* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download EM Waves
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Giant magnetoresistance wikipedia , lookup
Neutron magnetic moment wikipedia , lookup
Van Allen radiation belt wikipedia , lookup
Earth's magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotactic bacteria wikipedia , lookup
Electromotive force wikipedia , lookup
Metamaterial cloaking wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Superconducting magnet wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
Electricity wikipedia , lookup
Force between magnets wikipedia , lookup
Magnetoreception wikipedia , lookup
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
Magnetohydrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Magnetochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
Ferromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
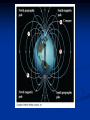
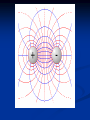
Nature of Electromagnetic Waves Chapter 3.1 Noteworthy Vocab. Electromagnetic Radiant Wave Energy Forces & Fields Magnetic & Electric Fields Atoms Protons, Electrons, Neutrons Wave “Rewind” Waves transfer Energy without transferring Matter. Mechanical Waves transfer energy by making particles of matter collide with one another. Ex: Sounds waves, Waves in ocean Mechanical Waves can’t travel in space How do you transfer energy through empty space? Ex - Energy from Sun Forces & Fields Earth has a force field = Gravitational Field Force is exerted on mass of object. Electromagnetic waves is produced by charged particles in motion. Electromagnetic Wave = Electric field + Magnetic Field Magnetic Fields Magnets are surrounded by a magnetic force field. Magnets exert magnetic force on other magnets & magnetic materials. Magnetic fields cause magnetized materials to line up along magnetic lines. Electric Fields • • • Atoms contain protons, electrons, & neutrons. - Protons & Electrons have electric charge Protons => Positive; Electrons => Negative A particle with a charge is surrounded by an electric field. Electric field exerts a force on other charged particles. Making Electromagnetic Waves Moving/Vibrating a charged particle back and forth causes changing electric and Magnetic Fields in many directions. Ex: Electron http://www.phy.ntnu.edu.tw/ntnujava/index.php?to pic=35