* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Opener –
Battle of Chancellorsville wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Sailor's Creek wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Cumberland Church wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Stones River wikipedia , lookup
Battle of White Oak Road wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Big Bethel wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Anaconda Plan wikipedia , lookup
Economy of the Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Hampton Roads wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Appomattox Station wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Port Royal wikipedia , lookup
Red River Campaign wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Roanoke Island wikipedia , lookup
Capture of New Orleans wikipedia , lookup
Second Battle of Corinth wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Perryville wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Pillow wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fredericksburg wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Shiloh wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Island Number Ten wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Harpers Ferry wikipedia , lookup
Second Battle of Bull Run wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Malvern Hill wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Lewis's Farm wikipedia , lookup
Battle of New Bern wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Wilson's Creek wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Cedar Creek wikipedia , lookup
Eastern Theater of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Antietam wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Maryland Campaign wikipedia , lookup
Conclusion of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Namozine Church wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Seven Pines wikipedia , lookup
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
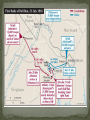
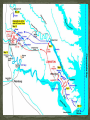
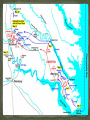
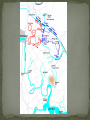
Thomas “Stonewall” Jackson – Confederate general, earned nickname at the Battle of Bull Run, West Point graduate & instructor at Virginia Military Institute, died of wounds suffered at Chancellorsville in May 1863. First Battle of Bull Run – July 21, 1861, first major battle of the Civil War, Confederate victory, Confederates called it the Battle of Manassas. George B. McClellan – placed in command of all Union armies following Bull Run, expert at preparing and training. Union commander – Irvin McDowell Confederate commander – P.G.T. Beauregard Union chooses to attack Beauregard’s forces at Manassas Junction. Manassas Junction was desired by both armies for its potential transportation of troops. Union armies to keep Confederate forces occupied north and east of Manassas Junction. 90-Day Enlistments Uniforms Training Regimental Flags Beauregard knew the Union was coming. Spies in Washington, DC Beauregard plans to flank the Union army before it attacks him. Confederate lines extend for 8 miles along Bull Run. Union commanders plans same left flank attack. Beauregard’s plan fails. Orders go missing or not understood by officers. Lucky break for the Confederates. Offensive attack fails – now fight defensive battle. Both sides fight surprisingly well. Union forces begin to push back the Confederates. Two regular army batteries push to the top of Henry House hill and Union infantry follows. Confederate General Bernard Bee tries to rally his troops. Bee sees Thomas J. Jackson’s Virginia Brigade standing firm and firing. Bee calls out, “There is Jackson standing like a stone wall! Rally behind the Virginians!” Bee’s troops rallied. Fresh Confederate troops support Bee’s flanks. Union guns are too far forward to get help from infantry. Union guns hold fire when they see blue coats. Thomas “Stonewall” Jackson orders the Virginia Brigade to charge by “giving them the bayonet”. Jackson instructs his men to “yell like furies” The “Rebel Yell” is born. Union offensive collapses. Inexperienced troops begin withdrawing, but there was no panic. Maneuver called for fighting in line to form column and go to the rear. Performing under fire makes this even more difficult. . This cartoon appeared in the August 10, 1861 issue of Harper’s Weekly. The woman is shunning her husband for leaving the army after is 90-day enlistment when his country needs him. Major General George B. McClellan Read pages 516-518. Robert E. Lee (1807 – 1870) Brilliant Confederate general Renamed army the “Army of Military genius probably the Northern Virginia” Devised the battle plan known as the “Seven Days Battle”. Commanded during Antietam, Chancellorsville, Fredericksburg and Gettysburg. single greatest factor in keeping the Confederacy alive. Began war a military advisor to Jefferson Davis. Placed in command of Confederate troops in April 1862. Union = 16,000 casualties (1,734 killed, 8,036 wounded, 6,053 captured or missing) out of 105,000. Confederacy = 20,000 casualties (3,494 killed, 15,758 wounded, and 952 captured or missing) out of 90,000. Robert E. Lee placed in command of the Army of Northern Virginia General Henry W. Halleck is now generalin-chief of the Union armies McClellan ordered to support General Pope in his “Overland” campaign against Richmond. Army of Northern Virginia (South) continues to win. Army of the Potomac (North) loses again. General McClellan placed back in command by Lincoln. Lee decides to invade the North. Seven Days’ Battles – series of clashes that forced the Union army to retreat from near Richmond. Second Battle of Bull Run (2nd Manassas) – Jackson’s troops met and defeated Pope’s Union forces on August 29-30, 1862. Battle of Antietam (Sharpsburg) – bloodiest singleday in U.S. history; McClellan defeats Lee in Maryland and drives the Army of Northern Virginia back towards Richmond. South Another victory could mean foreign assistance! North Another loss could mean the South may sue for peace and gain its independence. North may lose the war! A victory will allow Lincoln to issue the “Emancipation Proclamation”. What do you think Lincoln is saying to McClellan? What do you think McClellan is saying to Lincoln?