* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Early Empire
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Roman architecture wikipedia , lookup
Military of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Travel in Classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Promagistrate wikipedia , lookup
Alpine regiments of the Roman army wikipedia , lookup
Education in ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Switzerland in the Roman era wikipedia , lookup
Roman funerary practices wikipedia , lookup
Demography of the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Early Roman army wikipedia , lookup
History of the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Roman emperor wikipedia , lookup
Slovakia in the Roman era wikipedia , lookup
Food and dining in the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Romanization of Hispania wikipedia , lookup
Roman agriculture wikipedia , lookup
History of the Constitution of the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Roman technology wikipedia , lookup
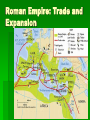
The Early Empire The Emperor Augustus Augustus A long period of peace began with Augustus known as the Pax Romana, or Roman Peace. This lasted 200 years. To make the empire strong and safe, Augustus built a professional army. The legions conquered new territories. Augustus rebuilt Rome with palaces, fountains, and splendid public buildings. Augustus He improved the government through the appointments of governors to each of Rome’s provinces. He also reformed the tax system and the legal system. Caligula Mental illness caused Caligula to act strange and treat people cruelly. He had many people murdered. He even appointed his horse as consul. Nero Nero was vicious man. He killed his mother and two of his wives. Nero He is best remembered for having “fiddled while Rome burned.” He was playing music miles from home when a fire destroyed much of the city. Vespasian When Vespasian took the throne, Rome finally was restored to peace and order. He put down several rebellions in the empire. Vespasian He began the construction of the Colosseum. The “Good Emperors” The “Good Emperors” At the beginning of AD 100s, a series of rulers came into power who were not related to Augustus or Vespasian. These five emperors---Nreva, Trajan, Hadrian, Antoninus Pius, and Marcus Aurelius were known as the “good emperors.” The “Good Emperors” Agriculture flourished, trade increased, and the standard living rose. The emperors supported public building projects. They built arches, bridges, and aqueducts. Hadrian Hadrian was known as one of the good emperors. He made Roman laws easier to understand and apply. Hadrian’s Wall Hadrian had a wall built to mark the boundaries of the Roman Empire in the north. Rome in A.D. 100s The Roman Empire was at its largest. People spoke different languages and practiced different customs. The people were united through Roman law and Roman rule. The economy was based on agriculture, industry, and trading. Roman Roads Roman road system reached a total length of 50,000 miles. Roman Money Rome’s trade was helped my a common currency. The Romans also created a standard system on weights and measures. Roman Empire: Trade and Expansion Some Romans built great fortunes and lived in luxury. However, most city dwellers and farmers remained poor, and many remained enslaved.