* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Powerpoint
Kentucky in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Lost Cause of the Confederacy wikipedia , lookup
Second Battle of Corinth wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Texas in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Wilson's Creek wikipedia , lookup
Fort Fisher wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Appomattox Station wikipedia , lookup
Battle of New Bern wikipedia , lookup
Blockade runners of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Donelson wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Seven Pines wikipedia , lookup
Red River Campaign wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Gaines's Mill wikipedia , lookup
First Battle of Bull Run wikipedia , lookup
East Tennessee bridge burnings wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Anaconda Plan wikipedia , lookup
Capture of New Orleans wikipedia , lookup
Economy of the Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
Confederate privateer wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Namozine Church wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Cedar Creek wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Lewis's Farm wikipedia , lookup
Ulysses S. Grant and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Baltimore riot of 1861 wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Shiloh wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Pillow wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Western Theater of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Conclusion of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Siege of Vicksburg wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
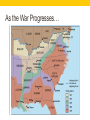
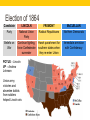
THE CIVIL WAR American History I - Unit 8B Ms. Brown Review • By the end of the war, 10% of Union troops were ______________. • black • In what ways did blacks faced discrimination in the Union army? • Paid less, poor equipment/clothes, labor assignments, lower ranks • Industries in the North prospered during the Civil War due to the mass production of ______________________. • weapons • For which reasons did the Confederacy face a food shortage during the Civil War? • Loss of slaves • Union occupation and destruction of land • Union blockade of trade • The Union victory at ________________, MS gave the Union control over the Mississippi River. • Vicksburg • Why is the Battle of Gettysburg considered a turning point in the war in favor of the Union? • The Confederacy was unable to invade the North, and Union victories increased 8.8 – THE CIVIL WAR ENDS Confederate Morale Decreased • By the end of 1863, Confederate morale had decreased greatly. • Big defeats at Vicksburg and • • • • Gettysburg Low on food and supplies for the troops and civilians Increasing desertions (runaways) Lack of unity increased hostility among states NC and GA held meetings to discuss possible separate peace with Union Grant and Sherman Seal the Deal for the Union • 1864 – Lincoln appointed Ulysses S. Grant to be the head commander of the Union army. • Grant appointed Tecumseh Sherman as commander of Union armies in Mississippi. • Grant went to fight Lee in VA. • Sherman led troops from MS to raid and destroy GA. Total War • Total war – attacking the enemy’s society (civilians and homefront), not just military forces. • Grant and Sherman believed total war necessary to defeat Confederacy because… • Civilians grew food and made supplies on which the army relied • The strength of the homefront influenced Confederate morale • Union aimed to destroy resources and kill morale crumbling of the Confederacy “Whatever happens, there will be no turning back…” • Union army could afford to lose men in battle, Confederacy could not • Grant vs. Lee in VA during May - June 1864 • Union lost 60,000 • Confederacy lost 32,000 • Democrats in the North called Grant a “butcher” but Grant pushed on because he told Lincoln he would not turn back. Gone with the Wind - Atlanta Burning “Sherman’s March” • Nov-Dec 1864 - Following “total war” Sherman led forces through GA, SC, and NC. • Burned major and minor cities in GA and SC, left complete destruction. • Spared NC – one of the last states to succeed and Union believed the war would end soon. As the War Progresses… Election of 1864 Candidate LINCOLN FREMONT McCLELLAN Party National Union Party Radical Republicans Northern Democrats Beliefs on War Continue fighting, force Confederate surrender Harsh punishment for southern states when they re-enter Union Immediate armistice with Confederacy POTUS – Lincoln VP – Andrew Johnson Union army victories and absentee ballots from soldiers helped Lincoln win. Richmond Falls • By March 1865, Richmond was surrounded by Union troops led by Grant and Sherman. • April 2, 1865 – Jefferson Davis left Richmond and set it on fire to keep Union troops from getting it Confederate Surrender • April 9, 1865 – Grant and Lee met at Appomattox Court House in VA Lee surrendered the Confederate troops to Grant. • Lincoln requested that Grant propose generous surrender terms to Lee. • Grant let Lee’s troops leave with their possessions, horses, and food rations. • Confederate officers were allowed to keep their weapons • Civil War officially over… but tensions between the North and the South will exist for a long time. A New Nation: Political Changes • Increased power of the federal government • Proved the federal government was stronger that state governments no state has tried to secede again • First national income tax (% of wages given directly to the federal government) • First military draft – federal government made men fight for the country • Lincoln used his presidential “wartime powers” • Lincoln suspend habeas corpus and jailed “suspicious” people without evidence or a trial heavily criticized for violating constitutional rights A New Nation: Economic Changes • National Bank Act – 1863, laws that chartered new federal banks and set rules about their operations tried to make investing money in the federal government safe for investors • Northern economy boomed – industries produced war goods and railroad supplies, agriculture made possible with the steel plow • Southern economy suffered – plantation system destroyed by loss of slaves and destruction of land • HUGE economic gap between North and South would last for decades A New Nation: Social Changes • December 6, 1865 – ratification of the 13th Amendment – officially abolished slavery • What would be in the future for millions of newly freed people? • Soldiers returned to civilian life and many experienced PTSD due to combat. • American Red Cross – founded 1881 by Clara Barton organization dedicated to the medical care of the sick or wounded in wars and natural disasters Lincoln’s Assassination • April 14, 1865 • Lincoln and wife watching play in Ford’s Theatre in DC shot in the head by John Wilkes Booth • Confederate sympathizer, organized a conspiracy with the intent of killing Lincoln, Johnson (VP), and Seward (Sec. of State) • Lincoln killed, Johnson unharmed, Seward attacked but survived • Lincoln died that night 1st POTUS assassinated • Booth found and shot on April 26, 1865. Final Thoughts… • The Civil War is over, but the pieces of the nation needed to be put back together. The man responsible for reassembling the Union has been assassinated, proving that tensions between the North and South will continue to exist. • How will the Union restore the southern states? How much punishment, if any, is necessary? • How will the reborn country integrate 4 million newly freed people into national life?