* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Vision Screening and Ophthalmology
Survey
Document related concepts
Mitochondrial optic neuropathies wikipedia , lookup
Blast-related ocular trauma wikipedia , lookup
Contact lens wikipedia , lookup
Diabetic retinopathy wikipedia , lookup
Visual impairment wikipedia , lookup
Keratoconus wikipedia , lookup
Cataract surgery wikipedia , lookup
Vision therapy wikipedia , lookup
Eyeglass prescription wikipedia , lookup
Visual impairment due to intracranial pressure wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
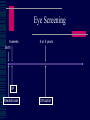
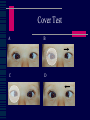
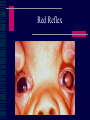
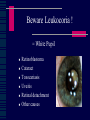
CHILD HEALTH SURVEILLANCE Vision Screening & Eye Problems Gordon N Dutton Emeritus Professor of Visual Science Paediatric Ophthalmologist Importance of surveillance Detects life threatening conditions - very rare Detects sight threatening conditions - common Detects genetic conditions - occasionally Detects cosmetic conditions - fairly common Eye Screening 6 weeks Birth 4 or 5 years GP Paediatrician Orthoptist 6 Week Check Vision: fixing & following External examination lids cornea pupil Red reflex direct ophthalmoscope Visual Assessment in Children Visual acuity Corneal light reflection Cover test Eye movements Tests of stereopsis Refraction Red reflex Dilated fundoscopy Visual Acuity in Kids Fixing and following light or toy “Objection to occlusion” Preferential looking tests Identifying or matching pictures or letters Vision reduced in both eyes Wrong test for age or ability Poor attention Refractive error Structural problem with eye Central visual problem Want glasses ! Vision reduced in one eye Loss of attention Refractive error Amblyopia Structural problem with eye Central problem Amblyopia Unilateral poor vision in childhood in a normal eye Treat by patching the “good eye” Glasses are often required Easier to reverse the younger the child If not reversed by age 7 or 8 then permanent Amblyopia Treatment Severity Age Full or part-time patching Always with glasses Preferably with close work What Is an Orthoptist? Responsible for the diagnosis and management of patients presenting with defects of binocular vision and disorders of eye movement, e.g. squint, amblyopia, diplopia and ocular muscle palsy. Screening Role Visual field assessment Corneal light reflex Strabismus = Squint – eyes not pointing in same direction Esotropia Convergent squint Associated with hypermetropia (longsightedness) Pseudoesotropia - frequently seen if prominent epicanthic folds (broad nasal bridge). Esotropia Accomodative Esotropia Exotropia Divergent squint Often intermittent Cover Test A B C D Refraction Test focus of eye by refraction with a retinoscope and lenses. Most glasses prescribed in childhood for hypermetropia (longsightedness). If difference in focus between the eyes (anisometropia) then risk of amblyopia. Red Reflex Blocked Nasolacrimal Duct Most resolve spontaneously Refer if no resolution by 1 year of age No antibiotics unless “white of eye” is red Massaging lacrimal sac may help Congenital Glaucoma Photophobia Watering Redness Enlarged eye Cloudy cornea Chalazion Apply local heat with a clean facecloth Massage towards eye 10 mins twice daily Surgery not required in child Beware Leukocoria ! = White Pupil Retinoblastoma Cataract Toxocariasis Uveitis Retinal detachment Other causes