* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Exam 1
Survey
Document related concepts
Woodward–Hoffmann rules wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
Aldol reaction wikipedia , lookup
Ene reaction wikipedia , lookup
Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Stille reaction wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Baylis–Hillman reaction wikipedia , lookup
Wolff–Kishner reduction wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Wolff rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Petasis reaction wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
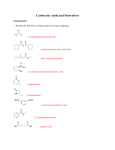
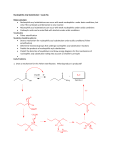
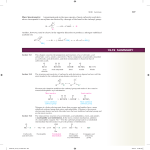
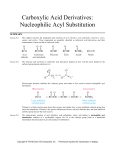
CHEM 243 STUDY GUIDE for EXAM #1 Exam: 10am & 1 pm sections: Thursday, April 28. . The exam will be over chapter 16, and small parts of 12, 14, 17 and 19. The best items to study and review are sample exam, in-class assignment #1, problem set #1 and the ‘mechanism’ worksheet (all posted on the web site). The important sections: For chap 12: 12.1 (Grignard only) For chap 14: 14. 18 14.20, 14.21 (color) For chap 16: 16.2,16.5, 16.6-16.16, 16.20, 16.22-16.23 For chap 17: 17.2, 17.3, 17.4 & 17.7 For chap 19; 19.21, 19.22 (Azo dye reaction) Know and be able draw the arrow pushing mechanism for these reactions: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution (in making Azo dyes,), Nucleophilic acyl substitutions Acid catalyzed ester & amide hydrolysis, Fisher esterification, trans esterification Hydroxide promoted ester hydrolysis Nucleophilic addition to aldehyde/ketone with Grignard reagents Determine reaction mechanisms from reaction outcome (see Mechanism work sheet). Be able to recognize the following functional groups: Aldehyde, Ketone, Carboxylic acid, ester, acid anhydride, amide and acyl halides (you do not have to know IUPAC naming) Know the relative reactivity’s of the carbonyl compounds—which are most likely to undergo acyl substitution reactions.--Predict reaction products of acyl chlorides and acid anhydrides with alcohols, amines and water. Know how Sodium Borohydride and Lithium Aluminum hydride react with aldehydes, ketones, esters, amides and acids (you do not need to know the mechanism) (sec 17.7) Know how Grignard reagents are formed and how they react with aldehydes, ketones, esters, amides and acids. (sec 17.14) Know how Soap is formed (sec 16.13) Be able to recognize the structure of ATP and Acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA) and how they are able to add an acetyl group (acetylate) to a nucleophile. (sec 16.23) Predict if a compounds would be a dye/colored. Be able to identify the chormophore and Auxochrome of a dye. Know the relationship of conjugation and wavelength of light absorbed.