* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Magnets - TeacherWeb
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Magnetosphere of Jupiter wikipedia , lookup
Friction-plate electromagnetic couplings wikipedia , lookup
Van Allen radiation belt wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Geomagnetic storm wikipedia , lookup
Magnetosphere of Saturn wikipedia , lookup
Edward Sabine wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Magnetometer wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic stripe card wikipedia , lookup
Neutron magnetic moment wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic nanoparticles wikipedia , lookup
Giant magnetoresistance wikipedia , lookup
Earth's magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotactic bacteria wikipedia , lookup
Magnetohydrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Magnetoreception wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
Magnetochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Superconducting magnet wikipedia , lookup
Force between magnets wikipedia , lookup
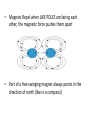
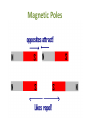
Magnetic Fields • A magnetic field consists of imaginary lines of flux moving around a magnet where the magnetic force is exerted • Magnetic field lines always form loops. The lines represent the invisible magnetic field surrounding a magnet The Earth itself is a magnet, with a magnetic north pole and south pole. S N The origin of the Earth’s magnetic field is said to be a result of the electric currents produced by the rotation of the ironnickel core. The Earth’s magnetic field continually traps moving charged particles coming from the sun, called solar wind. What is a Magnet? • A magnet is anything that attracts materials that has a magnetic field and will attract materials like iron, nickel and cobalt. • A material that has strong magnetic properties is called ferromagnetic (ferrum is a latin word for iron.) Uses for Magnets • • • • • • Holding things on your refrigerator! Credit cards Computers Electronics Compasses And many more! Properties of Magnets • Magnets attract when the OPPOSITE POLES of two magnetic objects are close to each other. • Magnets also strongly attract ferromagnetic materials such as iron, nickel and cobalt. • Magnets Repel when LIKE POLES are facing each other, the magnetic force pushes them apart • Part of a free swinging magnet always points in the direction of north (like in a compass!) Magnetic Poles • We call the ends of magnets “poles” • ALL magnets have a north (N) pole and a south (S) pole. • Like poles repel • Opposite poles attract Magnetic Poles How it looks throughout the object Electrons • Electrons are tiny negative particles that surround an atom and are what give magnets their magnetic properties • Spinning electrons produce a magnetic field • When many electrons are spinning in the same directions those individual magnetic fields combine to form a stronger magnet

















![magnetism review - Home [www.petoskeyschools.org]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/002621376_1-b85f20a3b377b451b69ac14d495d952c-150x150.png)