* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 1 Section 2.5 Ecological Niche
Survey
Document related concepts
Storage effect wikipedia , lookup
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
Introduced species wikipedia , lookup
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Occupancy–abundance relationship wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Restoration ecology wikipedia , lookup
Reconciliation ecology wikipedia , lookup
Renewable resource wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
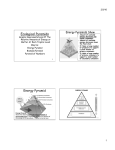
Grade 9 Academic Science – Ecology Ecological Niche Section 2.5 Pages 42-47 In ecology, a population is defined as a group of individuals of a single species living together within a specific habitat. A habitat offers features such as food, shelter, mating opportunities and conditions and ideal climatic conditions. An ecological niche is a very specific place occupied by an organism and the role of the organism within the place. As suggested in Science Perspective 9 (...your textbook...), an ecological niche is defined as “...the function a species serves in its ecosystem including what the species eats, what eats the species and how the species behaves.” To examine the ecological niche concept, we will look at five different species of warbler that occupy a similar but unique space in a coniferous tree. This “separation of space” was first reported by ecologist Robert H. MacArthur. Looking at the diagram, there are five different warblers: Species B – Cape May warbler Species C – Bay-breasted warbler Species D – Blackburnian warbler Species E – Black-throated green warbler Species F – Myrtle warbler. The diagram shows that each species occupies a somewhat different part of the tree. For example, the Cape May warbler uses the resources and shelter of the upper portion of the tree (Part B1 – shaded portion of the tree). By feeding and nesting in B1, the Cape May warbler avoids direct competition with the other warbler species. Species D, Blackburnian warbler, lives in a similar space, but its behaviour is significantly different from the Cape May warbler. The Blackburnian warbler spends most of its time in the outer branches of the tree and occupies lower branches as well as the crown. By feeding in different parts of the tree, direct competition is eliminated. Relative to the Blackburnian warbler, Species C Baybreasted warbler lives mainly in the inner branches. Thus, the Bay-breasted warbler lives below the Cape May warbler and inside of niche of the Blackburnian warbler. The principle of competition exclusion states that evolutionary forces pull the niches of similar organisms apart so that the organisms adapt differently giving rise to niche differentiation. As such, two species cannot occupy the same ecological niche in a community. When two or more species co-exist, their niches are different. If their niches do not differ, one species will go extinct. Evolutionary changes occur as the different species diverge and evolve to exploit the resources specific to their unique niche. This is called Adaptive Radiation. First hypothesized by Charles Darwin, this form of evolution is the diversification of a common ancestral species into a variety of differently adapted species. Using the diagram, describe how Darwin’s finches illustrate the ecological principles of (1) ecological niche and (2) adaptive radiation. Ecological Pyramid Although communities vary considerably in structure, certain basic processes are common to all communities. For example, all ecosystems cycle nitrogen, carbon, water and phosphorus. Another basic principle is the flow of energy through the community. All organisms take in energy and the energy flows in one direction (unidirectional) through the community. Feeding relationships within a community form a pyramid. According the Science Perspectives 9, an ecological pyramid is a representation of energy, numbers or biomass relationships in ecosystems...and displays relationships between trophic levels within an ecosystem. About 10% of the total energy at any given trophic level is passed into the next level. This is the Rule of Ten. The “unavailable” energy is used in biological processes (e.g., growth, movement, reproduction) or lost at thermal energy. As can be observed, all organisms must obtain nutrients and energy from their environment. In pyramid, organisms can be organized as producers (Trophic Level A) and consumers (all other trophic levels). In this diagram of an aquatic ecosystem, Trophic Level A consists of phytoplankton (i.e., microscopic green plants). The phytoplankton are primary producers (i.e., they photosynthesize to produce carbohydrates (energy)). In this pyramid, the bottom level is the widest because the biomass of phytoplankton is greater than the biomass of any other trophic levels. Trophic Level B is the level of primary consumers. These consumers are small crustaceans (i.e., microscopic arthropods) that feed on the phytoplankton. As noted by the Rule of Ten, some energy is lost between Level A and Level B. This loss of energy continues throughout the pyramid. For this reason, less energy is present in each subsequent trophic level. As shown, the biomass of crustaceans is less than the biomass of the phytoplankton...and so on. Explain...Why are there a limited number of trophic levels in an ecological pyramid? In an energy pyramid (shown), the trophic levels decrease in width from lower to higher levels. This is not always the case for ecological pyramids of biomass and ecological pyramids of numbers. Using examples, explain why an inverted pyramid is possible.