of authority in Islam Understanding Muslims Qur’an from the arabic verb qaraa = read/recite Sacred book of Muslims, considered the final book of Guidance from God. Sent down to Muhammad by the Angel Gabriel 114 suras, received over a period of 23 years. After Muhammad’s death in 632 the fragments were gathered into a text. Heavenly copy of the Qur an Source: Life Challenge Africa Sharing Lives Understanding Muslims Sources of authority in Islam The Sunnah example of Muhammad contained in the books of Ahadith (sing. Hadith): collections of his sayings and actions and the actions approved by him. Six prominent and most authentic collections: Bukhari, Muslim, Tirmidhi, Abu Dawud, Nasa’I and Ibn Majah. Sharing Lives Understanding Muslims Sources of authority in Islam The Sunnah The different topics included in the Hadith of al-Bukhari revelation – belief - menstrual periods -rubbing hands and feet with dust -times of the prayers -call to prayers -characteristics of prayer - friday prayer - the two festivals -invoking Allah for rain -prostration during recital of Qur’an -actions while praying - funerals - pilgrimage retiring to a mosque for remembrance of Allah- sales and trade -agriculture – gifts –witnesses –peacemaking conditions wills and testament- jihad -beginning of creation - prophets -military expeditions led by Muhammad -virtues of the Qur’an –wedlock – marriage - divorce --supporting the family -food, meals -- sacrifice on occasion of birth –drinks – patients –medicine – dress - good manners and form --divine will -oaths and vows--laws of inheritance –limits and punishments set by Allah--punishment of disbelievers at war with Allah --dealing with apostates ---mortgaging -interpretation of dreams -afflictions and the end of the world etc. Sharing Lives Understanding Muslims Sources of authority in Islam Law schools in Sunni Islam Each school give different weight in legal opinions to prescriptions in the Quran, the Sunnah, the consensus of legal scholars, analogy (to similar situations at the time of Muhammad), and reason or opinion. The Hanifi School • Allows room for reasoning •Followers: Balkans, Turkey, Central Asia, India, Pakistan, Bangladesh The Maliki School • uses just the Hijazi Hadith •Followers: mainly in North Africa, Sahel The Shafi’i School • allow much wider number of Hadith • Followers: Yemen, Egypt, Syria, S.E. Asia, E. Africa The Hanbali School • very conservative and intolerant • Followers: Saudi Arabia Sharing Lives Understanding Muslims Different groups within Islam Sharing Lives Understanding Muslims Different groups within Islam Shi’a Muslims • Consider Ali, Muhammad’s son-in-law, and his descendants, as the lawful heirs of the political as well as religious leadership of Muslims. • Reject consensus • Added to the six beliefs – believe in an infallible Imam (an incarnation of the Godhead) who has super-human knowledge. • Shia Muslims can be found in Iran and Iraq, Yemen, Bahrain, Syria, Lebanon. Sharing Lives Understanding Muslims Different groups within Islam Ahmadiyya movement Founded by Mirza Ghulam Ahmed Qadiami (of the Punjab) who died in 1908 AD. Beliefs: • Muhammad is not the final prophet. • Jesus died and is buried in Srinagar, Kashmir. • Mirza Ghulam is the Mahdi Sharing Lives Understanding Muslims Different groups within Islam The Baha’i Began in Iran in the mid 1800s as an outgrowth of Shi’a Islam. Believes in oneness of God, religion and mankind, gender equality, harmony of religion and science and independent investigation of truth. Does not consider Muhammad as the last and greatest prophet, but as one in a series of prophets. The Qur’an is not the last revelation. Others, including the Scriptures of Baha’i followed. About 7 million adherents worldwide. Persecuted in some Islamic countries e.g. Iran. Sharing Lives Understanding Muslims Different groups within Islam The Salafi Movement Term refers to the “virtuous ancesters”the first three generations of Muslims after Muhammad’s death. Founded by Muhammad ibn ‘Abd al-Wahhad (died in 1791) and sometimes called Wahhabism. It is a puritanical, literalist tradition. Rejects anything not rooted in the original sources of Islam. It is influential in Europe, due to influence and money from Saudi Arabia. Sharing Lives Understanding Muslims Different groups within Islam Sufism seek a direct personal experience of the Divine in mysticism. started in the first century after the death of Muhammad. Adherents are found worldwide The word ‘sufi’ originates from ‘suf’, the Arabic word for wool, referring to the simple clothes of wool the early Muslim ascetics wore. It can also refer to ‘safa’ (purity), which explains why Sufism emphasizes purity of heart and soul. The basis of religion is loving God – God has to be loved for himself not for rewards or fear of punishment. intoxication assisted by chanting the Qur’an, music, drums, recitation of poetry – God addressed as the Eternal Beloved. Sharing Lives Understanding Muslims Different groups within Islam Alevis •Between 15 and 20 million, mainly in Turkey; •Many similarities between Alevis and the Bektashis of the Balkans; •Alevis are followers of Ali (son-in-law of Muhammad); •High respect for mystical poems and musical ballads; •Worship involves singing an dancing; •Have a 12-day fast during the first month of the Muslim calendar; •Visit and pray at the tombs of saints; •Alevi women worship together with men; Sharing Lives Understanding Muslims Different groups within Islam Folk or Popular Islam Islam Muslims practice in everyday life: ritual ceremonies at birth, puberty, marriage, funerals etc. amulets, talismans, magic, astrology, evil spirit repellents, etc. divination, omens love magic and fertility rites divination, dreams, oracles/prophecies Sharing Lives Understanding Muslims The Islamic Year Islamic Culture and Customs Muharram Safar 12 lunar months Rabi al Awwal 28 or 29 days. Jumada al Ula Year eleven days shorter than solar year. Rabi al Thani Jumada al Akhirah Rajab Sha’ban Ramadan Shawal Dhu al Qa’dah Dhu Hijjah Sharing Lives Understanding Muslims Islamic Culture and Customs Festivals Idul Fitr: first day after Ramadan. Special food is prepared. Visit friends and relatives. Special activities for children Idul Adha: 10 till 13th of the twelfth month. Animals are sacrificed, commemorating Abraham’s willingness to sacrifice his son. Sharing Lives Understanding Muslims Islamic Culture and Customs Marriage Usually arranged by parents, with consent of son and daughter Performed in a simple ceremony in the presence of relatives, friends and neighbors. Diet Forbidden to eat pork and animals not slaughtered in the name of God Forbidden to drink alcohol Sharing Lives Understanding Muslims Christians and Muslims To Discuss: 1. Are there things Christians can learn from Muslim? If so, what? 2. Mention several similarities and differences between Muslims and Christians. Sharing Lives Understanding Muslims Some areas of Commonality Between Muslims and Christians 1. The Qur'an affirms the God of the Bible surah 29:45 and surah 22:40 2. The revelation of God’s will in a book 3. Accountability to God 4. The importance of prayer 5. Submission to the will of God: sura 3: 18, 19 and James 4:7 and “As God wills” (inshallah); sura 18:23,24 and James 4:12-15. 6. Importance of brotherhood 7. Frankness in witnessing Sharing Lives The Main Problems Understanding Muslims that Muslims have with Christians A. Our faith The Trinity – they sometimes think that we worship three Gods The Deity of the Lord Jesus Christ – He is only a prophet The death of the Lord Jesus on the cross (and therefore, by implication, the resurrection) The integrity of the Bible – Muslims think that it has been changed and corrupted B. Our history The Crusades: a Christian ‘jihad’. The Colonial Period: exploitation of people – lies, deception Support of Israel. Cultural & economic colonialism. C. Our morals Degeneration of Western societies: gay rights, legalized prostitution, drug abuse, domestic violence, high divorce rate. Spreading its immorality in movies and in tourism. Sharing Lives Understanding Muslims The Main Problems that Muslims have with Christians To discuss: 1. What is your first reaction to how Muslims look upon Christians and Christianity? 2. How can we respond to these matters? Sharing Lives Understanding Muslims Homework: Write down two questions that you would like to ask the Muslims you will be meeting in the mosque during the next lesson. Sharing Lives